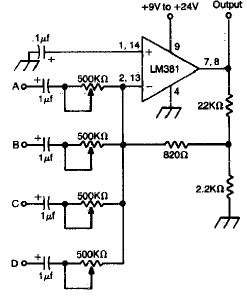
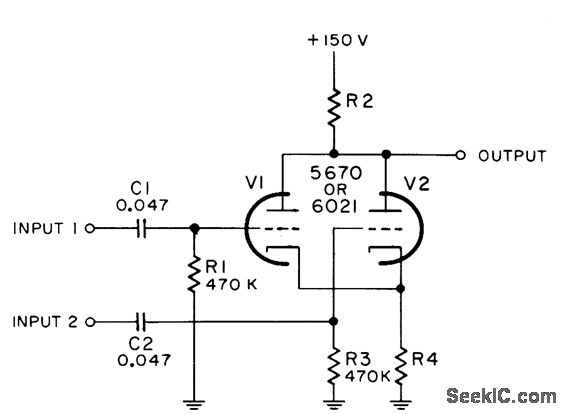
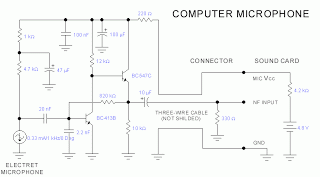
Stereo Mixer for Microphone with 2 Channels
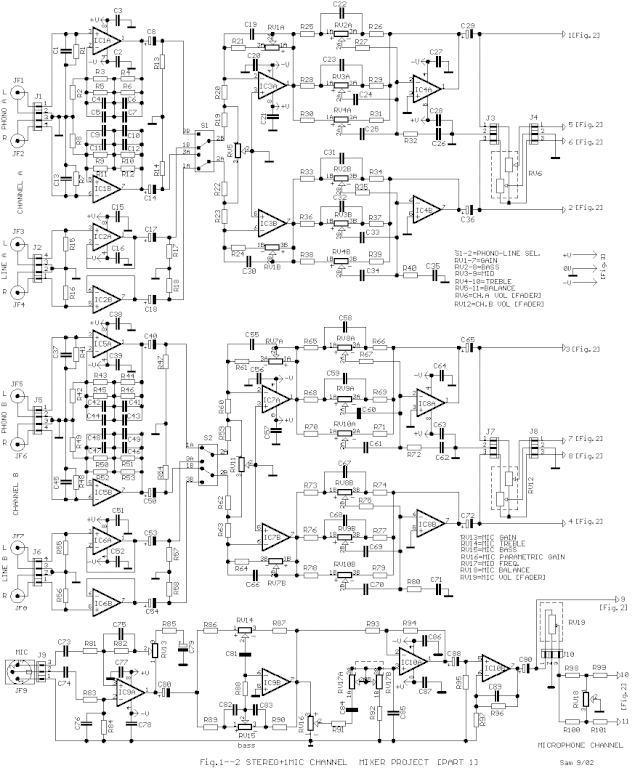
The circuit is designed to provide two channels on a stereo mixer intended for microphones, incorporating a crossfader operation. It utilizes the NE5532 integrated circuit.
The stereo mixer circuit features two independent channels, each capable of handling microphone input signals. The NE5532 operational amplifier is employed in both channels to ensure high fidelity and low noise performance, which is critical for audio applications. This op-amp is known for its excellent specifications, including low total harmonic distortion and high slew rate, making it suitable for audio processing.
Each channel includes a gain stage to amplify the microphone signal before it is mixed. The crossfader mechanism allows for smooth transitions between the two audio channels, enabling the user to blend the signals seamlessly. This is particularly useful in live sound environments or studio settings, where precise control over audio levels is necessary.
The circuit layout includes input connectors for the microphones, typically XLR or TRS jacks, followed by the gain stage implemented with the NE5532. The output of each channel feeds into the crossfader circuit, which consists of a potentiometer that adjusts the relative levels of the two signals. The output of the crossfader is then sent to a master output stage, which may include additional buffering or amplification to drive the final output to speakers or recording devices.
Power supply considerations for the NE5532 must also be addressed, typically requiring a dual power supply (e.g., ±15V) to ensure optimal performance. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the op-amps to minimize noise and maintain stability.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for mixing microphone signals with the added functionality of a crossfader, making it suitable for various audio applications.The circuit was designed to provide 2 channels on a stereo mixer that will be used for microphones while having a crossfader operation. NE5532 an intern.. 🔗 External reference
The stereo mixer circuit features two independent channels, each capable of handling microphone input signals. The NE5532 operational amplifier is employed in both channels to ensure high fidelity and low noise performance, which is critical for audio applications. This op-amp is known for its excellent specifications, including low total harmonic distortion and high slew rate, making it suitable for audio processing.
Each channel includes a gain stage to amplify the microphone signal before it is mixed. The crossfader mechanism allows for smooth transitions between the two audio channels, enabling the user to blend the signals seamlessly. This is particularly useful in live sound environments or studio settings, where precise control over audio levels is necessary.
The circuit layout includes input connectors for the microphones, typically XLR or TRS jacks, followed by the gain stage implemented with the NE5532. The output of each channel feeds into the crossfader circuit, which consists of a potentiometer that adjusts the relative levels of the two signals. The output of the crossfader is then sent to a master output stage, which may include additional buffering or amplification to drive the final output to speakers or recording devices.
Power supply considerations for the NE5532 must also be addressed, typically requiring a dual power supply (e.g., ±15V) to ensure optimal performance. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the op-amps to minimize noise and maintain stability.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for mixing microphone signals with the added functionality of a crossfader, making it suitable for various audio applications.The circuit was designed to provide 2 channels on a stereo mixer that will be used for microphones while having a crossfader operation. NE5532 an intern.. 🔗 External reference