Stereo Preamplifier Circuit (741)
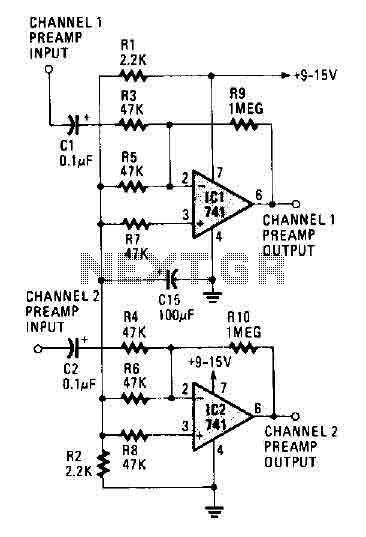
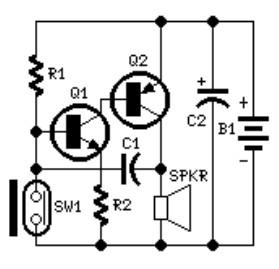
The circuit operates using two 741 operational amplifiers and achieves a gain exceeding 20 dB in each channel. Utilizing a higher-quality op-amp can improve the noise figure and bandwidth. Additionally, the circuit features a sharp roll-off at 20,000 Hertz.
This circuit design employs two 741 operational amplifiers configured in a non-inverting amplifier arrangement. Each op-amp amplifies the input signal, providing a substantial gain of over 20 dB per channel, which is suitable for a variety of audio applications. The choice of the 741 op-amp, while adequate for many purposes, can be enhanced by selecting a higher-performance op-amp. This substitution would yield improvements in both the noise figure and bandwidth, resulting in clearer audio output and a wider frequency response.
The circuit exhibits a sharp roll-off at 20,000 Hertz, indicating that frequencies above this threshold are significantly attenuated. This characteristic is crucial in audio applications, as it helps to eliminate unwanted high-frequency noise and interference, thereby enhancing the overall sound quality. The roll-off is typically achieved through the use of passive components such as capacitors and resistors in conjunction with the op-amps, which dictate the cutoff frequency and slope of attenuation.
In summary, this circuit is a fundamental audio amplifier design that can be optimized for better performance through the careful selection of op-amps and the design of the frequency response characteristics. The combination of these elements allows for effective amplification while maintaining sound fidelity across the desired frequency range.The circuit works with two 741 opamps and provides better than 20 dB gain in each channel. A better type op-amp will give a better noise figure and bandwidth. In this circuit, the sharp roll-off is at 20,000 Hertz. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design employs two 741 operational amplifiers configured in a non-inverting amplifier arrangement. Each op-amp amplifies the input signal, providing a substantial gain of over 20 dB per channel, which is suitable for a variety of audio applications. The choice of the 741 op-amp, while adequate for many purposes, can be enhanced by selecting a higher-performance op-amp. This substitution would yield improvements in both the noise figure and bandwidth, resulting in clearer audio output and a wider frequency response.
The circuit exhibits a sharp roll-off at 20,000 Hertz, indicating that frequencies above this threshold are significantly attenuated. This characteristic is crucial in audio applications, as it helps to eliminate unwanted high-frequency noise and interference, thereby enhancing the overall sound quality. The roll-off is typically achieved through the use of passive components such as capacitors and resistors in conjunction with the op-amps, which dictate the cutoff frequency and slope of attenuation.
In summary, this circuit is a fundamental audio amplifier design that can be optimized for better performance through the careful selection of op-amps and the design of the frequency response characteristics. The combination of these elements allows for effective amplification while maintaining sound fidelity across the desired frequency range.The circuit works with two 741 opamps and provides better than 20 dB gain in each channel. A better type op-amp will give a better noise figure and bandwidth. In this circuit, the sharp roll-off is at 20,000 Hertz. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713