fire alarm circuit with temperature
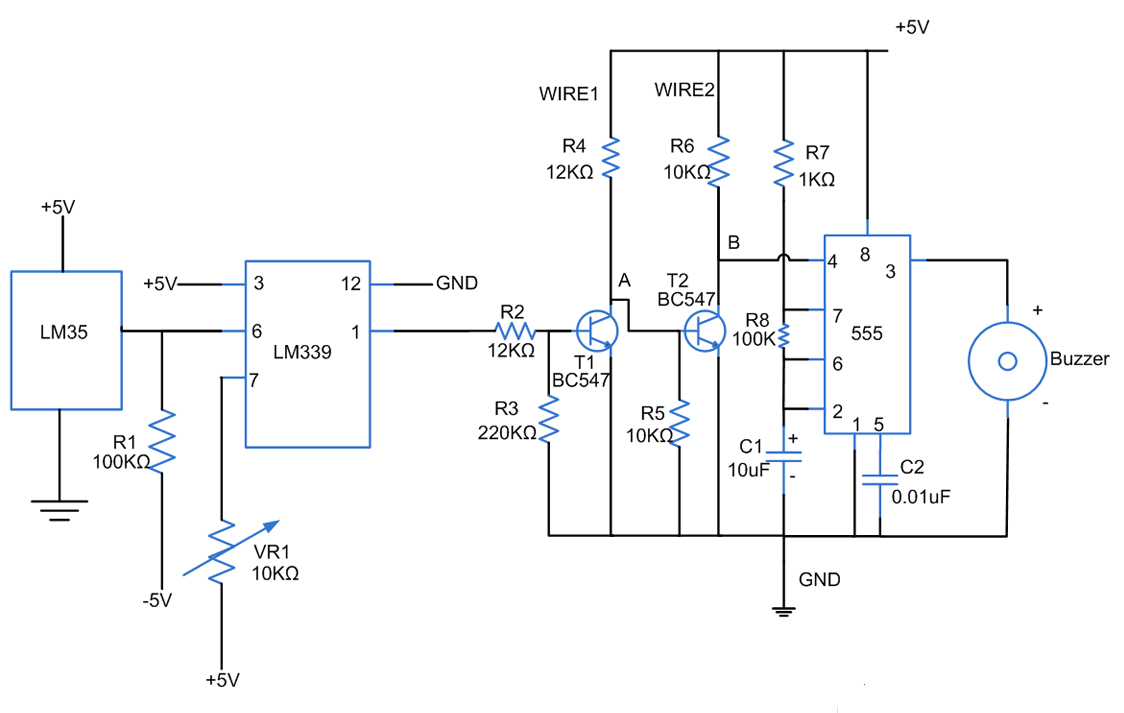
Fires can occur for several reasons, such as forgetting to turn off equipment like irons. A fire alarm circuit with a temperature sensor may be one option to secure homes from fire hazards. There are also fire alarm circuits that use Light Dependent Resistors (LDR), but they are considered less effective because they primarily detect light intensity. When smoke is present, the light intensity falling on the LDR decreases, triggering the circuit. However, this method is perceived as less effective. The fire alarm circuit described here utilizes the LM35 integrated circuit (IC) as a temperature sensor. When the temperature in a room reaches a predefined threshold, the circuit triggers an alarm. The LM35 sensor is favored for its temperature sensitivity and availability. The output from the LM35 is connected to the negative input of the LM339 comparator IC, with a positive reference voltage set through a variable resistor (VR1) of 10K ohms. This VR allows for the adjustment of the temperature sensor's sensitivity. The LM339 comparator, which contains four comparators, outputs to a BC547 transistor (T1). When the output is low, T1 acts as a cut-off switch, keeping the circuit open, which prevents the alarm connected to pin 4 (reset) of the 555 timer IC from sounding. If the LM35 detects a temperature that exceeds the set threshold, it triggers the alarm. Fire alarms can be installed around flammable materials or in areas with a high potential for fire. Using multiple sensors in parallel can enhance the circuit's effectiveness due to the low impedance of the LM IC.
The proposed fire alarm circuit leverages the LM35 temperature sensor for its high sensitivity and straightforward integration into alarm systems. The LM35 outputs an analog voltage proportional to the temperature, which is then fed into the LM339 comparator. The comparator compares this voltage against a reference voltage set by the variable resistor (VR1). By adjusting VR1, the temperature threshold for triggering the alarm can be customized to suit specific environments, ensuring that the alarm is activated only when necessary.
The LM339 comparator, known for its low power consumption and ability to handle multiple inputs, provides a reliable output that controls the BC547 transistor. When the temperature exceeds the set threshold, the LM339 outputs a high signal, which turns on the BC547 transistor. This action effectively closes the circuit, allowing current to flow to the reset pin of the 555 timer IC, which activates the alarm system.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component commonly used in timing applications. In this circuit, it functions as an alarm generator. When the reset pin is activated, the 555 timer generates a sound signal, alerting occupants of the potential fire hazard. The positioning of the fire alarm circuit is crucial; it should be installed in areas prone to fire risks, such as kitchens or near heating appliances.
For enhanced safety, the implementation of multiple LM35 sensors connected in parallel can be beneficial. This configuration allows for broader coverage and quicker detection of temperature changes across a larger area. The low impedance of the LM IC ensures that the sensors can operate effectively without significant signal loss, maintaining the integrity of the alarm system. Overall, this fire alarm circuit design provides a reliable solution for fire detection and prevention, utilizing readily available components for effective monitoring of temperature-related fire hazards.Fires can occur for several reasons, for example, forgot to turn off equipment that could cause such as irons, fire alarm circuit with a temperature sensor may be one option in an effort to secure our homes from fire hazards. Actually there is also a fire alarm circuits that use LDR, but I think it is less effective because it is basically a light
sensor, that is the presence of smoke then the intensity of light falling into the LDR will decrease and the triggering circuit. But as as I said seems less effective. This fire alarm circuit use IC LM35 as temperature sensor. Wherein when the temperature in a room setting has been reached it will be triggering the circuit to sound an alarm.
One that I like from the LM35 sensor is its sensitivity to temperature so as suitable for the temperature sensor, it is also easy to obtain. The LM35 output is fed to pin IC LM339 comparator IC is negative with a positive setting with a value input through the VR1 10K.
VR is what will the temperature sensor sensitivity setting used. While the LM 339 is a comparator IC that has a 4 in it. Output on the comparator IC LM339 is fed to the transistor T1 BC547, how it works when output low / low, T1 in a state that serves as a cut-off switch is open, so it will work like a switch T2 is closed and the resulting pin 4 (reset) on the IC 555 to be low. And because the reset input 555 is low, the alarm does not work. and so if there is a trigger that caused the LM35 IC temperature which gives a chance has been reached.
As for the installation of fire alarms can be placed around flammable materials or places where the potential occurrence of fire, and it seems like if we use multiple sensors to a circuit (diparalel) will work well for this LM IC impedance is low, 🔗 External reference
The proposed fire alarm circuit leverages the LM35 temperature sensor for its high sensitivity and straightforward integration into alarm systems. The LM35 outputs an analog voltage proportional to the temperature, which is then fed into the LM339 comparator. The comparator compares this voltage against a reference voltage set by the variable resistor (VR1). By adjusting VR1, the temperature threshold for triggering the alarm can be customized to suit specific environments, ensuring that the alarm is activated only when necessary.
The LM339 comparator, known for its low power consumption and ability to handle multiple inputs, provides a reliable output that controls the BC547 transistor. When the temperature exceeds the set threshold, the LM339 outputs a high signal, which turns on the BC547 transistor. This action effectively closes the circuit, allowing current to flow to the reset pin of the 555 timer IC, which activates the alarm system.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component commonly used in timing applications. In this circuit, it functions as an alarm generator. When the reset pin is activated, the 555 timer generates a sound signal, alerting occupants of the potential fire hazard. The positioning of the fire alarm circuit is crucial; it should be installed in areas prone to fire risks, such as kitchens or near heating appliances.
For enhanced safety, the implementation of multiple LM35 sensors connected in parallel can be beneficial. This configuration allows for broader coverage and quicker detection of temperature changes across a larger area. The low impedance of the LM IC ensures that the sensors can operate effectively without significant signal loss, maintaining the integrity of the alarm system. Overall, this fire alarm circuit design provides a reliable solution for fire detection and prevention, utilizing readily available components for effective monitoring of temperature-related fire hazards.Fires can occur for several reasons, for example, forgot to turn off equipment that could cause such as irons, fire alarm circuit with a temperature sensor may be one option in an effort to secure our homes from fire hazards. Actually there is also a fire alarm circuits that use LDR, but I think it is less effective because it is basically a light
sensor, that is the presence of smoke then the intensity of light falling into the LDR will decrease and the triggering circuit. But as as I said seems less effective. This fire alarm circuit use IC LM35 as temperature sensor. Wherein when the temperature in a room setting has been reached it will be triggering the circuit to sound an alarm.
One that I like from the LM35 sensor is its sensitivity to temperature so as suitable for the temperature sensor, it is also easy to obtain. The LM35 output is fed to pin IC LM339 comparator IC is negative with a positive setting with a value input through the VR1 10K.
VR is what will the temperature sensor sensitivity setting used. While the LM 339 is a comparator IC that has a 4 in it. Output on the comparator IC LM339 is fed to the transistor T1 BC547, how it works when output low / low, T1 in a state that serves as a cut-off switch is open, so it will work like a switch T2 is closed and the resulting pin 4 (reset) on the IC 555 to be low. And because the reset input 555 is low, the alarm does not work. and so if there is a trigger that caused the LM35 IC temperature which gives a chance has been reached.
As for the installation of fire alarms can be placed around flammable materials or places where the potential occurrence of fire, and it seems like if we use multiple sensors to a circuit (diparalel) will work well for this LM IC impedance is low, 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713