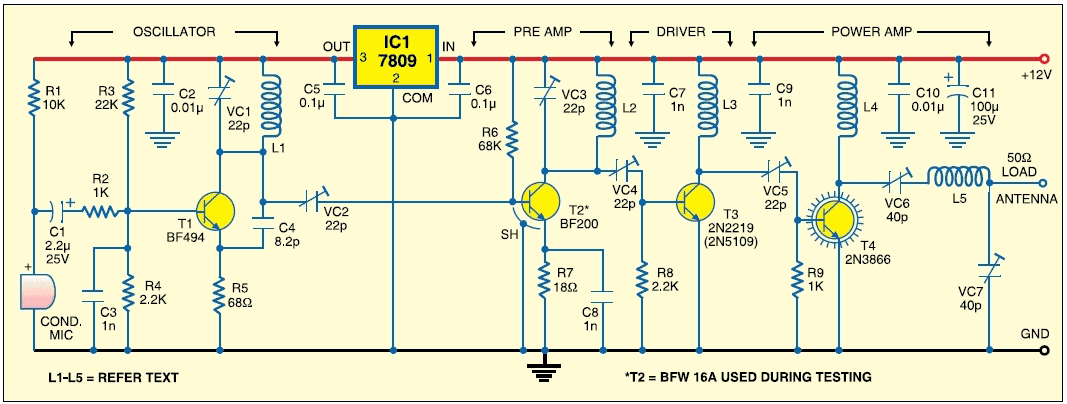
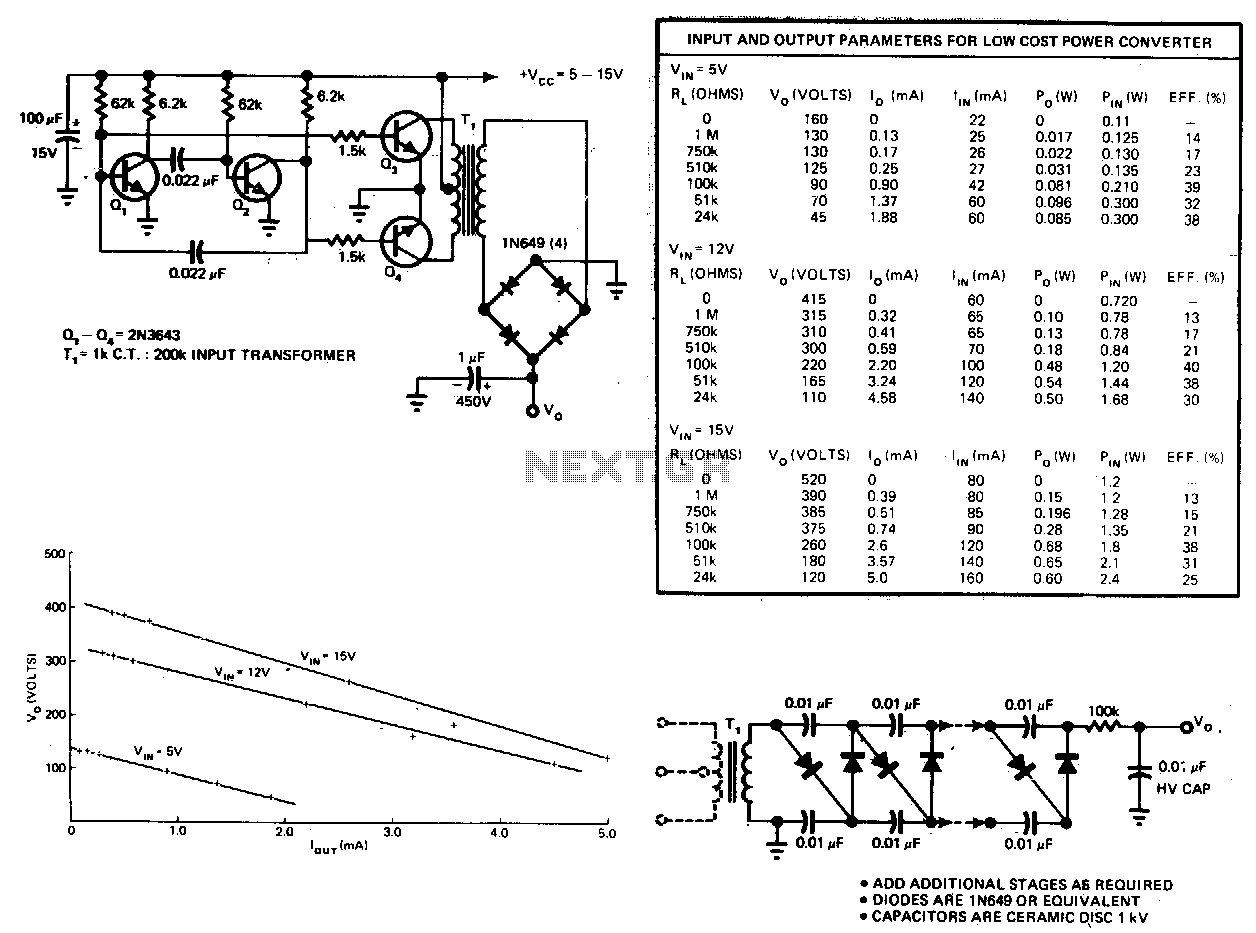
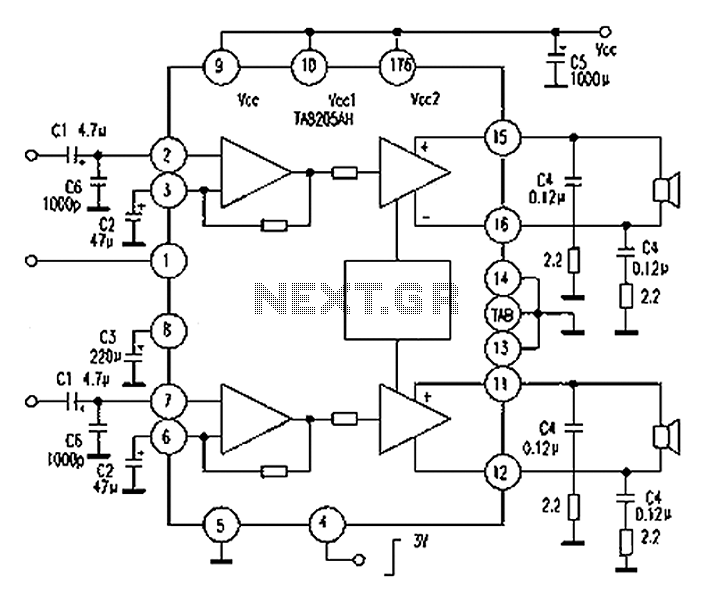
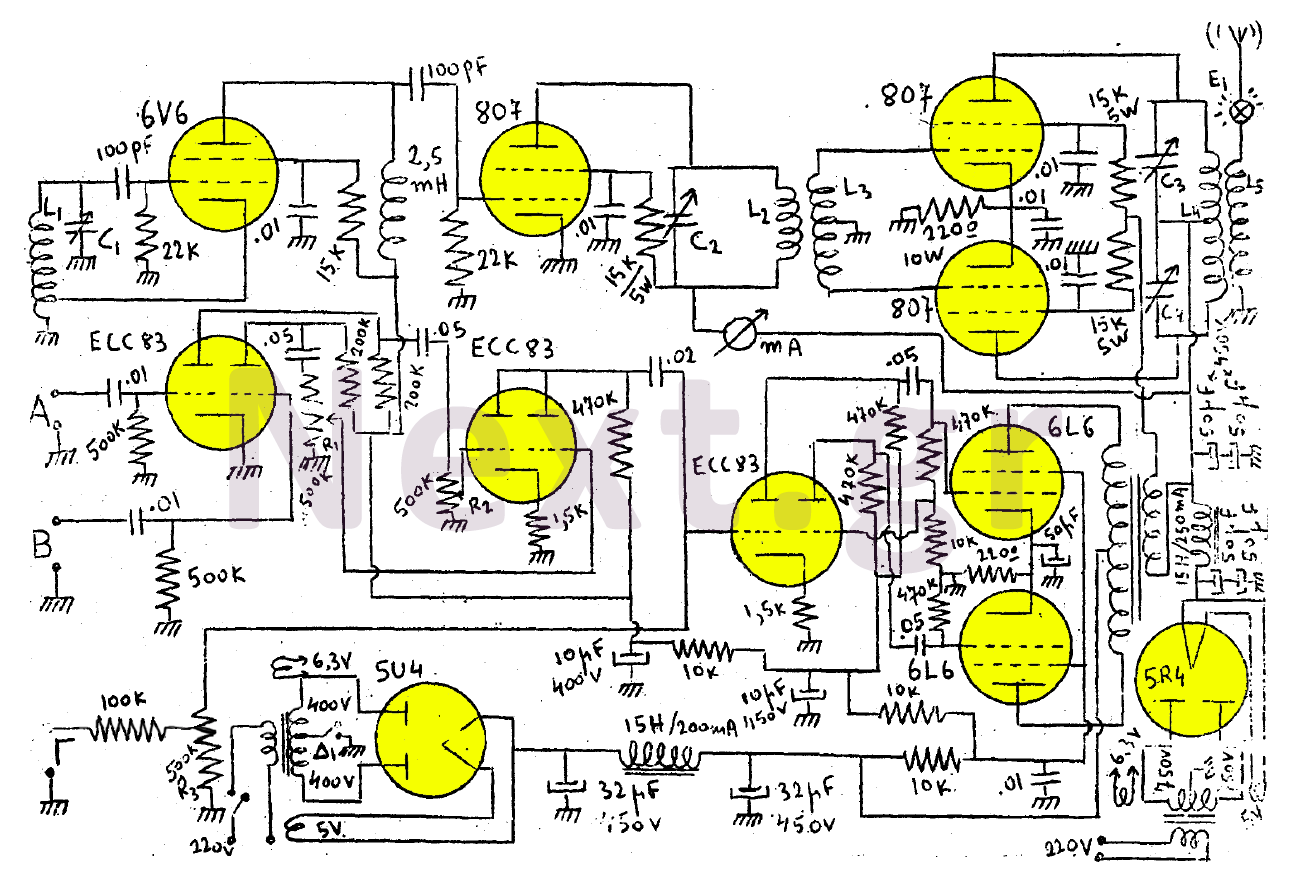
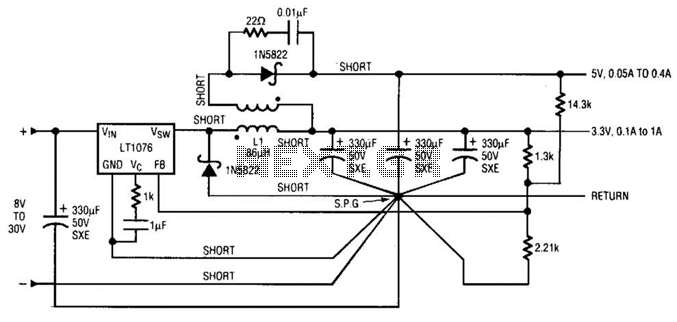
Subwoofer Amplifier Power Supply Circuit
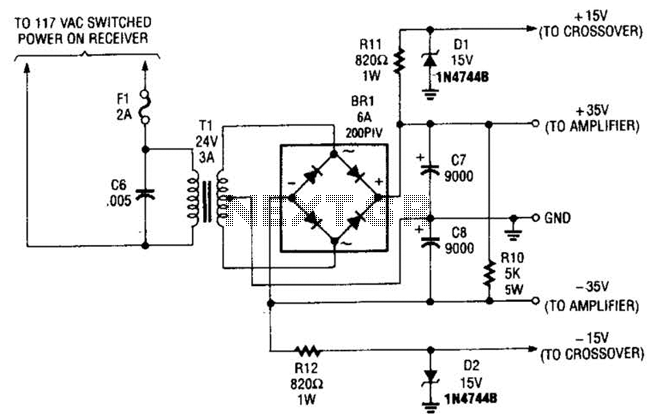
This power supply is designed to power a 100-W low-frequency amplifier and is capable of supporting various mono or stereo amplifiers within the medium power range, specifically those that require 30 to 35 V.
The power supply circuit is engineered to deliver stable voltage and sufficient current to ensure optimal performance of the connected amplifiers. It typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and voltage regulation components.
The transformer steps down the mains voltage to the required secondary voltage of 30 to 35 V. The rectifier, often implemented using a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage from the transformer into pulsating DC. This output is then smoothed by large filter capacitors, which reduce the ripple voltage to provide a more stable DC output.
For amplifiers demanding consistent performance during varying load conditions, additional voltage regulation may be integrated. This could involve linear voltage regulators or switching regulators, depending on the efficiency requirements and thermal management considerations.
Protection features such as fuses or circuit breakers can be included to safeguard against overload conditions, ensuring the longevity of both the power supply and the connected amplifiers. Furthermore, proper heat dissipation measures, including heat sinks or ventilation, are crucial for maintaining safe operating temperatures.
Overall, this power supply design is versatile and robust, making it suitable for a range of audio amplification applications. Although intended to power a 100-W low-frequency amplifier, this power supply should handle many mono or stereo amplifiers in the medium power range that require 30 to 35 V.
The power supply circuit is engineered to deliver stable voltage and sufficient current to ensure optimal performance of the connected amplifiers. It typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and voltage regulation components.
The transformer steps down the mains voltage to the required secondary voltage of 30 to 35 V. The rectifier, often implemented using a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage from the transformer into pulsating DC. This output is then smoothed by large filter capacitors, which reduce the ripple voltage to provide a more stable DC output.
For amplifiers demanding consistent performance during varying load conditions, additional voltage regulation may be integrated. This could involve linear voltage regulators or switching regulators, depending on the efficiency requirements and thermal management considerations.
Protection features such as fuses or circuit breakers can be included to safeguard against overload conditions, ensuring the longevity of both the power supply and the connected amplifiers. Furthermore, proper heat dissipation measures, including heat sinks or ventilation, are crucial for maintaining safe operating temperatures.
Overall, this power supply design is versatile and robust, making it suitable for a range of audio amplification applications. Although intended to power a 100-W low-frequency amplifier, this power supply should handle many mono or stereo amplifiers in the medium power range that require 30 to 35 V.