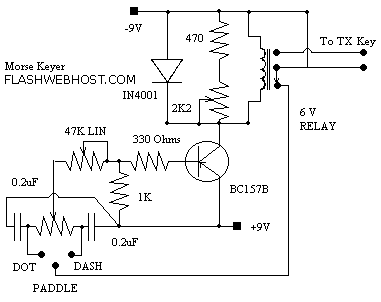
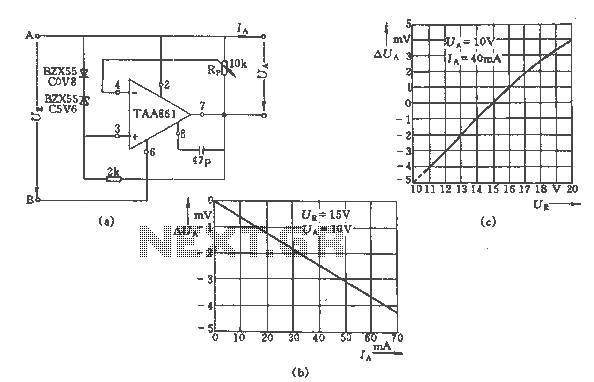
switch debounce circuit
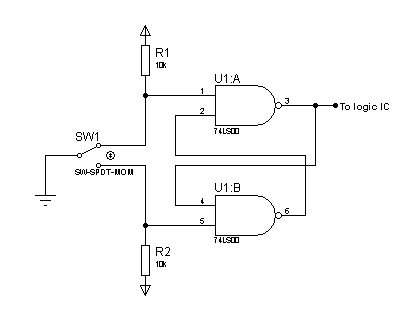
In most digital electronics projects that utilize various types of switches, switch bounces are frequently encountered. These are additional glitches that occur following the actual operation of the switch. These small pulses can disrupt the proper functioning of the circuit, such as counters, leading to inaccuracies in counting. This issue arises from switch bounce. An illustration is provided that depicts switch bounces alongside a clean pulse. The upper image represents a clean pulse without switch bounce, while the lower image illustrates the bounces generated from switching. The circuit below is an RS latch designed to serve as a switch debouncer. It consists of two 2-input NAND gates, with outputs fed back to the inputs of the other gate.
The phenomenon of switch bounce occurs when a mechanical switch is actuated, causing it to make and break contact several times before settling into a stable state. This results in multiple transitions in a very short time, which can be interpreted by digital circuits as multiple signals rather than a single intended action. In applications such as counters, this can lead to erroneous counts, as the counter may increment or decrement multiple times due to the unintended pulses.
To mitigate the effects of switch bounce, a debouncing circuit is commonly employed. The RS latch configuration using NAND gates is one effective method for achieving this. In this setup, the two 2-input NAND gates are connected in such a way that they create a feedback loop. When the switch is pressed, one of the NAND gates changes its output state, which in turn affects the input of the other NAND gate. This feedback mechanism ensures that the output stabilizes quickly, effectively filtering out the rapid fluctuations caused by switch bounce.
The RS latch operates as follows: when the switch is pressed, the first NAND gate detects the change and outputs a low signal. The output of this gate is fed back to the second NAND gate, which alters its output state based on the feedback. This process continues until the switch is released, at which point the circuit returns to its stable state. The result is a clean, debounced signal that can be reliably used in digital applications without the interference of switch bounce.
This debouncing technique is crucial in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of digital systems that rely on mechanical switches, enhancing the overall performance of the electronic circuit.In most digital electronics projects that uses different kinds of switches, switch bounces are commonly encountered. These are extra glitches after the real switch operation. These are tiny pulses that affect the actual operation of the circuit like counters. It is clearly seen that in certain push on the switch, the counting is not accurate. This is causee by the switch bounce. Here now is the image that shows switch bounces and a clean pulse. As you can see in the top image, this is an image of a clean pulse without a switch bounce. On the other hand, below it, shows the bounces formed from switching. The circuit below is a RS latch that is used as a switch debouncer. It`s composed by two 2-input NAND gates with outputs feedbacks to the input of another. (other explation from malvino) 🔗 External reference
The phenomenon of switch bounce occurs when a mechanical switch is actuated, causing it to make and break contact several times before settling into a stable state. This results in multiple transitions in a very short time, which can be interpreted by digital circuits as multiple signals rather than a single intended action. In applications such as counters, this can lead to erroneous counts, as the counter may increment or decrement multiple times due to the unintended pulses.
To mitigate the effects of switch bounce, a debouncing circuit is commonly employed. The RS latch configuration using NAND gates is one effective method for achieving this. In this setup, the two 2-input NAND gates are connected in such a way that they create a feedback loop. When the switch is pressed, one of the NAND gates changes its output state, which in turn affects the input of the other NAND gate. This feedback mechanism ensures that the output stabilizes quickly, effectively filtering out the rapid fluctuations caused by switch bounce.
The RS latch operates as follows: when the switch is pressed, the first NAND gate detects the change and outputs a low signal. The output of this gate is fed back to the second NAND gate, which alters its output state based on the feedback. This process continues until the switch is released, at which point the circuit returns to its stable state. The result is a clean, debounced signal that can be reliably used in digital applications without the interference of switch bounce.
This debouncing technique is crucial in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of digital systems that rely on mechanical switches, enhancing the overall performance of the electronic circuit.In most digital electronics projects that uses different kinds of switches, switch bounces are commonly encountered. These are extra glitches after the real switch operation. These are tiny pulses that affect the actual operation of the circuit like counters. It is clearly seen that in certain push on the switch, the counting is not accurate. This is causee by the switch bounce. Here now is the image that shows switch bounces and a clean pulse. As you can see in the top image, this is an image of a clean pulse without a switch bounce. On the other hand, below it, shows the bounces formed from switching. The circuit below is a RS latch that is used as a switch debouncer. It`s composed by two 2-input NAND gates with outputs feedbacks to the input of another. (other explation from malvino) 🔗 External reference