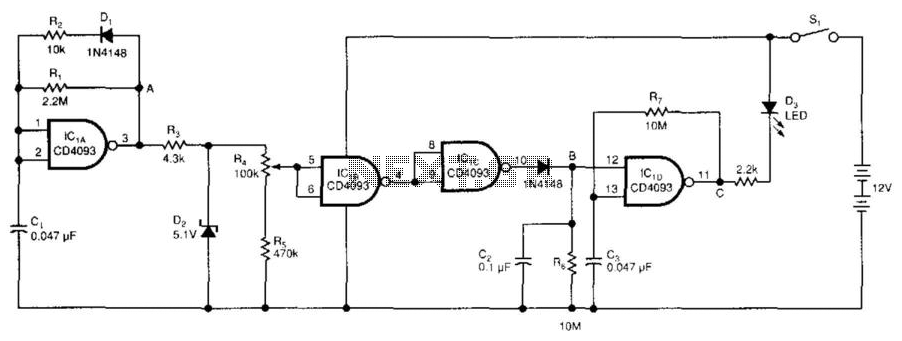
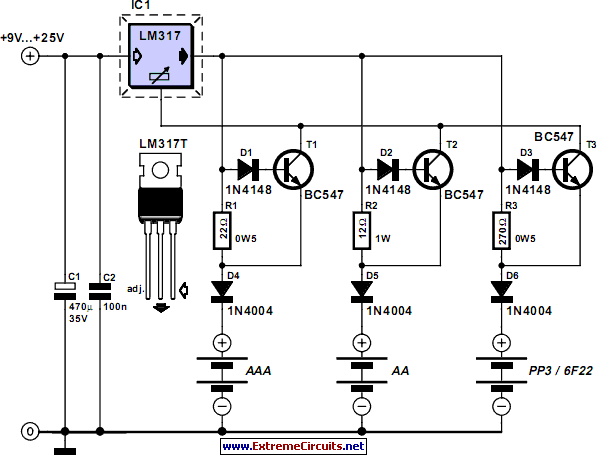
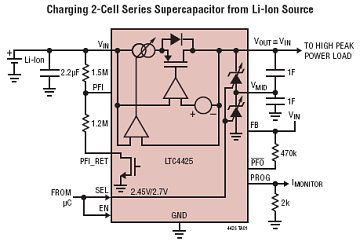
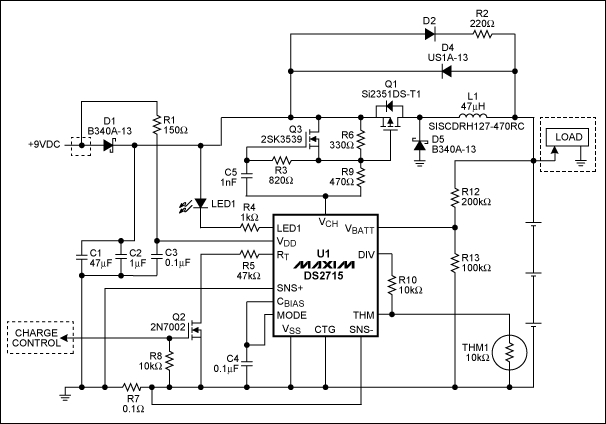
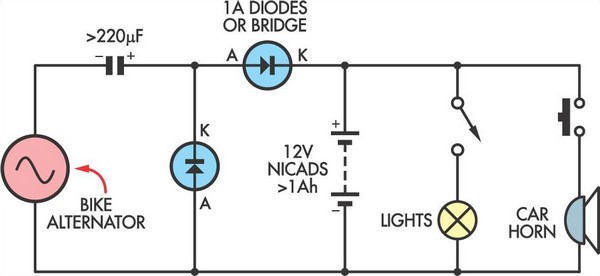
Nickel-cadmium battery charger LM324 constituted
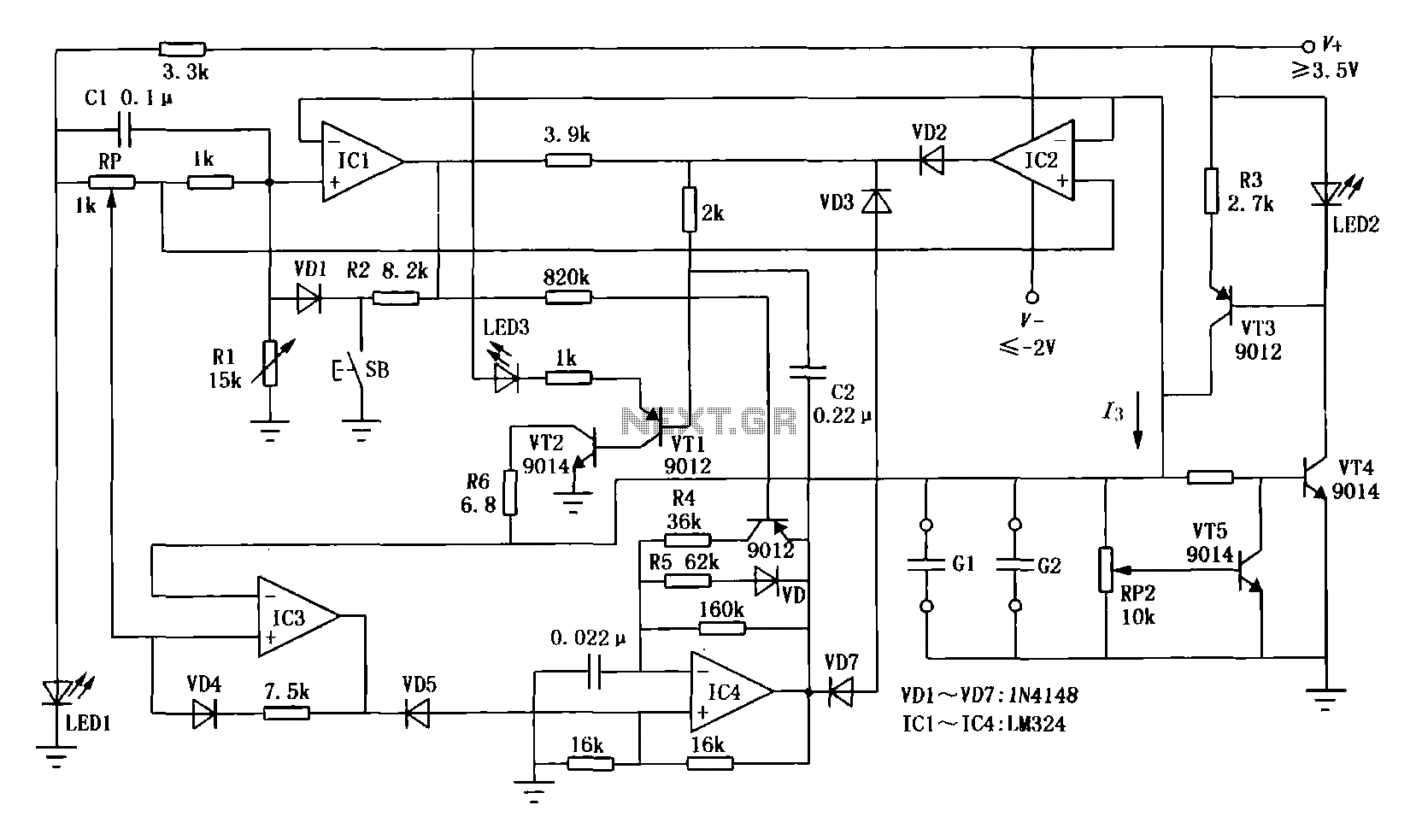
The first circuit is designed for discharging nickel-cadmium batteries before recharging to eliminate the "memory effect." After discharging, the power is automatically converted to the state of charge. The charging process utilizes pulse-width modulation for constant current, along with a pulsating pulse discharge. It fully monitors the voltage across the battery and implements dual control, allowing for charging in parallel with an anti-charging function.
The described circuit serves a critical function in maintaining the health and efficiency of nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries by addressing the common "memory effect" that can occur with repeated partial discharge and recharge cycles. The circuit begins with a discharge phase, where the battery voltage is carefully monitored to ensure complete discharge. This is essential for resetting the battery's internal memory, allowing it to deliver maximum capacity upon recharging.
Once the discharge is complete, the circuit transitions to the charging phase. It employs pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques to maintain a constant current during charging, which is vital for preventing overheating and prolonging battery life. The PWM method allows for precise control over the charging current, adapting to the battery's needs in real-time.
Additionally, the circuit incorporates a pulsating pulse discharge feature. This function helps to rejuvenate the battery by applying short bursts of discharge, which can help to break down any crystalline formations that may have developed on the battery cells, thereby restoring capacity.
The dual control mechanism ensures that the circuit can operate efficiently in both charging and discharging modes. This system allows for simultaneous charging of multiple batteries while preventing reverse current flow, which could damage the batteries or the circuit itself. The anti-charging feature acts as a safeguard, ensuring that batteries are not subjected to harmful conditions during the charging process.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for managing the lifecycle of nickel-cadmium batteries, promoting optimal performance and longevity through careful monitoring and control of the discharge and charging processes.The first circuit of nickel-cadmium battery discharge before recharging to eliminate the "memory effect, after you put the power automatically converted to the state of charge. Charging a width modulation constant current, constant current charge plus pulsating pulse discharge, fully detect the voltage across the battery, and the implementation of dual control, charging in parallel with anti-anti-charging function.
The described circuit serves a critical function in maintaining the health and efficiency of nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries by addressing the common "memory effect" that can occur with repeated partial discharge and recharge cycles. The circuit begins with a discharge phase, where the battery voltage is carefully monitored to ensure complete discharge. This is essential for resetting the battery's internal memory, allowing it to deliver maximum capacity upon recharging.
Once the discharge is complete, the circuit transitions to the charging phase. It employs pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques to maintain a constant current during charging, which is vital for preventing overheating and prolonging battery life. The PWM method allows for precise control over the charging current, adapting to the battery's needs in real-time.
Additionally, the circuit incorporates a pulsating pulse discharge feature. This function helps to rejuvenate the battery by applying short bursts of discharge, which can help to break down any crystalline formations that may have developed on the battery cells, thereby restoring capacity.
The dual control mechanism ensures that the circuit can operate efficiently in both charging and discharging modes. This system allows for simultaneous charging of multiple batteries while preventing reverse current flow, which could damage the batteries or the circuit itself. The anti-charging feature acts as a safeguard, ensuring that batteries are not subjected to harmful conditions during the charging process.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for managing the lifecycle of nickel-cadmium batteries, promoting optimal performance and longevity through careful monitoring and control of the discharge and charging processes.The first circuit of nickel-cadmium battery discharge before recharging to eliminate the "memory effect, after you put the power automatically converted to the state of charge. Charging a width modulation constant current, constant current charge plus pulsating pulse discharge, fully detect the voltage across the battery, and the implementation of dual control, charging in parallel with anti-anti-charging function.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713