Telephone Line Tester Circuit
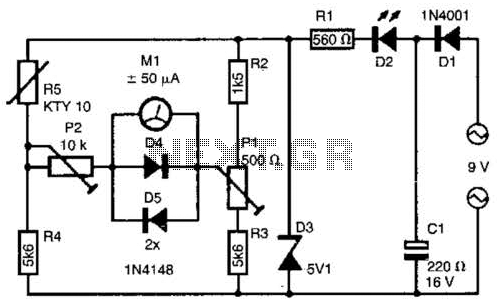
The telephone line tester comprises a meter used to measure line voltage in both the on-hook and off-hook states, three resistors (including one variable resistor), a pushbutton switch, and a modular telephone connector. When the circuit is connected to the telephone line, pressing the switch should yield a meter reading of 5 to 10 V, indicating that the line is functioning correctly.
The telephone line tester is designed to provide a straightforward method for verifying the operational status of a telephone line. The core component of the tester is a voltmeter, which is calibrated to display the voltage levels present on the line. The circuit includes three resistors arranged to form a voltage divider, with one resistor being adjustable to allow for calibration of the meter reading based on the specific characteristics of the telephone line.
The modular telephone connector enables easy interfacing with standard telephone lines, ensuring that the tester can be used with a variety of telephone systems. The pushbutton switch serves to activate the measurement process, allowing the user to obtain a reading only when desired. This feature helps conserve battery life if the tester is powered by a battery.
When the tester is connected to the telephone line and the pushbutton is pressed, the meter should indicate a voltage between 5 and 10 V. A reading within this range confirms that the line is operational and capable of carrying a signal. If the voltage is significantly lower or absent, it suggests a fault in the line, which may require further investigation or repair.
Overall, the telephone line tester is a practical tool for technicians and engineers, providing a quick and reliable means of assessing the status of telephone lines in various environments. The simplicity of its design allows for ease of use while delivering accurate voltage measurements essential for troubleshooting telephone systems. The telephone-line tester consists of nothing more than a meter (that`s used to measure line voltage in the on- and off-hook state), three resistors (one of which is variable), a pushbutton switch, and a modular telephone connector. When the circuit is connected to the telephone line, a meter reading of 5 to 10 V (when SI is pressed) indicates that the line is okay. 🔗 External reference
The telephone line tester is designed to provide a straightforward method for verifying the operational status of a telephone line. The core component of the tester is a voltmeter, which is calibrated to display the voltage levels present on the line. The circuit includes three resistors arranged to form a voltage divider, with one resistor being adjustable to allow for calibration of the meter reading based on the specific characteristics of the telephone line.
The modular telephone connector enables easy interfacing with standard telephone lines, ensuring that the tester can be used with a variety of telephone systems. The pushbutton switch serves to activate the measurement process, allowing the user to obtain a reading only when desired. This feature helps conserve battery life if the tester is powered by a battery.
When the tester is connected to the telephone line and the pushbutton is pressed, the meter should indicate a voltage between 5 and 10 V. A reading within this range confirms that the line is operational and capable of carrying a signal. If the voltage is significantly lower or absent, it suggests a fault in the line, which may require further investigation or repair.
Overall, the telephone line tester is a practical tool for technicians and engineers, providing a quick and reliable means of assessing the status of telephone lines in various environments. The simplicity of its design allows for ease of use while delivering accurate voltage measurements essential for troubleshooting telephone systems. The telephone-line tester consists of nothing more than a meter (that`s used to measure line voltage in the on- and off-hook state), three resistors (one of which is variable), a pushbutton switch, and a modular telephone connector. When the circuit is connected to the telephone line, a meter reading of 5 to 10 V (when SI is pressed) indicates that the line is okay. 🔗 External reference