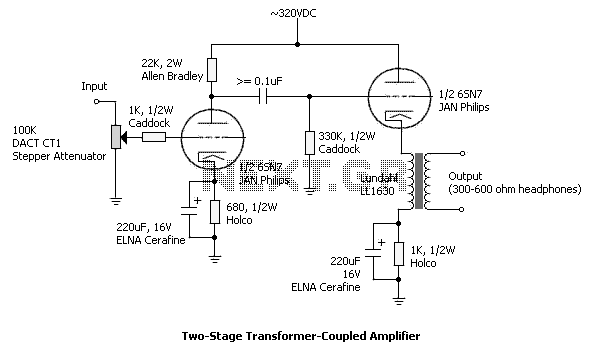
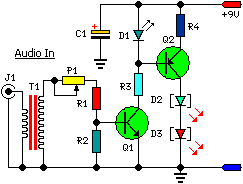
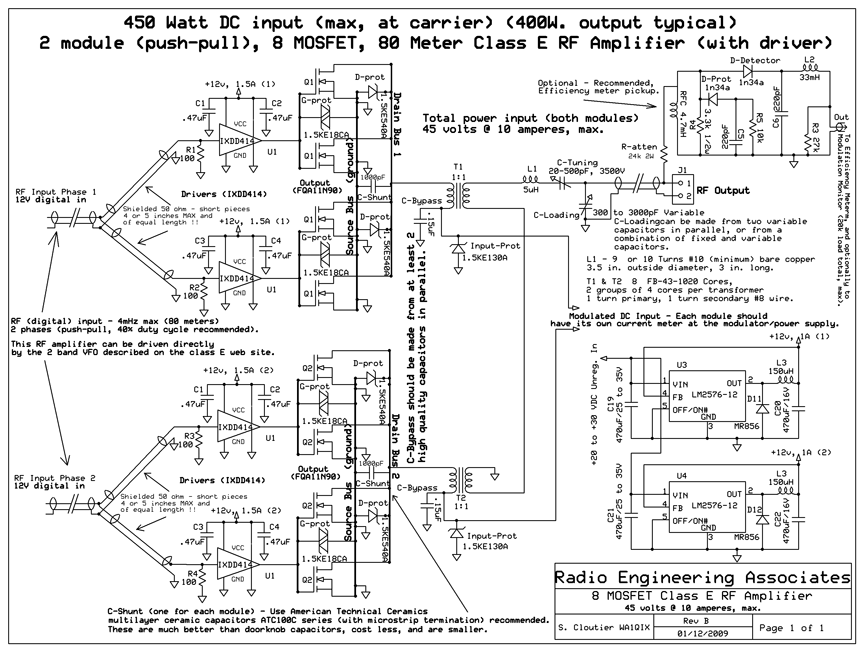
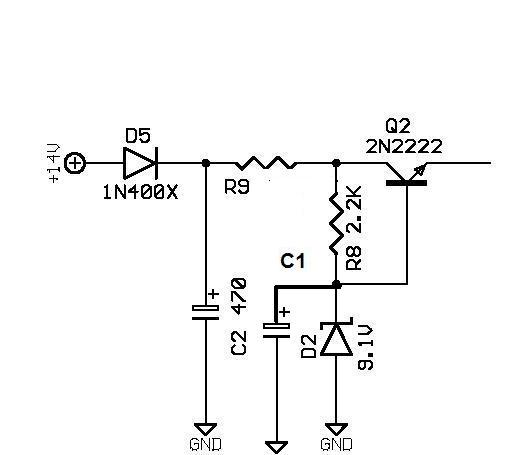
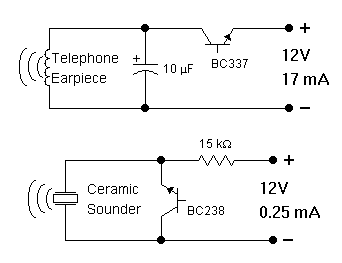
Telephone ring amplifier
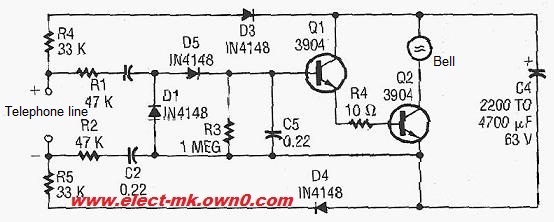
Telephone ring amplifier circuit diagram for a service speakerphone ringing bell. The circuit includes two resistors: one with a resistance of 33 kilo ohms and another with a resistance of 47 kilo ohms.
The telephone ring amplifier circuit serves to enhance the ringing signal of a telephone, making it audible through a service speakerphone. This circuit is particularly useful in environments where the standard ringing sound is insufficient due to background noise or distance from the telephone.
The primary components of the circuit include two resistors, a 33 kΩ resistor and a 47 kΩ resistor, which are used to set the gain of the amplifier and control the ringing signal's amplitude. The resistors are connected in a configuration that allows for proper signal conditioning.
In addition to the resistors, the circuit may include an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a non-inverting mode to amplify the incoming ringing signal from the telephone line. The op-amp increases the voltage level of the ringing signal, making it more audible through the speakerphone.
Capacitors may also be included to filter out any noise and ensure that only the ringing frequency passes through to the amplifier stage. The output of the op-amp can be connected to a speaker or a piezo buzzer, which converts the amplified electrical signal back into sound.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit typically requires a DC voltage source, which can be derived from the telephone line or an external adapter. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power supply pins of the op-amp to stabilize the voltage and prevent oscillations.
This telephone ring amplifier circuit is a practical solution for enhancing the ringing sound in various applications, ensuring that the ringing signal is loud enough to be heard clearly in noisy environments.Telephone ring amplifier of Service Speaker phone ringing bell Circuit diagram Electronic items Resistance of 33 kilo ohms 2 Resistance 47 Kilo Ohm. 🔗 External reference
The telephone ring amplifier circuit serves to enhance the ringing signal of a telephone, making it audible through a service speakerphone. This circuit is particularly useful in environments where the standard ringing sound is insufficient due to background noise or distance from the telephone.
The primary components of the circuit include two resistors, a 33 kΩ resistor and a 47 kΩ resistor, which are used to set the gain of the amplifier and control the ringing signal's amplitude. The resistors are connected in a configuration that allows for proper signal conditioning.
In addition to the resistors, the circuit may include an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a non-inverting mode to amplify the incoming ringing signal from the telephone line. The op-amp increases the voltage level of the ringing signal, making it more audible through the speakerphone.
Capacitors may also be included to filter out any noise and ensure that only the ringing frequency passes through to the amplifier stage. The output of the op-amp can be connected to a speaker or a piezo buzzer, which converts the amplified electrical signal back into sound.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit typically requires a DC voltage source, which can be derived from the telephone line or an external adapter. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power supply pins of the op-amp to stabilize the voltage and prevent oscillations.
This telephone ring amplifier circuit is a practical solution for enhancing the ringing sound in various applications, ensuring that the ringing signal is loud enough to be heard clearly in noisy environments.Telephone ring amplifier of Service Speaker phone ringing bell Circuit diagram Electronic items Resistance of 33 kilo ohms 2 Resistance 47 Kilo Ohm. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713