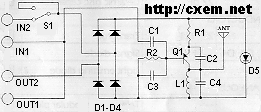
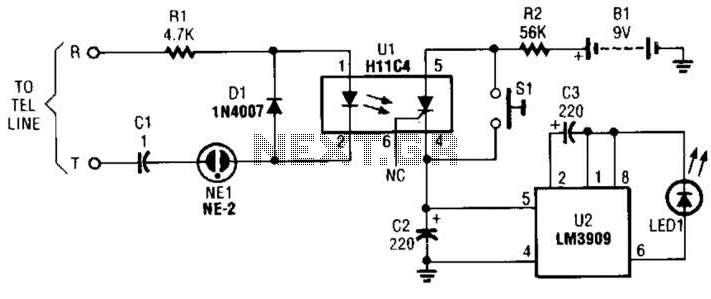
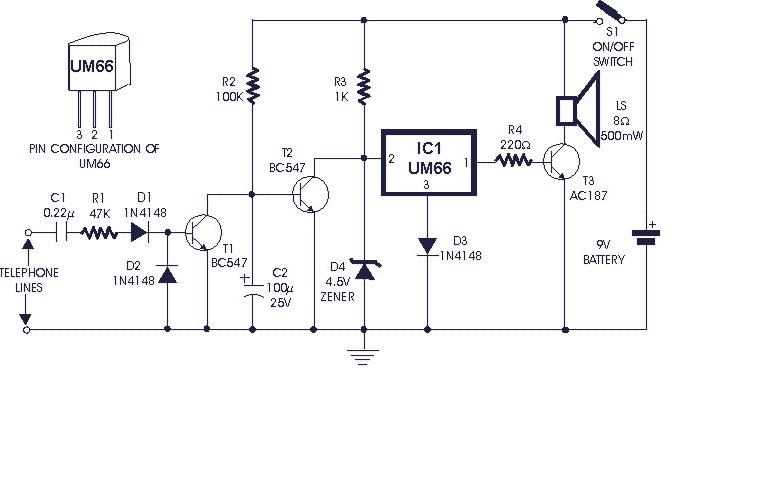
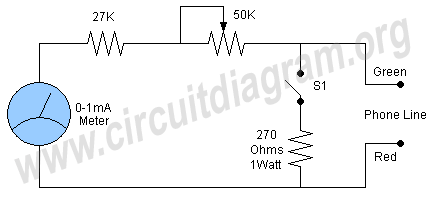
TELEPHONE RINGER
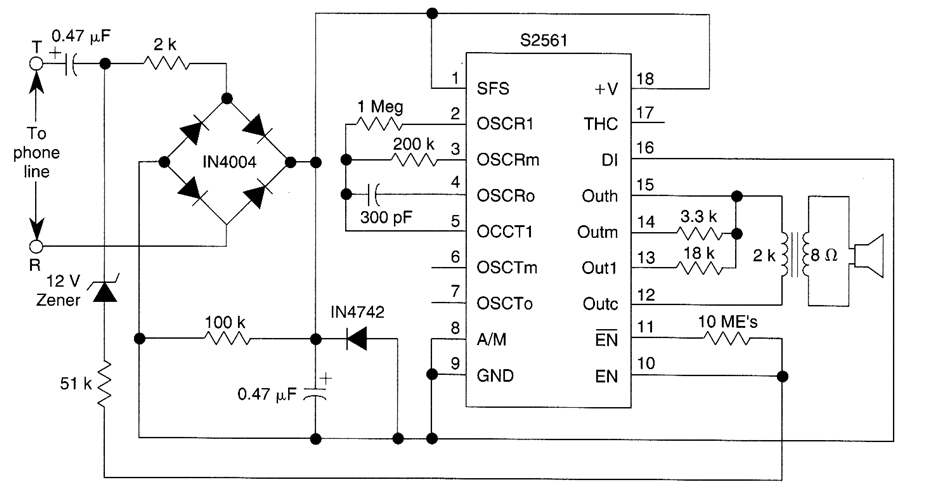
This telephone ringer utilizes an AMI chip with part number S2561 and can be powered directly from the telephone line. The audio output is approximately 50 mW when supplied with a 10-V source.
The circuit design of the telephone ringer based on the AMI S2561 chip incorporates several key components to ensure efficient operation and reliable performance. The S2561 chip is specifically designed for telephone applications, providing a compact solution for ringing signals.
The power supply for the ringer is derived from the telephone line, which typically operates at a voltage range of 48 V during idle conditions and can drop to around 10 V during ringing. The circuit must include a voltage regulator or a suitable rectifier to ensure that the S2561 chip receives a stable 10-V supply, which is essential for maintaining consistent audio output.
The audio output stage of the circuit is designed to deliver around 50 mW of power, sufficient for driving a typical telephone ringer speaker. This is achieved through a combination of amplification circuits that may include transistors or operational amplifiers configured to boost the signal from the S2561 chip to the desired power level.
Furthermore, the circuit may incorporate filtering components, such as capacitors and inductors, to eliminate any unwanted noise and ensure that the ringing tone is clear and audible. The output stage should also be protected with appropriate components to prevent damage from voltage spikes that may occur on the telephone line.
In summary, the telephone ringer circuit utilizing the AMI S2561 chip is a robust solution for generating ringing signals, powered directly from the telephone line, with an output capable of delivering 50 mW of audio power when operated at a 10-V supply. Proper attention to power regulation, amplification, and signal conditioning is essential for optimal performance.Using an AMI chip P/N S2561, this telephone ringer can be powered line. Audio output is about 50 mW when powered from a 10-V source.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design of the telephone ringer based on the AMI S2561 chip incorporates several key components to ensure efficient operation and reliable performance. The S2561 chip is specifically designed for telephone applications, providing a compact solution for ringing signals.
The power supply for the ringer is derived from the telephone line, which typically operates at a voltage range of 48 V during idle conditions and can drop to around 10 V during ringing. The circuit must include a voltage regulator or a suitable rectifier to ensure that the S2561 chip receives a stable 10-V supply, which is essential for maintaining consistent audio output.
The audio output stage of the circuit is designed to deliver around 50 mW of power, sufficient for driving a typical telephone ringer speaker. This is achieved through a combination of amplification circuits that may include transistors or operational amplifiers configured to boost the signal from the S2561 chip to the desired power level.
Furthermore, the circuit may incorporate filtering components, such as capacitors and inductors, to eliminate any unwanted noise and ensure that the ringing tone is clear and audible. The output stage should also be protected with appropriate components to prevent damage from voltage spikes that may occur on the telephone line.
In summary, the telephone ringer circuit utilizing the AMI S2561 chip is a robust solution for generating ringing signals, powered directly from the telephone line, with an output capable of delivering 50 mW of audio power when operated at a 10-V supply. Proper attention to power regulation, amplification, and signal conditioning is essential for optimal performance.Using an AMI chip P/N S2561, this telephone ringer can be powered line. Audio output is about 50 mW when powered from a 10-V source.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713