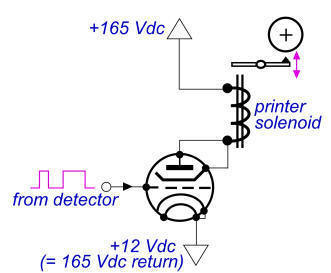
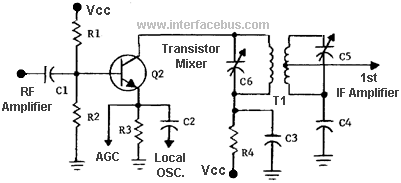
Telephone Scrambler Circuit
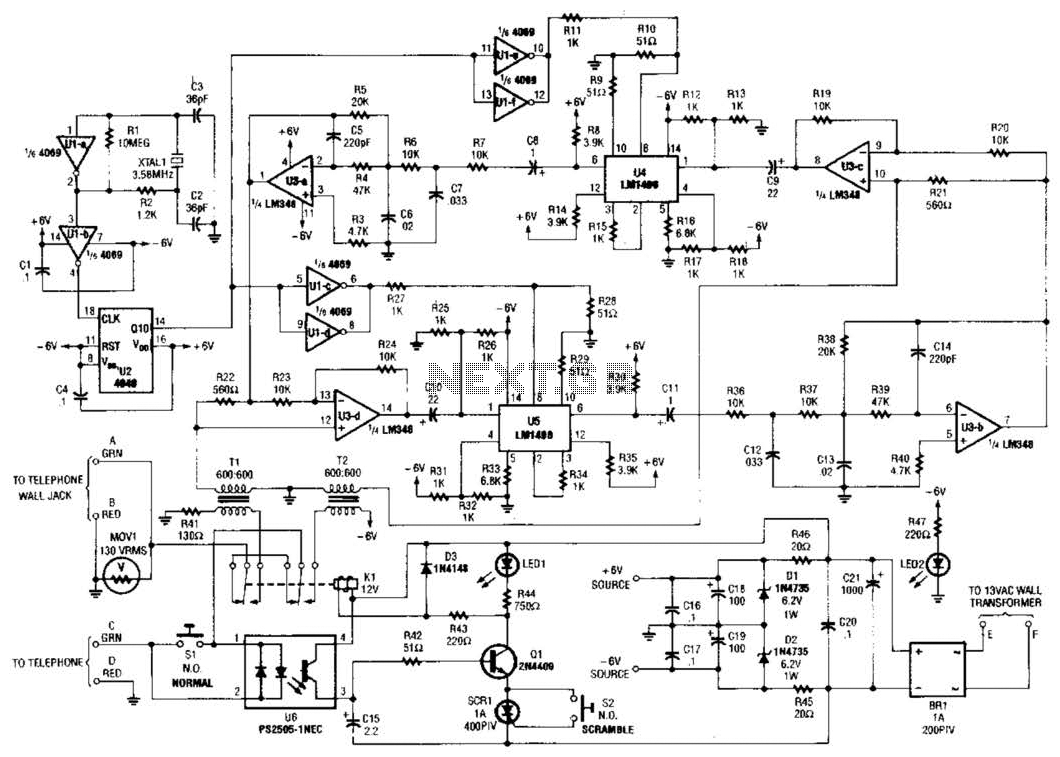
Two hybrids (T1 and T2) are utilized to facilitate a direct connection to a telephone line. This circuit employs a standard speech-inversion algorithm, which inverts the frequency of an audio signal around a central frequency. An LM1496 balanced modulator is implemented to heterodyne the speech range with a 3.58-kHz signal.
The circuit design incorporates two hybrids, T1 and T2, which serve as critical components for interfacing with the telephone line. These hybrids enable the separation of the incoming and outgoing audio signals, ensuring that both can coexist without interference. The speech-inversion algorithm is a key feature of this design, functioning to invert the frequency of audio signals. This inversion occurs around a designated center frequency, which is vital for maintaining the intelligibility of the audio while providing a layer of security against eavesdropping.
The LM1496 balanced modulator plays a pivotal role in the circuit by facilitating the heterodyning process. By mixing the speech frequencies with a stable 3.58-kHz signal, the modulator generates sidebands that contain the inverted audio information. This process effectively translates the audio signal into a frequency range suitable for transmission over the telephone line. The choice of the 3.58-kHz carrier frequency is significant, as it aligns with commonly used frequencies in telecommunication applications, ensuring compatibility and optimizing performance.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines hybrid technology with modulation techniques to achieve secure and efficient audio transmission over telephone lines, utilizing the LM1496 to perform crucial signal processing tasks. The design is well-suited for applications requiring speech inversion, providing both functionality and security in communication systems. Two hybrids (Tl and T2) are used to allow direct connection to a telephone line. This circuit uses the common speech-inversion algorithm where the frequency of an audio signal is inverted about a center frequency. An LM1496 balanced modulator is used to heterodyne the speech range against a 3.58-kHz signal. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates two hybrids, T1 and T2, which serve as critical components for interfacing with the telephone line. These hybrids enable the separation of the incoming and outgoing audio signals, ensuring that both can coexist without interference. The speech-inversion algorithm is a key feature of this design, functioning to invert the frequency of audio signals. This inversion occurs around a designated center frequency, which is vital for maintaining the intelligibility of the audio while providing a layer of security against eavesdropping.
The LM1496 balanced modulator plays a pivotal role in the circuit by facilitating the heterodyning process. By mixing the speech frequencies with a stable 3.58-kHz signal, the modulator generates sidebands that contain the inverted audio information. This process effectively translates the audio signal into a frequency range suitable for transmission over the telephone line. The choice of the 3.58-kHz carrier frequency is significant, as it aligns with commonly used frequencies in telecommunication applications, ensuring compatibility and optimizing performance.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines hybrid technology with modulation techniques to achieve secure and efficient audio transmission over telephone lines, utilizing the LM1496 to perform crucial signal processing tasks. The design is well-suited for applications requiring speech inversion, providing both functionality and security in communication systems. Two hybrids (Tl and T2) are used to allow direct connection to a telephone line. This circuit uses the common speech-inversion algorithm where the frequency of an audio signal is inverted about a center frequency. An LM1496 balanced modulator is used to heterodyne the speech range against a 3.58-kHz signal. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713