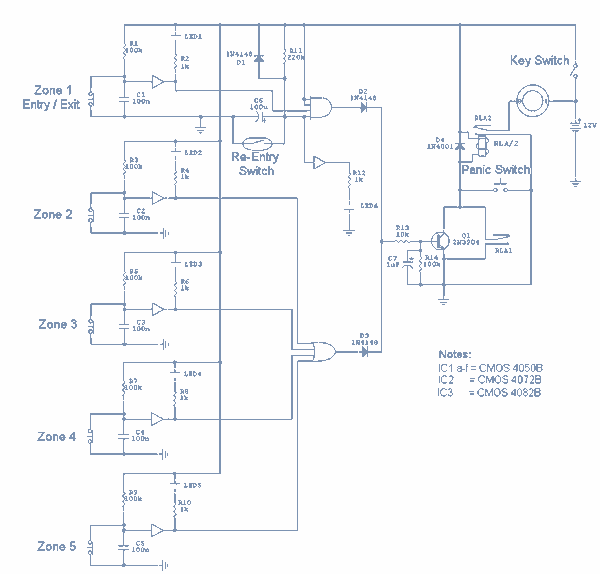
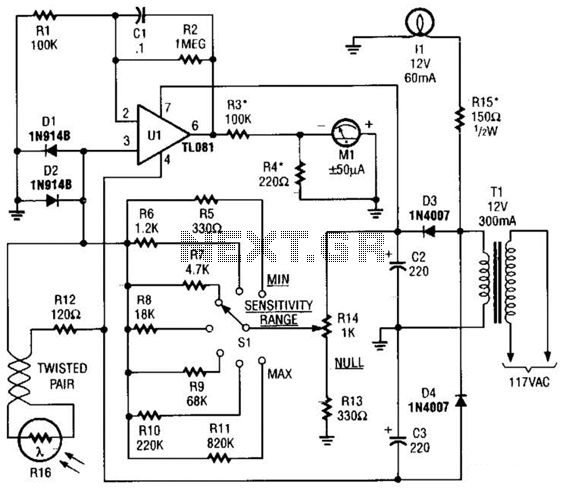
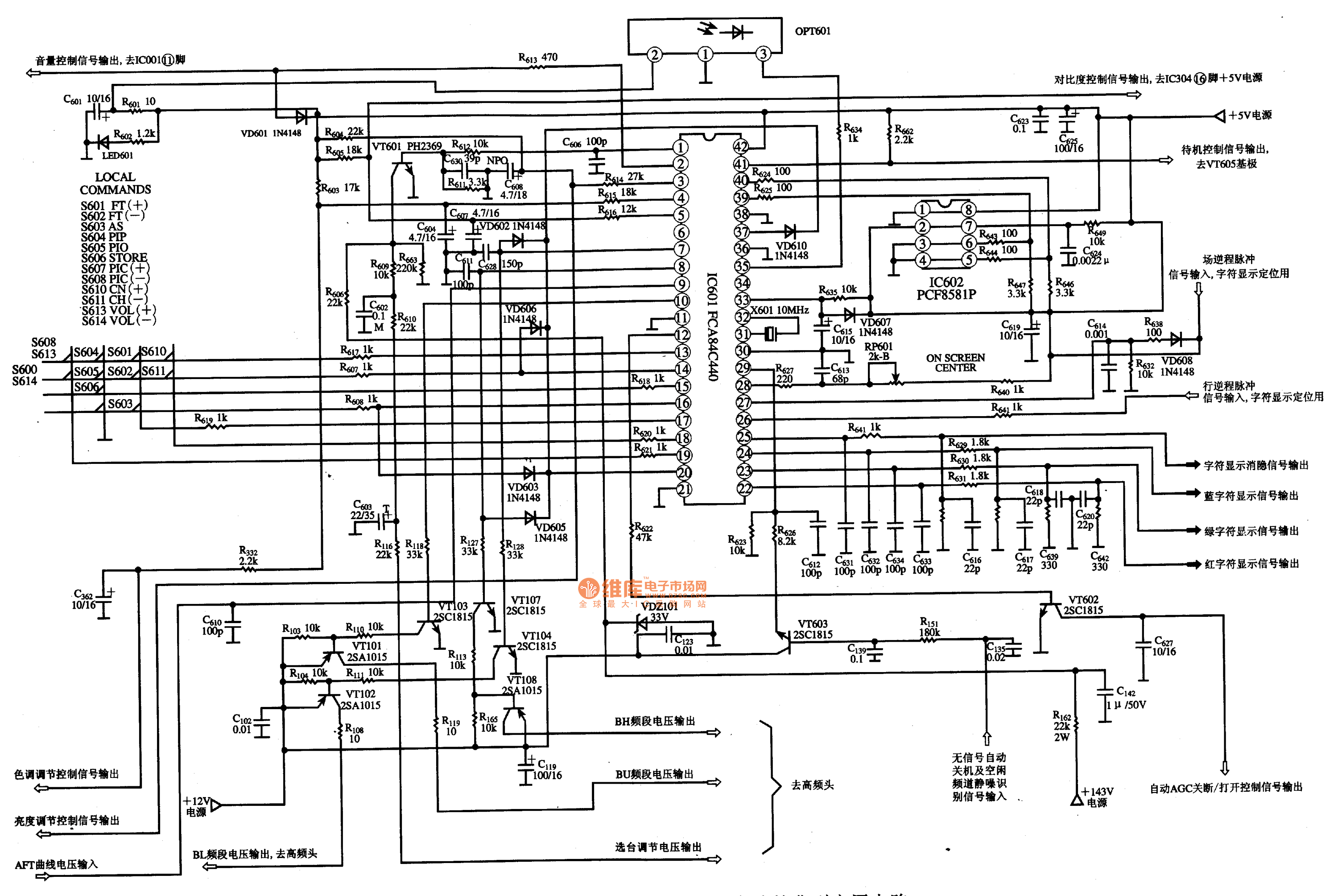
Temperature controlled relay circuit
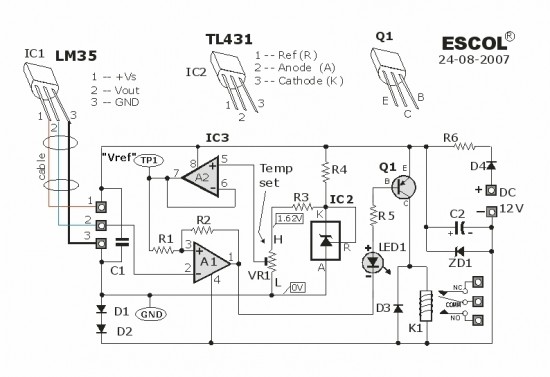
This temperature-controlled relay circuit is a simple yet highly accurate thermal control circuit that can be used in applications requiring automatic temperature regulation.
The temperature-controlled relay circuit operates by monitoring the ambient temperature and activating or deactivating a connected load based on predefined temperature thresholds. The core components of the circuit typically include a temperature sensor, a relay, and a control unit, which may consist of an operational amplifier or a microcontroller.
The temperature sensor, often a thermistor or an LM35, detects changes in temperature and converts this information into an electrical signal. This signal is then fed into the control unit, which processes the input and determines whether the temperature is above or below the set point. If the temperature exceeds the upper threshold, the control unit energizes the relay, closing the circuit and powering the connected load, such as a heater or fan. Conversely, if the temperature falls below the lower threshold, the relay deactivates, turning off the load.
To ensure precision, the circuit may incorporate hysteresis, which prevents rapid on-off cycling of the relay near the set point. This is achieved by setting two distinct temperature thresholds: one for activating the load and another for deactivating it. The use of a relay allows for high-power devices to be controlled safely, isolating the low-power control circuit from the high-voltage load.
For applications requiring user interaction, a potentiometer can be included to allow for easy adjustment of the temperature set points. Additionally, LED indicators may be integrated to provide visual feedback on the operational status of the circuit, indicating when the load is active.
Overall, this temperature-controlled relay circuit is versatile and can be adapted for various applications, including HVAC systems, incubators, and refrigeration units, ensuring efficient thermal management in an array of environments.This temperature controlled relay circuit is a simple yet highly accurate thermal control circuit which can be used in applications where automatic tempera. 🔗 External reference
The temperature-controlled relay circuit operates by monitoring the ambient temperature and activating or deactivating a connected load based on predefined temperature thresholds. The core components of the circuit typically include a temperature sensor, a relay, and a control unit, which may consist of an operational amplifier or a microcontroller.
The temperature sensor, often a thermistor or an LM35, detects changes in temperature and converts this information into an electrical signal. This signal is then fed into the control unit, which processes the input and determines whether the temperature is above or below the set point. If the temperature exceeds the upper threshold, the control unit energizes the relay, closing the circuit and powering the connected load, such as a heater or fan. Conversely, if the temperature falls below the lower threshold, the relay deactivates, turning off the load.
To ensure precision, the circuit may incorporate hysteresis, which prevents rapid on-off cycling of the relay near the set point. This is achieved by setting two distinct temperature thresholds: one for activating the load and another for deactivating it. The use of a relay allows for high-power devices to be controlled safely, isolating the low-power control circuit from the high-voltage load.
For applications requiring user interaction, a potentiometer can be included to allow for easy adjustment of the temperature set points. Additionally, LED indicators may be integrated to provide visual feedback on the operational status of the circuit, indicating when the load is active.
Overall, this temperature-controlled relay circuit is versatile and can be adapted for various applications, including HVAC systems, incubators, and refrigeration units, ensuring efficient thermal management in an array of environments.This temperature controlled relay circuit is a simple yet highly accurate thermal control circuit which can be used in applications where automatic tempera. 🔗 External reference