Temperature-to-Frequency Converter: Enabling Simple Telemetry
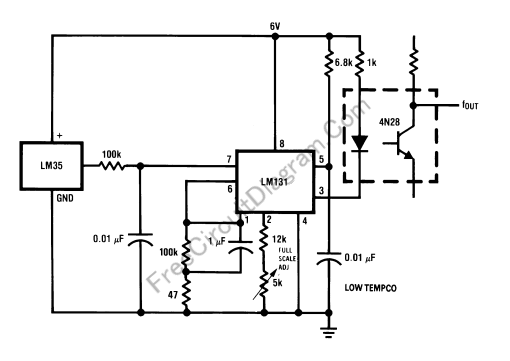
When a DC voltage signal is transmitted over long distances, it experiences attenuation with unpredictable characteristics introduced by the transmission medium, such as cable resistance that varies with temperature changes. In contrast, carrying information using frequency rather than a DC voltage level results in a more stable signal, despite potential distortion of its amplitude characteristics due to nonlinear processes in the medium. Notably, frequency information can be transmitted over a standard voice radio transmitter, allowing for longer-distance communication. The circuit depicted in the schematic diagram below generates an audio frequency that varies in proportion to the temperature being measured, utilizing the LM35 temperature sensor chip. If optical isolation is not required, the 4N28 opto-coupler can be omitted, enabling a direct connection of a 1k resistor to pin 3 of the LM131 IC, with the output signal tapped from that junction. The output will produce a frequency range of 20Hz to 1500Hz corresponding to temperatures from 2 to 150 degrees Celsius. This frequency signal, which carries temperature information, can be effectively transmitted using narrow-band standard voice communication radio.
The circuit utilizes an LM35 temperature sensor, which provides an analog output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. This sensor is known for its precision and ease of use, making it suitable for various temperature measurement applications. The output from the LM35 is fed into the LM131 integrated circuit, which is configured to convert the analog voltage signal into a frequency-modulated signal. The LM131 is a well-regarded frequency-to-voltage converter, and its configuration allows for the output frequency to vary with the input voltage, thus providing a frequency output that corresponds to the temperature being measured.
In scenarios where optical isolation is not necessary, the inclusion of an opto-coupler, such as the 4N28, can be bypassed. This simplifies the circuit and reduces component count, which can be beneficial for compact designs or cost-sensitive applications. The 1k resistor connected to pin 3 of the LM131 serves to set the output frequency range, ensuring it operates within the desired limits of 20Hz to 1500Hz. This frequency range is particularly advantageous for transmission over voice radio, as it falls within the capabilities of narrow-band communication systems.
The ability to transmit temperature data over considerable distances using standard radio equipment opens up numerous applications, particularly in remote monitoring and telemetry systems. The frequency-modulated output can be easily demodulated at the receiving end, allowing for accurate temperature readings to be reconstructed from the transmitted signal. This method of transmission is not only efficient but also resilient to some degree of interference, making it suitable for various environmental conditions. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical approach to temperature sensing and data transmission, leveraging frequency modulation for effective long-distance communication.If you send a DC voltage signal to carry the information for a long distance, then the signal will suffer attenuation with unpredictable characteristic introduced by the medium, for example the cable resistance that vary with temperature changes. If you carry the information with frequency, not a DC voltage level, then the frequency will be stabl
e even though it`s amplitude characteristic is distorted by nonlinear process of the medium. More interesting, you can send the frequency information over a general voice radio transmitter to send the information for much longer distance. The circuit described in the schematic diagram below produce an audio frequency which varies proportional to temperature being measured.
The temperature sensing uses LM35 sensor chip. If you don`t need the optical isolation then you can omit 4N28 opto-coupler, connect 1k resistor directly to pin 3 of LM131 IC, and tap the output signal from that junction. The output will produce 20Hz to 1500Hz signal corresponding with 2-150 Celsius degree. This frequency signal carrying temperature information should be easily transmitted using narrow-band standard voice communication radio.
[Circuit`s schematic diagram source: National Semiconductor Application Notes] 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an LM35 temperature sensor, which provides an analog output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. This sensor is known for its precision and ease of use, making it suitable for various temperature measurement applications. The output from the LM35 is fed into the LM131 integrated circuit, which is configured to convert the analog voltage signal into a frequency-modulated signal. The LM131 is a well-regarded frequency-to-voltage converter, and its configuration allows for the output frequency to vary with the input voltage, thus providing a frequency output that corresponds to the temperature being measured.
In scenarios where optical isolation is not necessary, the inclusion of an opto-coupler, such as the 4N28, can be bypassed. This simplifies the circuit and reduces component count, which can be beneficial for compact designs or cost-sensitive applications. The 1k resistor connected to pin 3 of the LM131 serves to set the output frequency range, ensuring it operates within the desired limits of 20Hz to 1500Hz. This frequency range is particularly advantageous for transmission over voice radio, as it falls within the capabilities of narrow-band communication systems.
The ability to transmit temperature data over considerable distances using standard radio equipment opens up numerous applications, particularly in remote monitoring and telemetry systems. The frequency-modulated output can be easily demodulated at the receiving end, allowing for accurate temperature readings to be reconstructed from the transmitted signal. This method of transmission is not only efficient but also resilient to some degree of interference, making it suitable for various environmental conditions. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical approach to temperature sensing and data transmission, leveraging frequency modulation for effective long-distance communication.If you send a DC voltage signal to carry the information for a long distance, then the signal will suffer attenuation with unpredictable characteristic introduced by the medium, for example the cable resistance that vary with temperature changes. If you carry the information with frequency, not a DC voltage level, then the frequency will be stabl
e even though it`s amplitude characteristic is distorted by nonlinear process of the medium. More interesting, you can send the frequency information over a general voice radio transmitter to send the information for much longer distance. The circuit described in the schematic diagram below produce an audio frequency which varies proportional to temperature being measured.
The temperature sensing uses LM35 sensor chip. If you don`t need the optical isolation then you can omit 4N28 opto-coupler, connect 1k resistor directly to pin 3 of LM131 IC, and tap the output signal from that junction. The output will produce 20Hz to 1500Hz signal corresponding with 2-150 Celsius degree. This frequency signal carrying temperature information should be easily transmitted using narrow-band standard voice communication radio.
[Circuit`s schematic diagram source: National Semiconductor Application Notes] 🔗 External reference