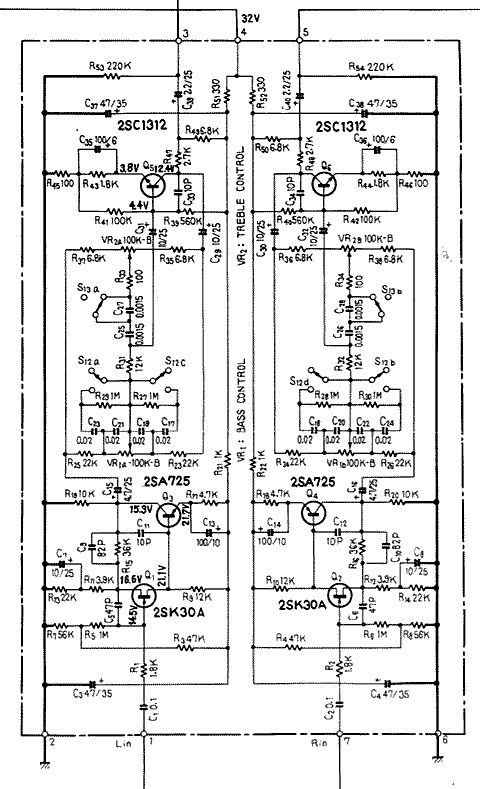
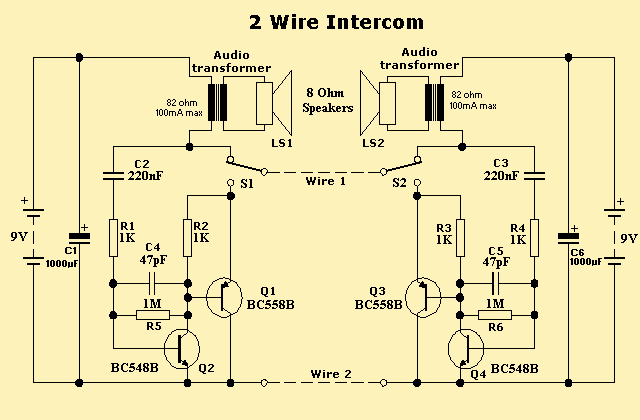
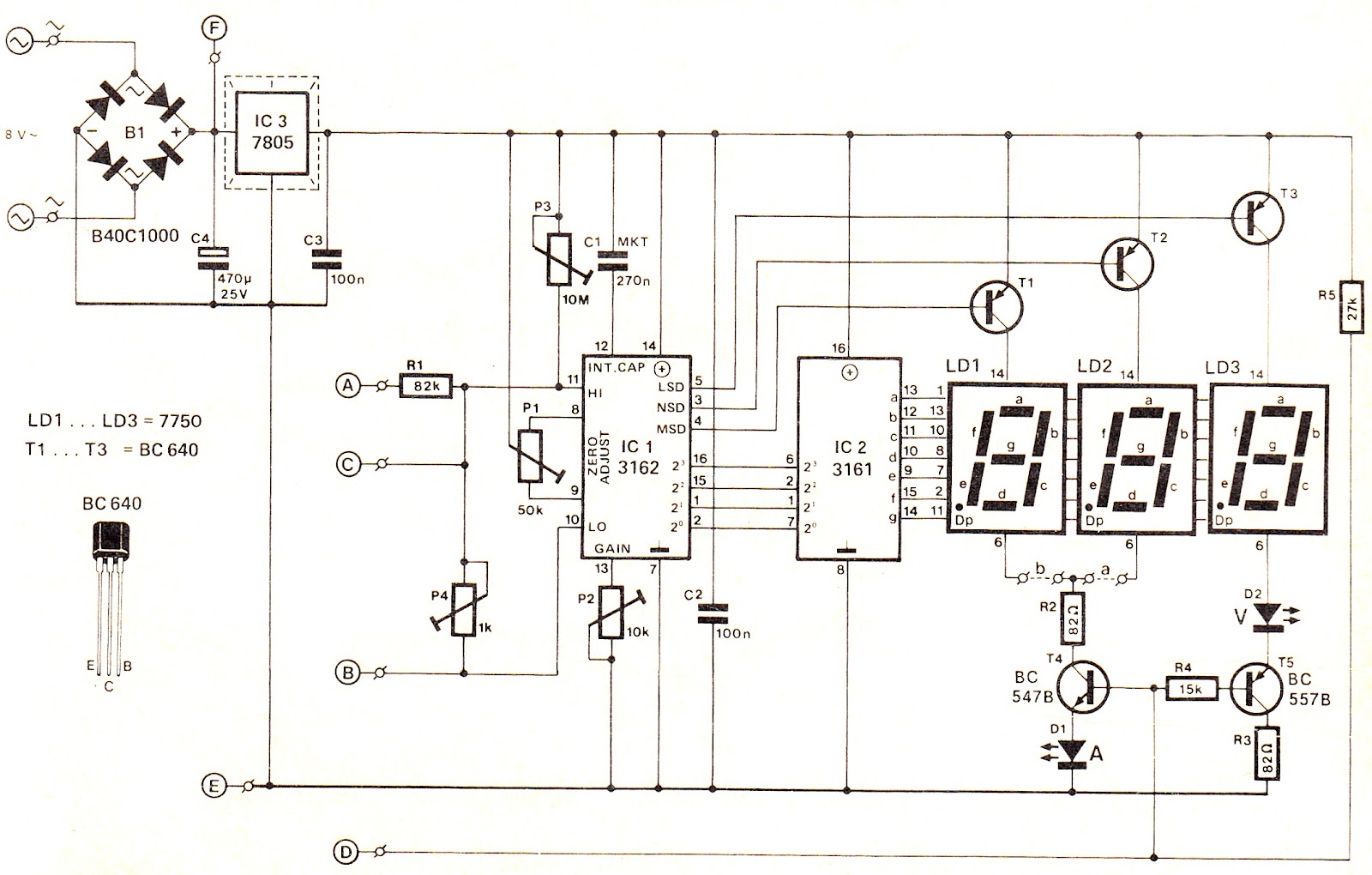
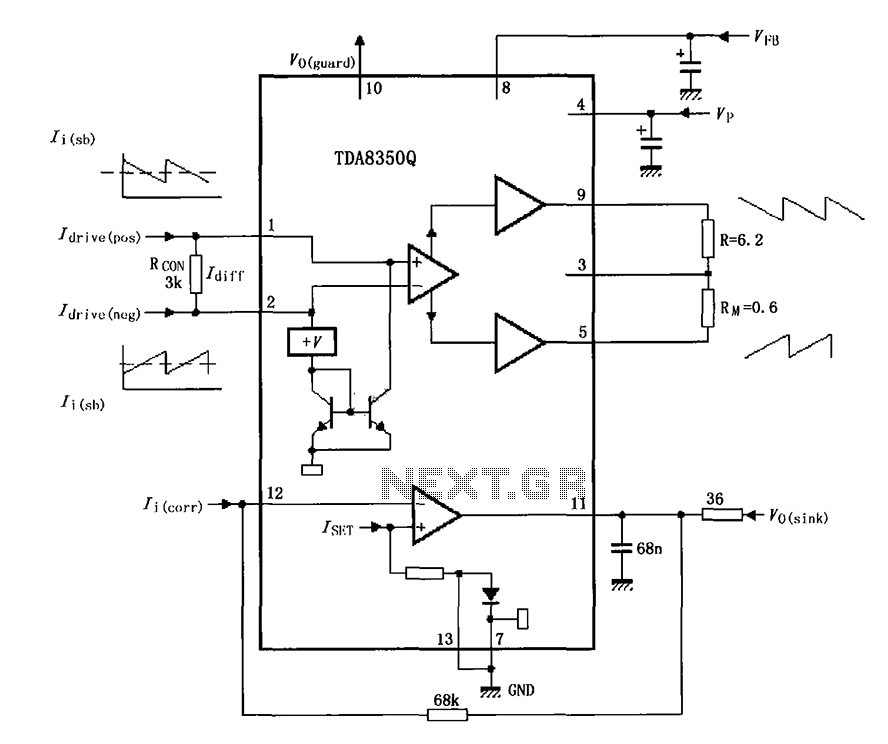
Simple Ham Radio Circuit Audio Filter With 741 IC

This circuit will filter out interference signals and ensure that the signal received from the Morse code station stands out.
The described circuit functions as a signal processing system specifically designed to enhance the clarity of Morse code transmissions by minimizing the impact of unwanted interference. The primary components of this circuit typically include a bandpass filter, an amplifier, and a demodulator.
The bandpass filter is crucial in allowing only the desired frequency range associated with Morse code signals to pass through while attenuating frequencies outside this range. This is essential for isolating the Morse code signal from background noise and other unwanted signals.
Following the filtering stage, the amplified signal is directed to an amplifier. The amplifier boosts the filtered signal to a level suitable for further processing. This stage is vital in ensuring that the signal strength is sufficient for the demodulation process, which converts the modulated Morse code signal back into a readable format.
The demodulator then interprets the amplified Morse code signal, converting it into a format that can be understood by the receiving equipment or operator. This may involve translating the signal into audio tones or visual representations, allowing for effective communication.
In summary, this circuit is designed to enhance the reception of Morse code signals by filtering out noise and interference, amplifying the desired signals, and processing them for clear communication. This comprehensive approach ensures reliable Morse code transmission and reception in various operational conditions.This circuit will help to filter out the interference signal and ensure that the signal received from the Morse code station stand out. The .. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a signal processing system specifically designed to enhance the clarity of Morse code transmissions by minimizing the impact of unwanted interference. The primary components of this circuit typically include a bandpass filter, an amplifier, and a demodulator.
The bandpass filter is crucial in allowing only the desired frequency range associated with Morse code signals to pass through while attenuating frequencies outside this range. This is essential for isolating the Morse code signal from background noise and other unwanted signals.
Following the filtering stage, the amplified signal is directed to an amplifier. The amplifier boosts the filtered signal to a level suitable for further processing. This stage is vital in ensuring that the signal strength is sufficient for the demodulation process, which converts the modulated Morse code signal back into a readable format.
The demodulator then interprets the amplified Morse code signal, converting it into a format that can be understood by the receiving equipment or operator. This may involve translating the signal into audio tones or visual representations, allowing for effective communication.
In summary, this circuit is designed to enhance the reception of Morse code signals by filtering out noise and interference, amplifying the desired signals, and processing them for clear communication. This comprehensive approach ensures reliable Morse code transmission and reception in various operational conditions.This circuit will help to filter out the interference signal and ensure that the signal received from the Morse code station stand out. The .. 🔗 External reference