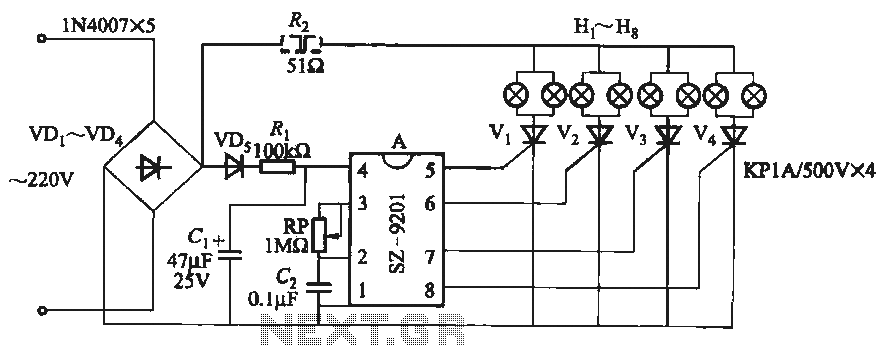
Temperature to Voltage Converter Circuit
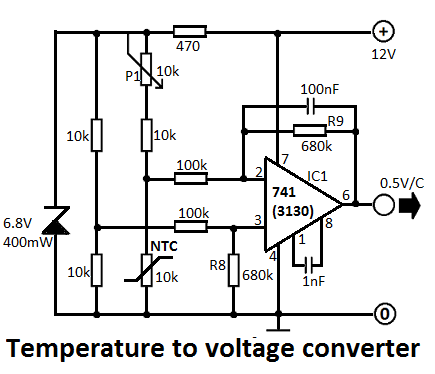
This simple temperature-to-voltage converter circuit allows for precise measurement of room temperature using an NTC resistor or thermistor.
The temperature-to-voltage converter circuit typically employs a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor, which exhibits a decrease in resistance as temperature increases. This property makes it suitable for temperature sensing applications. The circuit can be designed using an operational amplifier (op-amp) to convert the resistance change of the thermistor into a corresponding voltage output.
In a basic configuration, the thermistor is connected in a voltage divider arrangement with a fixed resistor. The output voltage from this divider is then fed into the non-inverting input of the op-amp. The op-amp can be configured in a non-inverting amplifier mode, where it amplifies the voltage signal from the thermistor. The gain of the op-amp can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback and input resistors.
To enhance the accuracy of the temperature measurement, the circuit may include calibration adjustments. This can be achieved by incorporating a potentiometer in the feedback loop of the op-amp, allowing for fine-tuning of the output voltage to match known temperature values.
The output voltage from the op-amp can be interfaced with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital temperature readings, or it can be used to drive an analog display such as an LED or an analog meter. The entire circuit can be powered using a standard DC power supply, ensuring stable operation across a range of environmental conditions.
In summary, the temperature-to-voltage converter circuit utilizing an NTC thermistor and an op-amp provides a reliable method for measuring room temperature, with potential applications in HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and home automation.With this simple temperature to voltage converter circuit we can do a precise measurement of the temperature in a room. A NTC resistor or a thermistor is u.. 🔗 External reference
The temperature-to-voltage converter circuit typically employs a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor, which exhibits a decrease in resistance as temperature increases. This property makes it suitable for temperature sensing applications. The circuit can be designed using an operational amplifier (op-amp) to convert the resistance change of the thermistor into a corresponding voltage output.
In a basic configuration, the thermistor is connected in a voltage divider arrangement with a fixed resistor. The output voltage from this divider is then fed into the non-inverting input of the op-amp. The op-amp can be configured in a non-inverting amplifier mode, where it amplifies the voltage signal from the thermistor. The gain of the op-amp can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback and input resistors.
To enhance the accuracy of the temperature measurement, the circuit may include calibration adjustments. This can be achieved by incorporating a potentiometer in the feedback loop of the op-amp, allowing for fine-tuning of the output voltage to match known temperature values.
The output voltage from the op-amp can be interfaced with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital temperature readings, or it can be used to drive an analog display such as an LED or an analog meter. The entire circuit can be powered using a standard DC power supply, ensuring stable operation across a range of environmental conditions.
In summary, the temperature-to-voltage converter circuit utilizing an NTC thermistor and an op-amp provides a reliable method for measuring room temperature, with potential applications in HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and home automation.With this simple temperature to voltage converter circuit we can do a precise measurement of the temperature in a room. A NTC resistor or a thermistor is u.. 🔗 External reference