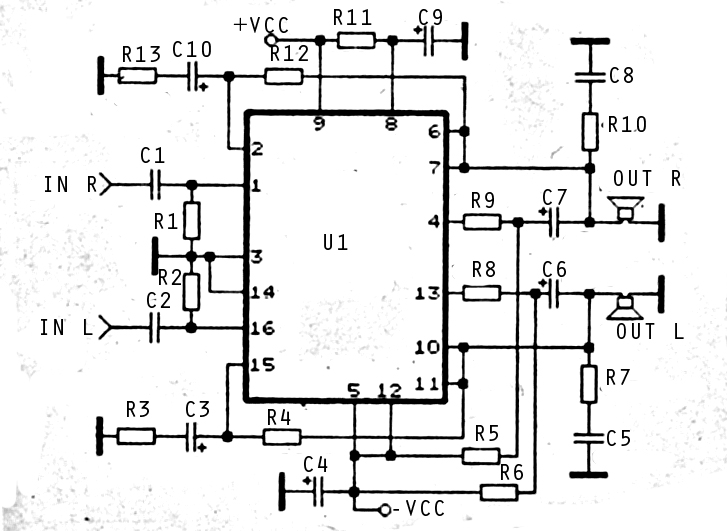
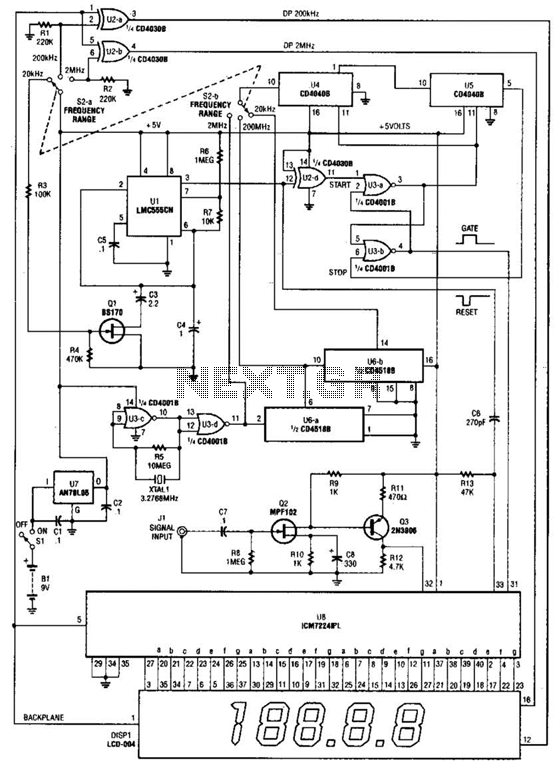
Guitar noise circuit diagram
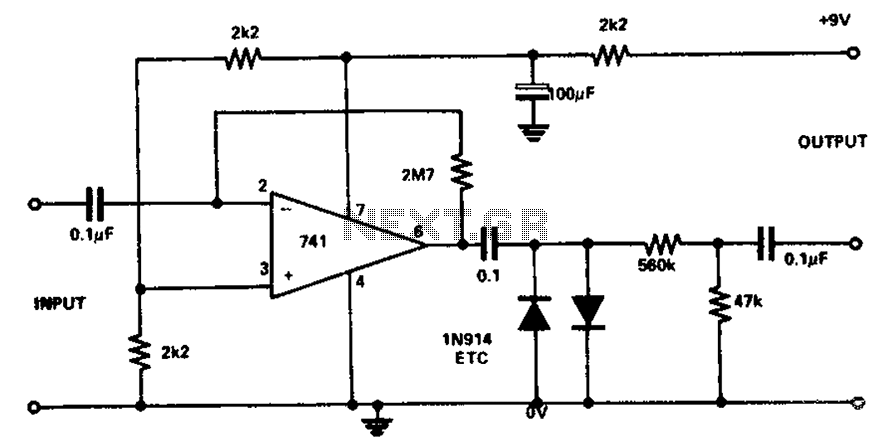
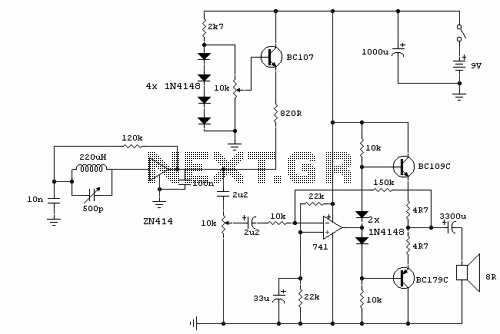
The circuit utilizes the 741 operational amplifier, which has a maximum gain of 20,000. However, the design achieves a gain of 2.7 million, resulting in output distortion. This distortion is attributed to noise effects. Two clamping diodes are employed to limit the output, while two additional diodes influence the gain. The circuit configuration is designed to produce a new sound while also preserving the original sound.
The described circuit leverages the operational amplifier (op-amp) model 741, known for its versatility in various applications. The maximum theoretical gain of the 741 is 20,000; however, in this design, the op-amp is configured to achieve an extraordinary gain of 2.7 million. This excessive gain can lead to significant output distortion, primarily due to noise interference, which is common in high-gain amplifier circuits.
To mitigate the distortion effects, the circuit incorporates two clamping diodes. These diodes function to prevent the output voltage from exceeding certain levels, thereby reducing the likelihood of clipping and maintaining signal integrity. The clamping action helps to stabilize the output, ensuring that the amplifier operates within a linear range.
Additionally, two other diodes are included in the design to influence the gain characteristics of the circuit. These diodes play a crucial role in shaping the frequency response and enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier. The combined effect of the clamping and gain-modifying diodes results in a circuit capable of generating a new sound profile while still preserving the nuances of the original audio signal.
The circuit's design is particularly useful in audio applications where maintaining sound quality is paramount. It can be employed in various audio processing tasks, such as effects units or sound synthesis, where both the manipulation of sound and fidelity to the original source are desired. Careful consideration of component selection and circuit layout will further enhance performance and minimize unwanted artifacts in the output. Circuit Description: The maximum gain circuit 741 to 20000, but the design of the circuit while filling a gain of 2.7 million, and then causes the output distortion. This disto rtion caused by noise effects. Two clamping diodes to reduce output low, while the two diodes that points multiplier impact becomes low. Since the sandwich will produce a new sound, the circuit can also be used to maintain the original sound.
The described circuit leverages the operational amplifier (op-amp) model 741, known for its versatility in various applications. The maximum theoretical gain of the 741 is 20,000; however, in this design, the op-amp is configured to achieve an extraordinary gain of 2.7 million. This excessive gain can lead to significant output distortion, primarily due to noise interference, which is common in high-gain amplifier circuits.
To mitigate the distortion effects, the circuit incorporates two clamping diodes. These diodes function to prevent the output voltage from exceeding certain levels, thereby reducing the likelihood of clipping and maintaining signal integrity. The clamping action helps to stabilize the output, ensuring that the amplifier operates within a linear range.
Additionally, two other diodes are included in the design to influence the gain characteristics of the circuit. These diodes play a crucial role in shaping the frequency response and enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier. The combined effect of the clamping and gain-modifying diodes results in a circuit capable of generating a new sound profile while still preserving the nuances of the original audio signal.
The circuit's design is particularly useful in audio applications where maintaining sound quality is paramount. It can be employed in various audio processing tasks, such as effects units or sound synthesis, where both the manipulation of sound and fidelity to the original source are desired. Careful consideration of component selection and circuit layout will further enhance performance and minimize unwanted artifacts in the output. Circuit Description: The maximum gain circuit 741 to 20000, but the design of the circuit while filling a gain of 2.7 million, and then causes the output distortion. This disto rtion caused by noise effects. Two clamping diodes to reduce output low, while the two diodes that points multiplier impact becomes low. Since the sandwich will produce a new sound, the circuit can also be used to maintain the original sound.