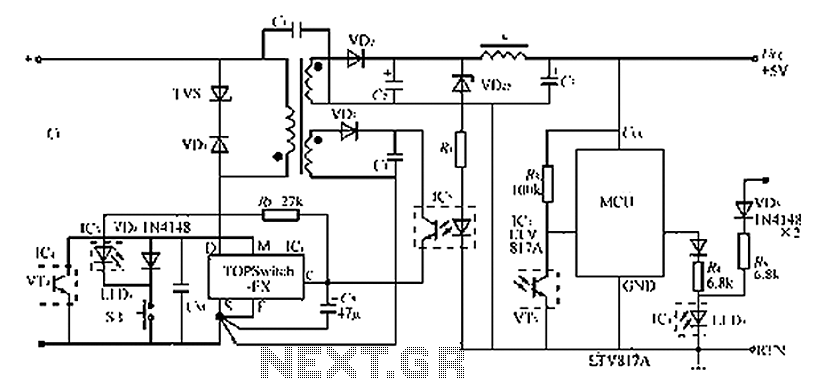
UV sensor schematic circuit
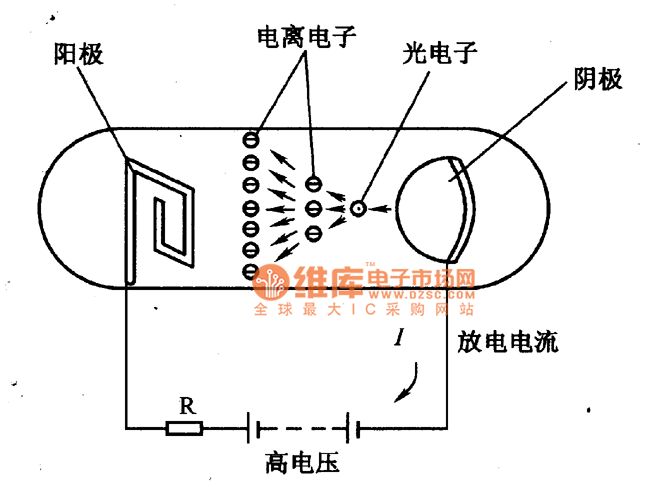
The figure illustrates a schematic circuit of a UV sensor. When voltage is applied between the cathode and anode, and UV radiation passes through the quartz glass tube on the cathode's optical surface, the cathode material, which is coated for electron emission, releases photoelectrons. Under the influence of a strong electric field, photoelectrons are generated.
The UV sensor circuit operates based on the photoelectric effect, where the absorption of UV radiation by the cathode material leads to the emission of electrons. The cathode is typically constructed from a material that has a low work function, allowing it to emit electrons efficiently when exposed to UV light. The quartz glass tube serves as a protective barrier while allowing UV wavelengths to pass through, ensuring that the sensor responds accurately to UV radiation.
In this circuit, the anode collects the emitted photoelectrons, creating a measurable current proportional to the intensity of the UV radiation. The output current can be amplified and processed to provide a readable signal, which may be displayed on a meter or used in a feedback loop for further control applications.
The schematic may include additional components such as resistors to limit current, capacitors for filtering noise, and operational amplifiers for signal conditioning. The design should ensure that the sensor is calibrated for the specific wavelength range of interest, as different materials may respond variably to UV light. Proper shielding and grounding techniques should also be implemented to minimize electromagnetic interference, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the sensor's output.
Overall, the UV sensor circuit is a critical component in applications ranging from environmental monitoring to industrial safety, where the detection of UV radiation is essential for assessing exposure levels.The figure is a schematic circuit of UV sensor. When UV sensor is coupled by voltage between the cathode and anode, and the UV radiation gets through the quartz glass tube on the cathode of the optical surface, because of the cathode material coated with electron emission, cathode will release photoelectrons.Influenced by the strong electric field, photoel.. 🔗 External reference
The UV sensor circuit operates based on the photoelectric effect, where the absorption of UV radiation by the cathode material leads to the emission of electrons. The cathode is typically constructed from a material that has a low work function, allowing it to emit electrons efficiently when exposed to UV light. The quartz glass tube serves as a protective barrier while allowing UV wavelengths to pass through, ensuring that the sensor responds accurately to UV radiation.
In this circuit, the anode collects the emitted photoelectrons, creating a measurable current proportional to the intensity of the UV radiation. The output current can be amplified and processed to provide a readable signal, which may be displayed on a meter or used in a feedback loop for further control applications.
The schematic may include additional components such as resistors to limit current, capacitors for filtering noise, and operational amplifiers for signal conditioning. The design should ensure that the sensor is calibrated for the specific wavelength range of interest, as different materials may respond variably to UV light. Proper shielding and grounding techniques should also be implemented to minimize electromagnetic interference, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the sensor's output.
Overall, the UV sensor circuit is a critical component in applications ranging from environmental monitoring to industrial safety, where the detection of UV radiation is essential for assessing exposure levels.The figure is a schematic circuit of UV sensor. When UV sensor is coupled by voltage between the cathode and anode, and the UV radiation gets through the quartz glass tube on the cathode of the optical surface, because of the cathode material coated with electron emission, cathode will release photoelectrons.Influenced by the strong electric field, photoel.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713