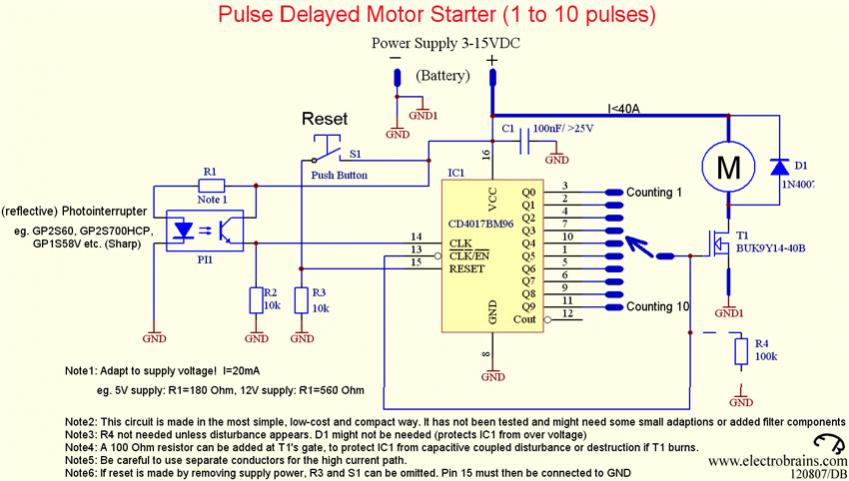
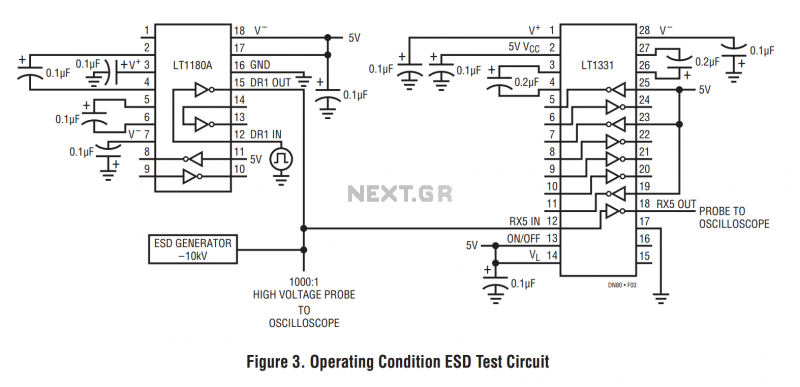
thermometer circuit using lm335

The circuit illustrated below represents a simple thermometer circuit based on the LM335 temperature sensor. This circuit comprises two main components: the LM335 sensor and its adjustment circuitry. The output from the LM335 generates a voltage of 10 millivolts per degree Celsius, meaning that at 25 degrees Celsius, the output is 2.982 VDC. A reference circuit provides a zero reference voltage, which is adjusted to 2.832 volts, calculated as (2.982 volts - (25 degrees x 10 millivolts/degree)). To measure the temperature directly in degrees Celsius, the positive lead from a high impedance digital voltmeter (DVM) should be connected to the output pin of the LM335, while the negative lead should be connected to the 2.732-volt reference pin. The output of 10 millivolts per degree Celsius is equivalent to 10 millivolts per Kelvin, as a change of one degree Celsius corresponds to a change of one Kelvin. The only difference between the two temperature scales is their offset. The melting point of ice is 0 degrees Celsius or 273.15 Kelvin, and the boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius or 373.15 Kelvin.
The LM335 is a precision temperature sensor that operates over a wide temperature range, typically from -40 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius. It is a three-terminal device that outputs a linear voltage proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. The sensor's output is directly related to the temperature, allowing for straightforward conversion to a digital readout using a multimeter or an analog display.
The adjustment circuitry is crucial for calibrating the output voltage to ensure accurate temperature readings. This may include operational amplifiers configured as voltage followers to buffer the output signal, as well as resistive voltage dividers to set the reference voltage accurately. The reference voltage is essential for establishing a baseline measurement, ensuring that the output from the LM335 can be interpreted correctly.
For practical applications, the circuit can be implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) for enhanced stability and durability. Additionally, it is advisable to use high-precision resistors in the adjustment circuitry to minimize errors and enhance the accuracy of the temperature readings. The circuit can be powered using a standard DC power supply, ensuring that the LM335 operates within its specified voltage range for optimal performance.
In summary, this thermometer circuit utilizing the LM335 sensor provides a reliable method for temperature measurement, with the ability to easily interface with digital voltmeters for straightforward reading and calibration. The design emphasizes accuracy and simplicity, making it suitable for various temperature sensing applications.This circuit in below is show the simple form of the thermometer circuit. The circuit is based on LM335 as sensing the temperature. This is the figure of the circuit. The circuit consists of two parts: The LM335 and its adjustment. The output of the LM335 is 10 millivolts per degree C, with 25 degrees C corresponding to 2. 982 VDC. A reference circ uit provides a zero reference voltage. It is adjusted to (2. 982 volts - (25 degrees x 10 milli volts/degree) = 2. 832 volts. To read the temperature of the LM335 directly in degrees C, connect the + lead from a high impedance DVM to the output pin and the end of the DVM to the 2. 732 volt pin. The factor of 10 milli volts per degree C is equivalent to 10 milli volts per degree K, since a change of one degree C is equal to a change of one degree K.
The difference in the two scales is only their offsets. The melting point of water ice is 0 degrees C and 273. 15 degrees K. The boiling point of water is 100 degrees C and 373. 15 degrees K. 🔗 External reference
The LM335 is a precision temperature sensor that operates over a wide temperature range, typically from -40 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius. It is a three-terminal device that outputs a linear voltage proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. The sensor's output is directly related to the temperature, allowing for straightforward conversion to a digital readout using a multimeter or an analog display.
The adjustment circuitry is crucial for calibrating the output voltage to ensure accurate temperature readings. This may include operational amplifiers configured as voltage followers to buffer the output signal, as well as resistive voltage dividers to set the reference voltage accurately. The reference voltage is essential for establishing a baseline measurement, ensuring that the output from the LM335 can be interpreted correctly.
For practical applications, the circuit can be implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) for enhanced stability and durability. Additionally, it is advisable to use high-precision resistors in the adjustment circuitry to minimize errors and enhance the accuracy of the temperature readings. The circuit can be powered using a standard DC power supply, ensuring that the LM335 operates within its specified voltage range for optimal performance.
In summary, this thermometer circuit utilizing the LM335 sensor provides a reliable method for temperature measurement, with the ability to easily interface with digital voltmeters for straightforward reading and calibration. The design emphasizes accuracy and simplicity, making it suitable for various temperature sensing applications.This circuit in below is show the simple form of the thermometer circuit. The circuit is based on LM335 as sensing the temperature. This is the figure of the circuit. The circuit consists of two parts: The LM335 and its adjustment. The output of the LM335 is 10 millivolts per degree C, with 25 degrees C corresponding to 2. 982 VDC. A reference circ uit provides a zero reference voltage. It is adjusted to (2. 982 volts - (25 degrees x 10 milli volts/degree) = 2. 832 volts. To read the temperature of the LM335 directly in degrees C, connect the + lead from a high impedance DVM to the output pin and the end of the DVM to the 2. 732 volt pin. The factor of 10 milli volts per degree C is equivalent to 10 milli volts per degree K, since a change of one degree C is equal to a change of one degree K.
The difference in the two scales is only their offsets. The melting point of water ice is 0 degrees C and 273. 15 degrees K. The boiling point of water is 100 degrees C and 373. 15 degrees K. 🔗 External reference