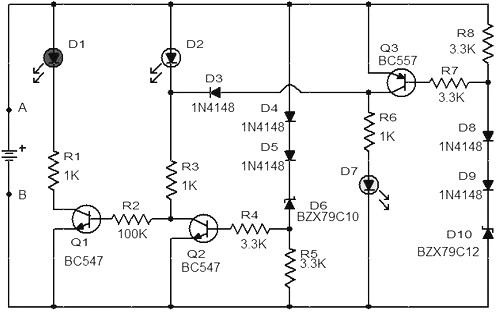
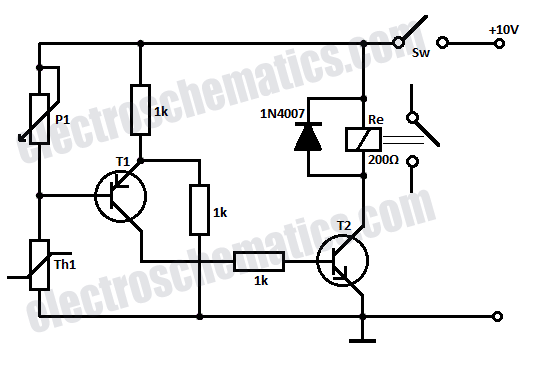
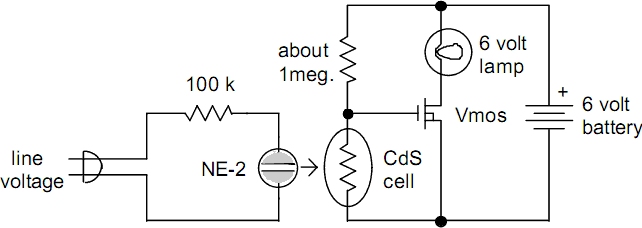
Three of the five band equalizer circuit transistor
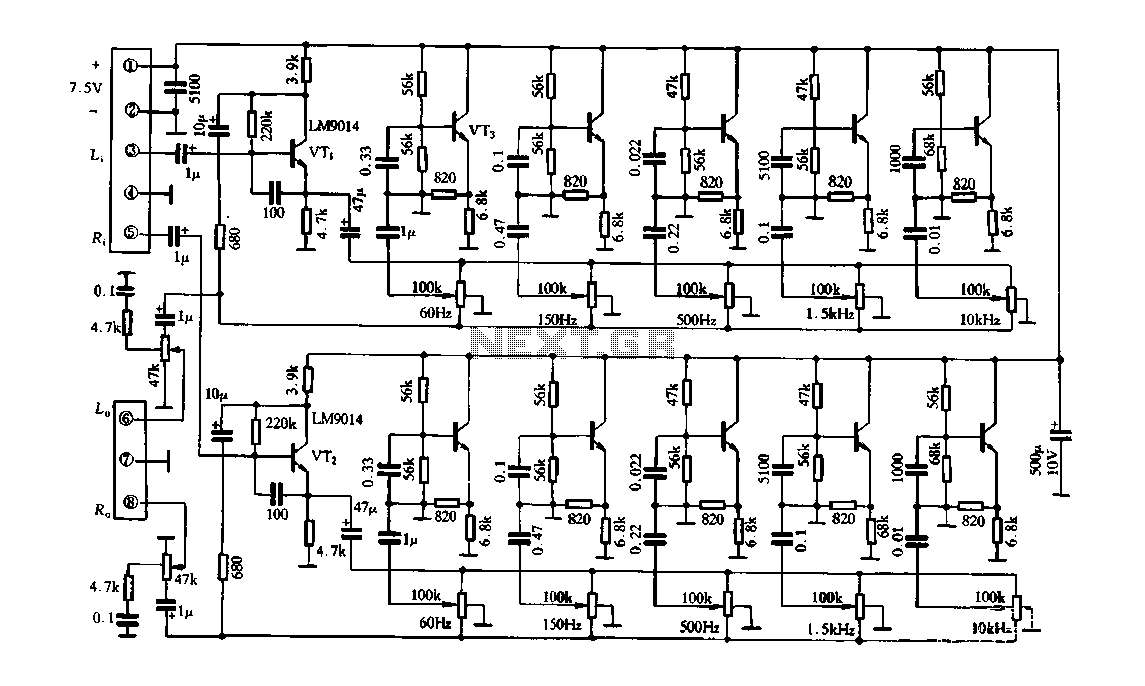
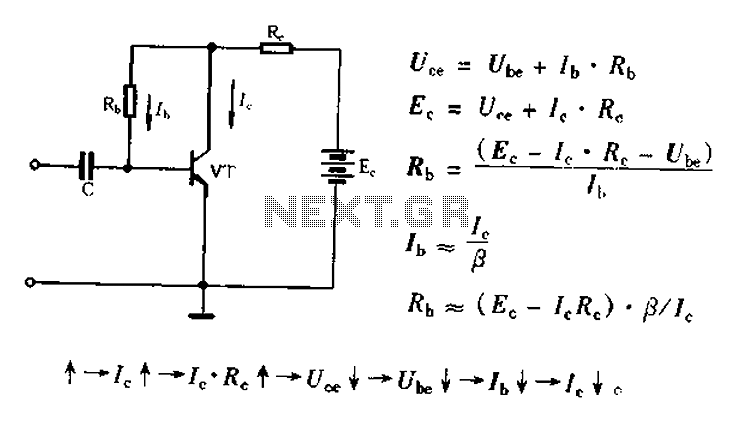
Figure 4-33 illustrates a circuit configuration that includes a common amplifier along with analog inductive circuits. In this setup, the transistor in the analog inductive circuit is utilized, and an increase in the bias resistor enhances circuit stability. A potentiometer is connected to the feedback loop of the amplifier, with its center tap grounded.
The circuit depicted in Figure 4-33 employs a common amplifier configuration, which is a foundational element in analog electronics. The common amplifier is characterized by its ability to provide significant voltage gain while maintaining stability within the circuit. The inclusion of analog inductive circuits allows for the manipulation of inductive components, which can be essential for various applications such as filtering or signal processing.
In this configuration, the transistor plays a crucial role in the analog inductive circuit. By increasing the bias resistor, the operating point of the transistor is adjusted, leading to improved thermal stability and performance. This adjustment is critical in ensuring that the amplifier operates within its optimal range, minimizing distortion and enhancing linearity.
The feedback loop of the amplifier is an integral part of its design, as it dictates the gain and stability of the overall system. The potentiometer connected to this feedback loop allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response. By adjusting the potentiometer, the feedback can be modified, which influences the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier. The center tap of the potentiometer being grounded is a common practice, as it provides a reference point for the feedback voltage, ensuring consistent performance across varying conditions.
Overall, this circuit configuration exemplifies the interplay between biasing, feedback, and stability in amplifier design, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in electronic systems.Figure 4-33 and using substantially the same circuit configuration, the common amplifier and analog inductive circuits are provided, but its analog inductive circuit transistor increases a bias resistor, the circuit more stable. Adjusting potentiometer connected to the feedback loop of the amplifier, the center tap to ground.
The circuit depicted in Figure 4-33 employs a common amplifier configuration, which is a foundational element in analog electronics. The common amplifier is characterized by its ability to provide significant voltage gain while maintaining stability within the circuit. The inclusion of analog inductive circuits allows for the manipulation of inductive components, which can be essential for various applications such as filtering or signal processing.
In this configuration, the transistor plays a crucial role in the analog inductive circuit. By increasing the bias resistor, the operating point of the transistor is adjusted, leading to improved thermal stability and performance. This adjustment is critical in ensuring that the amplifier operates within its optimal range, minimizing distortion and enhancing linearity.
The feedback loop of the amplifier is an integral part of its design, as it dictates the gain and stability of the overall system. The potentiometer connected to this feedback loop allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response. By adjusting the potentiometer, the feedback can be modified, which influences the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier. The center tap of the potentiometer being grounded is a common practice, as it provides a reference point for the feedback voltage, ensuring consistent performance across varying conditions.
Overall, this circuit configuration exemplifies the interplay between biasing, feedback, and stability in amplifier design, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in electronic systems.Figure 4-33 and using substantially the same circuit configuration, the common amplifier and analog inductive circuits are provided, but its analog inductive circuit transistor increases a bias resistor, the circuit more stable. Adjusting potentiometer connected to the feedback loop of the amplifier, the center tap to ground.