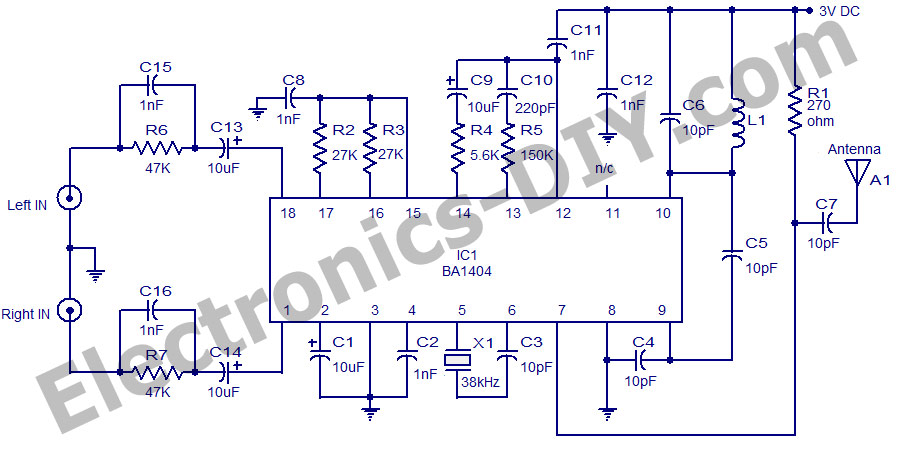
Toggle Flip Flop Laser Pointer Using CD4013
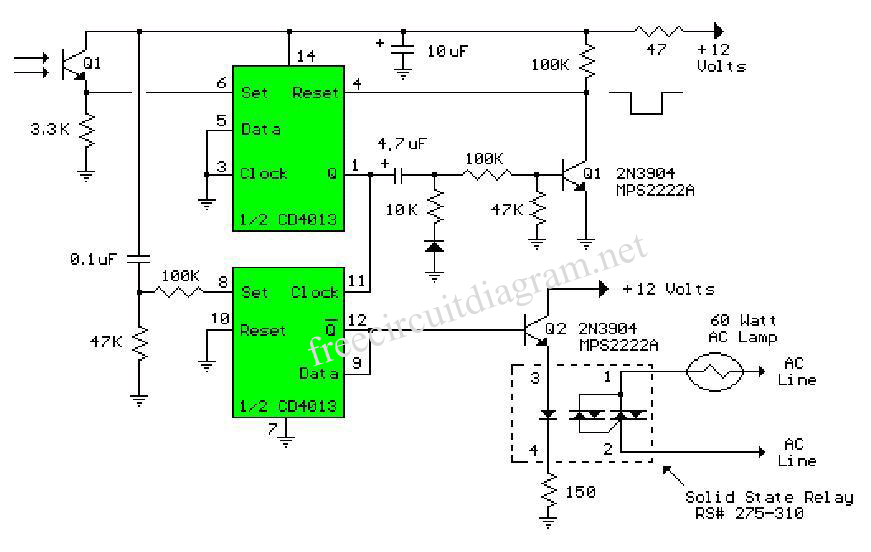
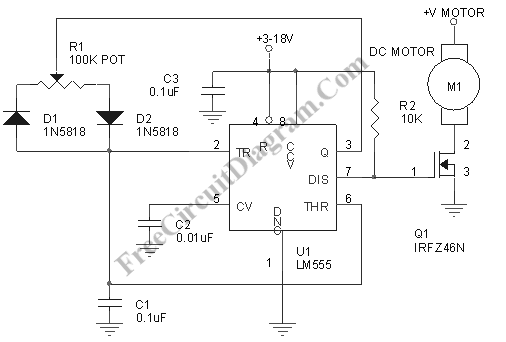
The circuit below is similar to the one above but can be used with a laser pointer to toggle the relay rather than a push button. The IR photo transistor Q1 (Radio Shack 276-145A) or similar is connected to the set input (pin 6). The photo transistor should be shielded from direct light.
This circuit utilizes an infrared (IR) photo transistor, specifically the Q1 component, which is crucial for detecting the laser pointer's beam. The photo transistor is connected to the set input of a relay module, allowing for remote activation of the relay through the modulation of light. When the laser pointer illuminates the photo transistor, it generates a current that triggers the relay, effectively toggling it on or off depending on the duration of the laser exposure.
To ensure optimal performance, the photo transistor must be shielded from ambient light sources that could cause false triggering. This can be achieved by placing the photo transistor in a housing that blocks out unwanted light while still allowing the infrared light from the laser pointer to reach it. The circuit design should also include appropriate resistors to limit the current flowing through the photo transistor and protect it from damage.
Additional components may be included in the circuit to enhance functionality, such as a capacitor for noise filtering, or a diode across the relay coil to prevent back EMF when the relay is deactivated. The relay itself can control various loads, making this circuit versatile for applications such as remote switching, security systems, or automation projects. Proper attention to the layout and connections will ensure reliable operation and longevity of the circuit.The circuit below is similar to the one above but can be used with a laser pointer to toggle the relay rather than a push button. The IR photo transistor Q1 (Radio Shack 276-145A) or similar is connected to the set input (pin 6). The photo transistor should be shielded from direct light. 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes an infrared (IR) photo transistor, specifically the Q1 component, which is crucial for detecting the laser pointer's beam. The photo transistor is connected to the set input of a relay module, allowing for remote activation of the relay through the modulation of light. When the laser pointer illuminates the photo transistor, it generates a current that triggers the relay, effectively toggling it on or off depending on the duration of the laser exposure.
To ensure optimal performance, the photo transistor must be shielded from ambient light sources that could cause false triggering. This can be achieved by placing the photo transistor in a housing that blocks out unwanted light while still allowing the infrared light from the laser pointer to reach it. The circuit design should also include appropriate resistors to limit the current flowing through the photo transistor and protect it from damage.
Additional components may be included in the circuit to enhance functionality, such as a capacitor for noise filtering, or a diode across the relay coil to prevent back EMF when the relay is deactivated. The relay itself can control various loads, making this circuit versatile for applications such as remote switching, security systems, or automation projects. Proper attention to the layout and connections will ensure reliable operation and longevity of the circuit.The circuit below is similar to the one above but can be used with a laser pointer to toggle the relay rather than a push button. The IR photo transistor Q1 (Radio Shack 276-145A) or similar is connected to the set input (pin 6). The photo transistor should be shielded from direct light. 🔗 External reference