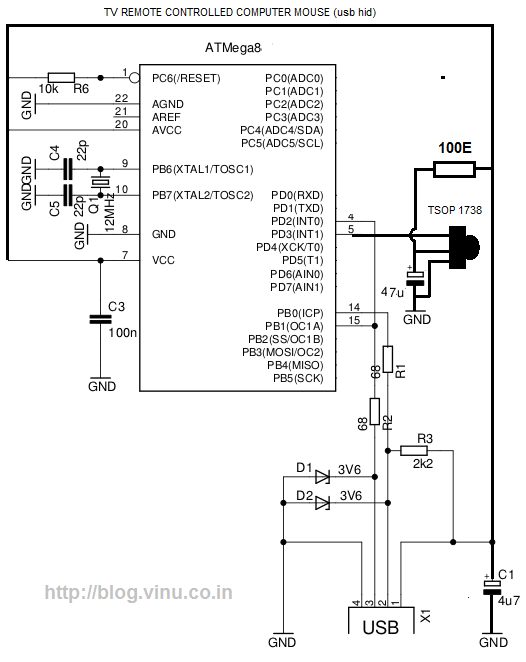
Radio Remote Control using DTMF Circuit
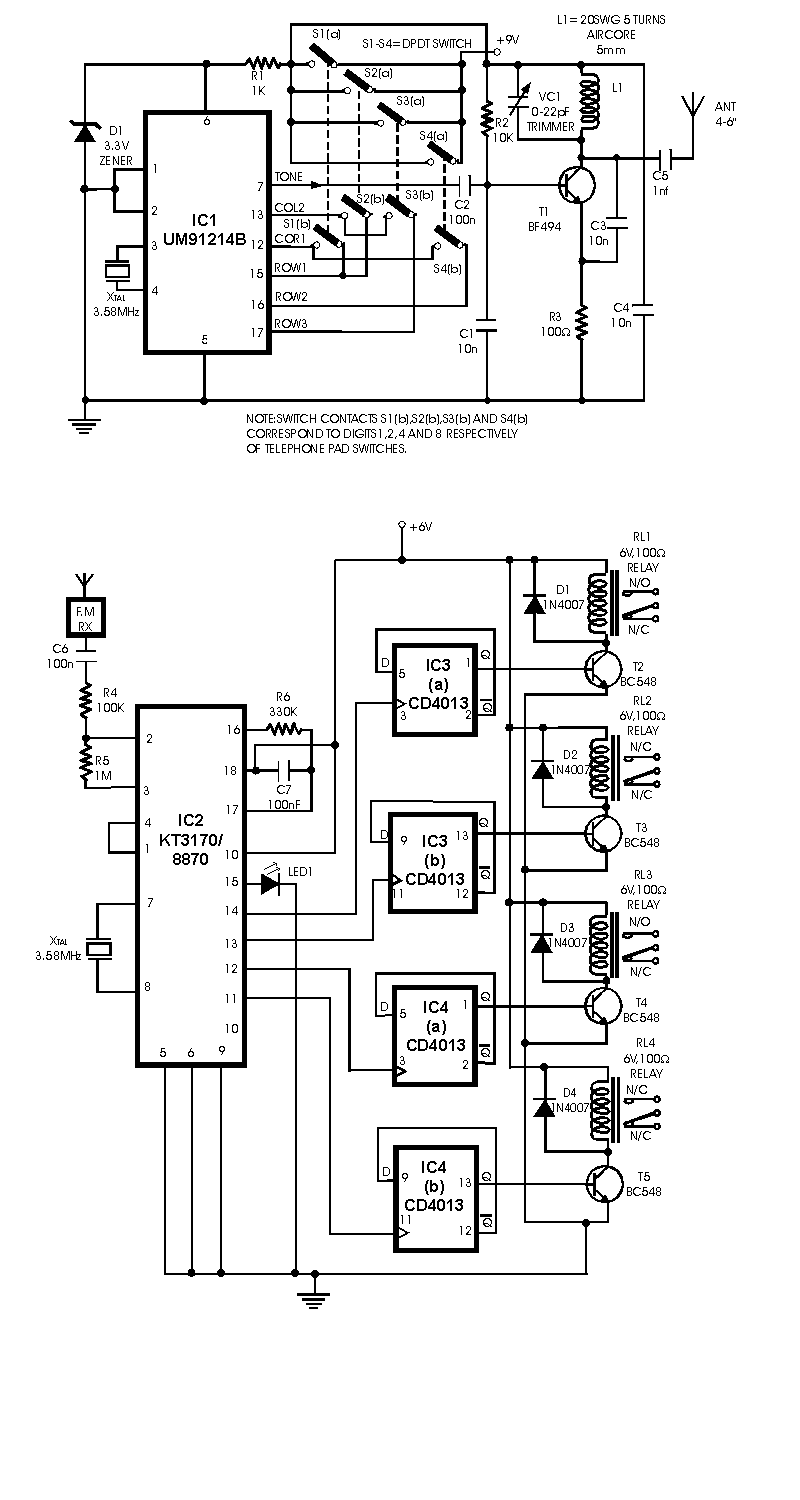
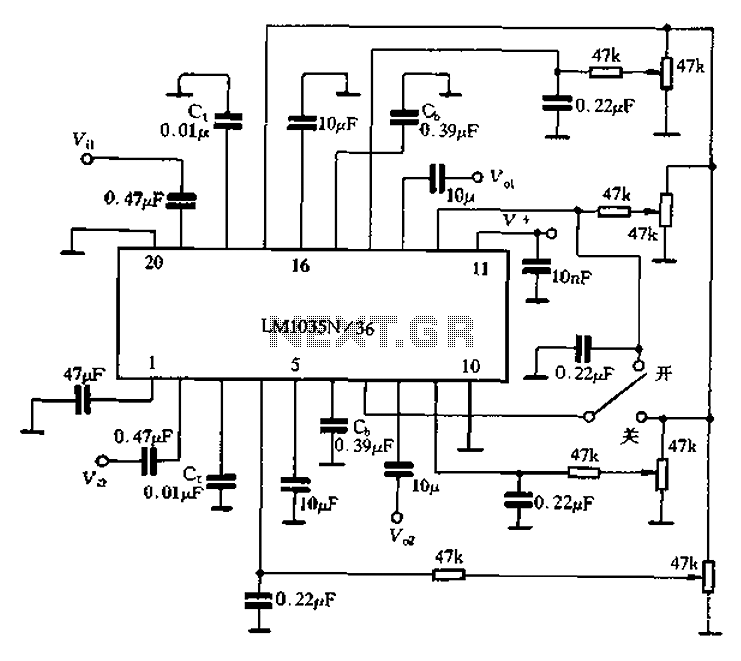
This circuit differs from similar circuits in view of its simplicity and a totally different concept of generating the control signals. Usually remote control circuits make use of infrared light to transmit control signals. Their use is thus limited to a very confined area and line-of-sight. However, this circuit makes use of radio frequency to transmit the control signals and hence it can be used for control from almost anywhere in the house. Here we make use of DTMF (dual-tone multi frequency) signals (used in telephones to dial the digits) as the control codes. The DTMF tones are used for frequency modulation of the carrier. At the receiver unit, these frequency modulated signals are intercepted to obtain DTMF tones at the speaker terminals.
This circuit design utilizes radio frequency (RF) technology to overcome the limitations imposed by infrared remote control systems, allowing for broader operational range and versatility. The core of the circuit is based on the generation and transmission of DTMF signals, which consist of two simultaneous audio frequencies. These frequencies are typically associated with the keypad tones of a telephone.
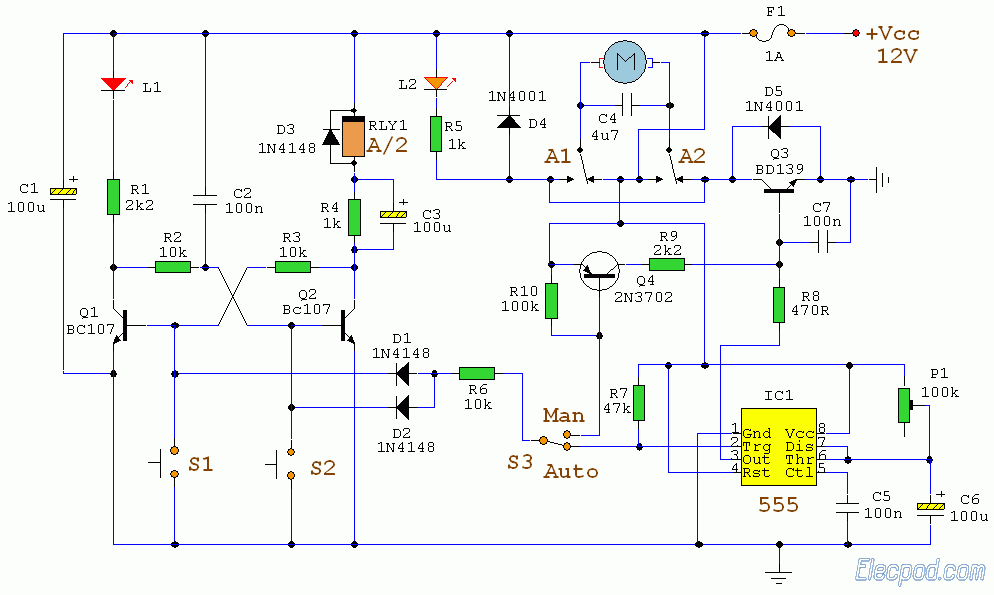
The transmitter section includes a DTMF encoder that converts the pressed key inputs into corresponding DTMF tones. These tones are then modulated onto a radio frequency carrier using a frequency modulation (FM) technique. The modulation process enables the information to be transmitted over a distance without the constraints of line-of-sight, typical of infrared systems.
At the receiver end, an RF receiver circuit is employed to capture the transmitted signals. The receiver is designed to demodulate the FM signals back into the original DTMF tones. This demodulation is crucial for restoring the control signals that can be interpreted by the subsequent control circuitry. The output from the receiver typically drives a speaker or can be interfaced with other electronic components to perform specific actions based on the received DTMF codes.
The overall architecture of this circuit offers significant advantages in terms of flexibility and range, making it suitable for various applications where remote control is needed without the limitations of traditional infrared systems. The use of DTMF signals not only simplifies the encoding process but also allows for multiple control commands to be sent through the same channel, enhancing the functionality of the remote control system.This circuit differs from similar circuits in view of its simplicity and a totally different concept of generating the control signals. Usually remote control circuits make use of infrared light to transmit control signals. Their use is thus limited to a very confined area and line-of-sight. However, this circuit makes use of radio frequency to transmit the control signals and hence it can be used for control from almost anywhere in the house.
Here we make use of DTMF (dual-tone multi frequency) signals (used in telephones to dial the digits) as the control codes. The DTMF tones are used for frequency modulation of the carrier. At the receiver unit, these frequency modulated signals are intercepted to obtain DTMF tones at the speaker terminals.
🔗 External reference
This circuit design utilizes radio frequency (RF) technology to overcome the limitations imposed by infrared remote control systems, allowing for broader operational range and versatility. The core of the circuit is based on the generation and transmission of DTMF signals, which consist of two simultaneous audio frequencies. These frequencies are typically associated with the keypad tones of a telephone.
The transmitter section includes a DTMF encoder that converts the pressed key inputs into corresponding DTMF tones. These tones are then modulated onto a radio frequency carrier using a frequency modulation (FM) technique. The modulation process enables the information to be transmitted over a distance without the constraints of line-of-sight, typical of infrared systems.
At the receiver end, an RF receiver circuit is employed to capture the transmitted signals. The receiver is designed to demodulate the FM signals back into the original DTMF tones. This demodulation is crucial for restoring the control signals that can be interpreted by the subsequent control circuitry. The output from the receiver typically drives a speaker or can be interfaced with other electronic components to perform specific actions based on the received DTMF codes.
The overall architecture of this circuit offers significant advantages in terms of flexibility and range, making it suitable for various applications where remote control is needed without the limitations of traditional infrared systems. The use of DTMF signals not only simplifies the encoding process but also allows for multiple control commands to be sent through the same channel, enhancing the functionality of the remote control system.This circuit differs from similar circuits in view of its simplicity and a totally different concept of generating the control signals. Usually remote control circuits make use of infrared light to transmit control signals. Their use is thus limited to a very confined area and line-of-sight. However, this circuit makes use of radio frequency to transmit the control signals and hence it can be used for control from almost anywhere in the house.
Here we make use of DTMF (dual-tone multi frequency) signals (used in telephones to dial the digits) as the control codes. The DTMF tones are used for frequency modulation of the carrier. At the receiver unit, these frequency modulated signals are intercepted to obtain DTMF tones at the speaker terminals.
🔗 External reference