Tone control low noise circuit Schematic Diagram
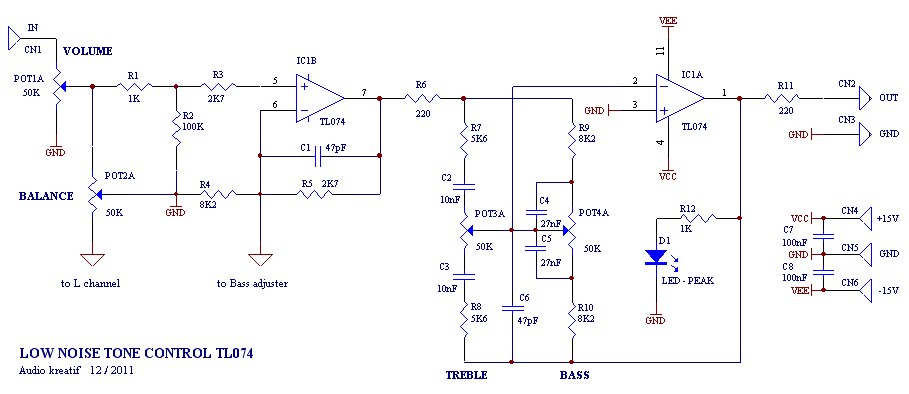
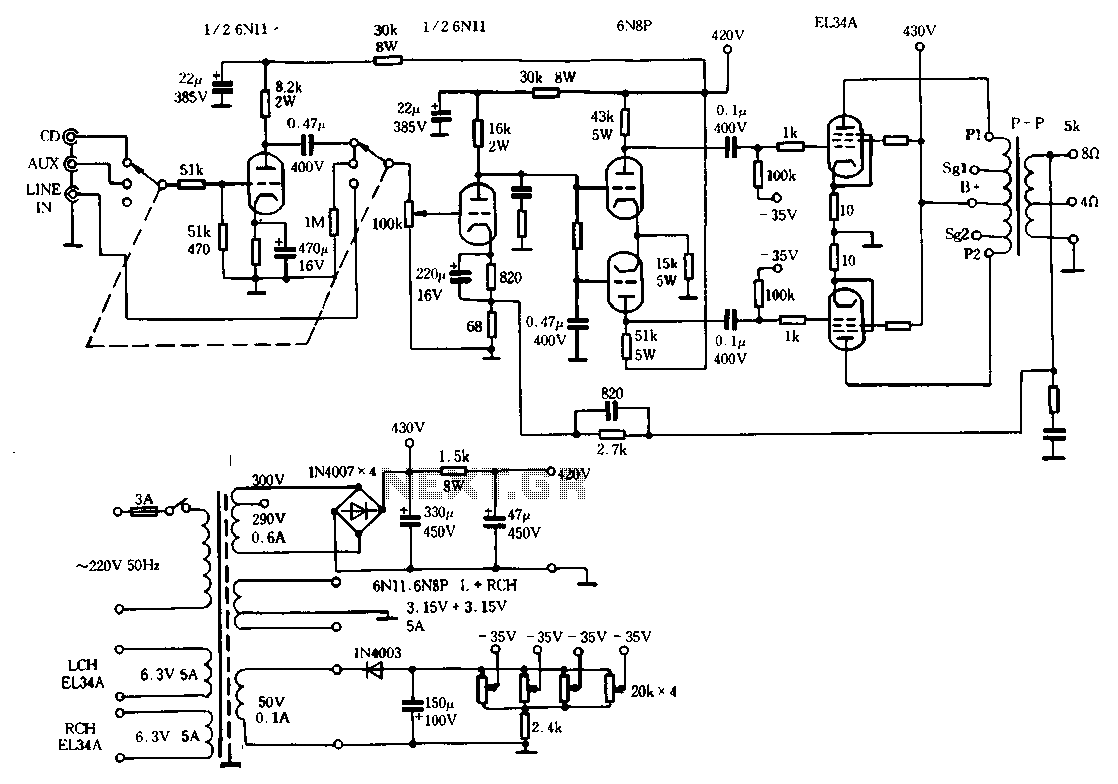
A tone control or pre-amplifier is an amplifier circuit that enhances audio signals. It is important to understand the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of various amplifier equipment, as the performance of different amplifiers may not show significant differences. The low noise tone control does not imply the absence of noise, but rather that it has lower noise levels compared to other tone control circuits available in the market, such as those using Ronica transistors, TL-084, TC-2, or LM833. Potentiometer 1 is used to adjust the intensity or level of the incoming signal, while potentiometer 2 serves as a balance control and is typically an optional component. A capacitor rated at 1-2uF/250V is suggested to be replaced with a 1K resistor (5%) to minimize hum and interference. Resistors R2 and R3 are utilized to adjust the impedance of OP-amp 1, while R4 and R5 are configured to increase the gain by a factor of 1.3. Although pre-amplifiers generally use a standard gain of 2, this design aims to minimize noise. The noise from OP-amp 1 can be mitigated, and this stage can also function as a buffer (jumper R5) for gain. Lower resistor values for R5 or R4 will reduce the gain but maintain a value above 1 due to the non-inverting input path, which helps reduce signal and noise levels. R4 may be substituted with a 10K trimpot to adjust the bass range. Capacitors C1 and C6 act as filters to limit excessive high frequencies, preventing oscillation. R6 is an optional component that helps customize the system's impedance. Ideally, R7 and R8 should be the same to ensure consistent gain on the tone control potentiometer panel. Capacitors C2 and C3 create a high pass filter, allowing mid frequencies to pass. C4 and C5, along with R9 and R10, form a low pass filter; the value of these capacitors determines the bass frequency response, with a maximum value of 47nF for softer bass. Potentiometers 3 and 4 adjust treble and bass levels, with higher values yielding greater gain. Resistor R11 adjusts output impedance, while R12 and the red LED indicator signal when the amplifier has reached peak output.
In this tone control circuit, the design focuses on minimizing noise while maintaining sound quality. The use of specific components, such as the chosen op-amps and resistors, is critical to achieving the desired audio characteristics. The circuit architecture allows for flexibility in tuning the audio output, accommodating user preferences for treble and bass adjustments. The inclusion of both high pass and low pass filters ensures that the audio signal is processed effectively, allowing for a balanced output that enhances the listening experience. The careful selection of component values plays a significant role in determining the overall performance of the circuit, particularly in terms of noise reduction and signal integrity. The visual indicators, such as the LED, provide essential feedback to the user regarding the amplifier's operational status, ensuring optimal performance during use. This circuit is suitable for various audio applications, including home audio systems and professional sound equipment, where precise control over sound quality is paramount.Tone control or pre-amplifier is an amplifier circuit supporters. Sometimes some of us do not know where a good amplifier, a raft alone and the results are not much different or even the same. Therefore we must know the character of the advantages and disadvantages of each amplifier equipment.
Tone control low noise here does not mean without nois e, but noise compared with the lowest tone control on the market, for example Ronica transistor 4, TL-084, TC-2 LM833 etc. Potensio 1 serves to regulate the intensity / level of the incoming signal is assisted potensio 2 as balance / counterbalance.
Potensio 2 is still installed and is usually an optional component. 1-2uF/250V capacitor R1 is actually a brand name, but I prefer to replace it with a 1K resistor / 5% normal for reasons to avoid hum and interference sensitive. R2 R3 while minimizing interruption to adjust the impedance OP-amp 1. R4 and R5 serves to increase the gain of 1. 3 times. Pre amplifiers typically use a strengthening standards by 2 times, but by most of us think it has a noise.
So I chose the value of 1. 3 times, but the most minimal noise signal from the volume is enough to make the lamp light peak. For low noise. Cause of noise in op amp 1, apex audio even eliminate this stage. Can This step is also used as a buffer (jumper R5), the strengthening of a time. Lower values increase the value of R5 or R4 with consequent gains to be less, but remains at a value above 1 times due to input non-inverting path to take, so that the signal and noise can be reduced. R4 can also be replaced with a 10K trimpot and middle leg into the bass range adjuster (bass resonance).
C1 and C6 as a filter to reduce the treble / high frequency of excessive or often called oscillation prevention. R6 is actually an optional component of the impedance a little help customize the system. Ideally the same as the R8 R7 to facilitate give the sign of the gain on potensio panel tone control.
C2 and C3 form a series circuit treble filter (high pass filter), its value is greater then the sound that passed the mid. C4 and C5 assisted by R9 and R10 form the low pass filter (filter bass), the greater the value of C is a bass sound that will be missed the soft / low (maximum of 47nF), the smaller the value of c is the bass signal that is passed will further dip (dig-dig, c4 = c5 = 22nF).
This value is suitable for 27-33nF, 47nF instead (depending on taste). Pot 3 & 4 pot set treble and bass levels, the greater the greater the value of this potensio gains (bass & treble including potensio volume). R11 adjusts the output impedance, while the R12 and the red LED indicator that shows if the amplifier Peak has been given a full signal.
You are reading the Circuits of Tone control low noise circuit And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference
In this tone control circuit, the design focuses on minimizing noise while maintaining sound quality. The use of specific components, such as the chosen op-amps and resistors, is critical to achieving the desired audio characteristics. The circuit architecture allows for flexibility in tuning the audio output, accommodating user preferences for treble and bass adjustments. The inclusion of both high pass and low pass filters ensures that the audio signal is processed effectively, allowing for a balanced output that enhances the listening experience. The careful selection of component values plays a significant role in determining the overall performance of the circuit, particularly in terms of noise reduction and signal integrity. The visual indicators, such as the LED, provide essential feedback to the user regarding the amplifier's operational status, ensuring optimal performance during use. This circuit is suitable for various audio applications, including home audio systems and professional sound equipment, where precise control over sound quality is paramount.Tone control or pre-amplifier is an amplifier circuit supporters. Sometimes some of us do not know where a good amplifier, a raft alone and the results are not much different or even the same. Therefore we must know the character of the advantages and disadvantages of each amplifier equipment.
Tone control low noise here does not mean without nois e, but noise compared with the lowest tone control on the market, for example Ronica transistor 4, TL-084, TC-2 LM833 etc. Potensio 1 serves to regulate the intensity / level of the incoming signal is assisted potensio 2 as balance / counterbalance.
Potensio 2 is still installed and is usually an optional component. 1-2uF/250V capacitor R1 is actually a brand name, but I prefer to replace it with a 1K resistor / 5% normal for reasons to avoid hum and interference sensitive. R2 R3 while minimizing interruption to adjust the impedance OP-amp 1. R4 and R5 serves to increase the gain of 1. 3 times. Pre amplifiers typically use a strengthening standards by 2 times, but by most of us think it has a noise.
So I chose the value of 1. 3 times, but the most minimal noise signal from the volume is enough to make the lamp light peak. For low noise. Cause of noise in op amp 1, apex audio even eliminate this stage. Can This step is also used as a buffer (jumper R5), the strengthening of a time. Lower values increase the value of R5 or R4 with consequent gains to be less, but remains at a value above 1 times due to input non-inverting path to take, so that the signal and noise can be reduced. R4 can also be replaced with a 10K trimpot and middle leg into the bass range adjuster (bass resonance).
C1 and C6 as a filter to reduce the treble / high frequency of excessive or often called oscillation prevention. R6 is actually an optional component of the impedance a little help customize the system. Ideally the same as the R8 R7 to facilitate give the sign of the gain on potensio panel tone control.
C2 and C3 form a series circuit treble filter (high pass filter), its value is greater then the sound that passed the mid. C4 and C5 assisted by R9 and R10 form the low pass filter (filter bass), the greater the value of C is a bass sound that will be missed the soft / low (maximum of 47nF), the smaller the value of c is the bass signal that is passed will further dip (dig-dig, c4 = c5 = 22nF).
This value is suitable for 27-33nF, 47nF instead (depending on taste). Pot 3 & 4 pot set treble and bass levels, the greater the greater the value of this potensio gains (bass & treble including potensio volume). R11 adjusts the output impedance, while the R12 and the red LED indicator that shows if the amplifier Peak has been given a full signal.
You are reading the Circuits of Tone control low noise circuit And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference