Transformerless joule thief circuit
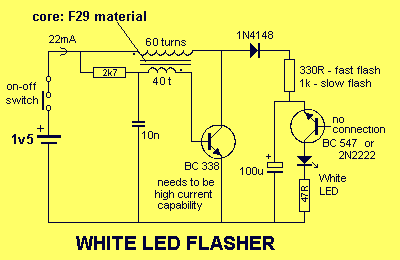
This circuit is very similar to a Joule Thief, but it utilizes two transistors, does not include a transformer core, and employs only one inductor.
The described circuit operates on principles akin to those of a Joule Thief, which is a type of boost converter designed to extract energy from low-voltage sources. The use of two transistors instead of one allows for enhanced efficiency and improved performance, particularly in terms of switching speed and output voltage regulation.
In this configuration, the two transistors are typically arranged in a complementary push-pull configuration. This arrangement enables one transistor to conduct while the other is in the off state, effectively alternating between the two to maintain oscillation. The inductor plays a crucial role in energy storage and transfer, charging when one transistor is conducting and releasing energy to the output when the other transistor is active.
The absence of a transformer core simplifies the design, reducing component count and size, which can be advantageous in compact applications. The circuit's reliance on a single inductor means that careful attention must be paid to the inductor's specifications, such as inductance value and saturation current, to ensure optimal performance.
The circuit can be powered by a low-voltage source, such as a single-cell lithium battery or a pair of AA batteries, making it suitable for applications where energy efficiency is paramount. The output voltage can be significantly higher than the input voltage, allowing for the powering of devices that require higher voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a minimalist approach to energy conversion, leveraging the properties of transistors and inductors to achieve efficient voltage boosting without the complexity of additional components like transformer cores.This is a circuit very similar to a Joule Thief, except that it is using 2 transistors, no transformer core, and only one inductor. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates on principles akin to those of a Joule Thief, which is a type of boost converter designed to extract energy from low-voltage sources. The use of two transistors instead of one allows for enhanced efficiency and improved performance, particularly in terms of switching speed and output voltage regulation.
In this configuration, the two transistors are typically arranged in a complementary push-pull configuration. This arrangement enables one transistor to conduct while the other is in the off state, effectively alternating between the two to maintain oscillation. The inductor plays a crucial role in energy storage and transfer, charging when one transistor is conducting and releasing energy to the output when the other transistor is active.
The absence of a transformer core simplifies the design, reducing component count and size, which can be advantageous in compact applications. The circuit's reliance on a single inductor means that careful attention must be paid to the inductor's specifications, such as inductance value and saturation current, to ensure optimal performance.
The circuit can be powered by a low-voltage source, such as a single-cell lithium battery or a pair of AA batteries, making it suitable for applications where energy efficiency is paramount. The output voltage can be significantly higher than the input voltage, allowing for the powering of devices that require higher voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a minimalist approach to energy conversion, leveraging the properties of transistors and inductors to achieve efficient voltage boosting without the complexity of additional components like transformer cores.This is a circuit very similar to a Joule Thief, except that it is using 2 transistors, no transformer core, and only one inductor. 🔗 External reference