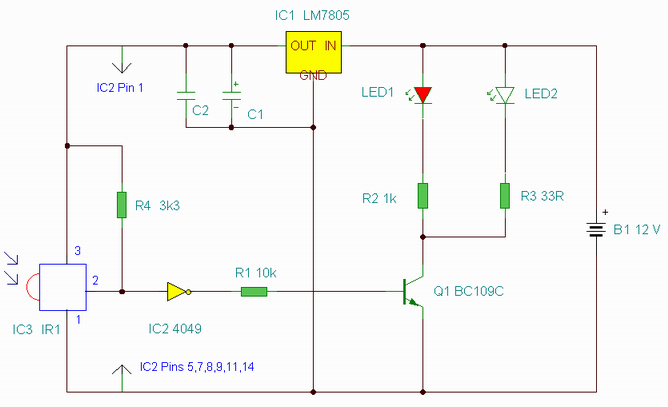
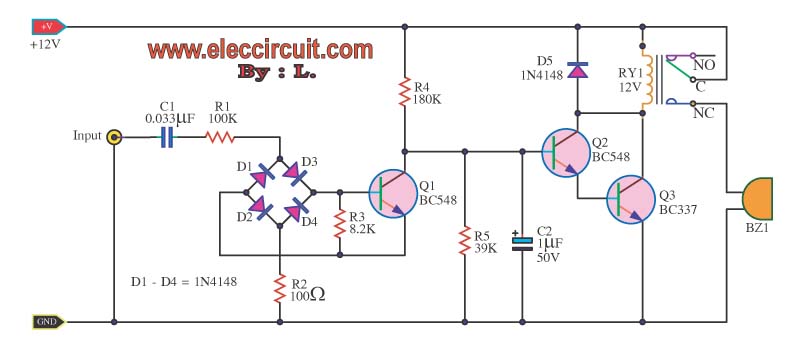
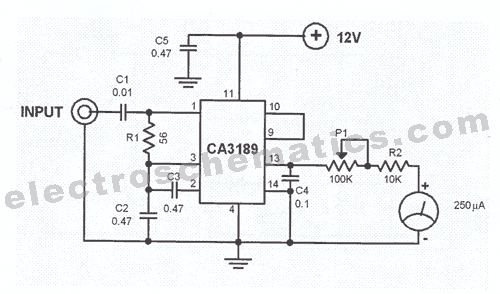
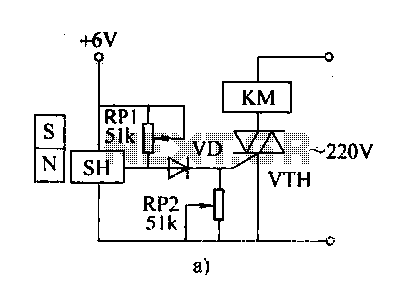
Transistor circuit of a pressure gauge
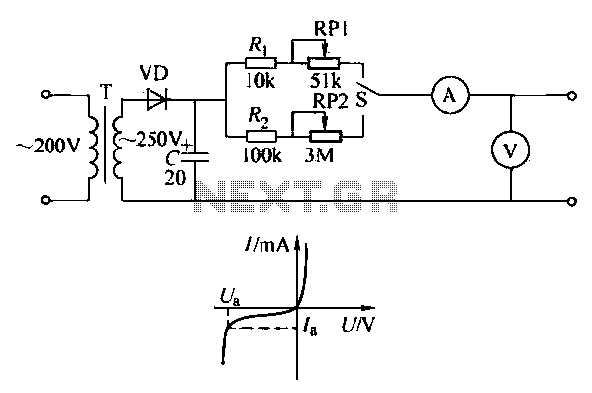
To ensure proper operation of the transistor in a circuit, it is essential to measure the reverse breakdown voltage of the transistor. This is particularly important for tubes with high reverse breakdown voltage requirements, such as those used in OCL power amplifiers and differential amplifiers, which may exceed tens of volts. A transistor withstand voltage test circuit can be utilized for this purpose. For TV video amplifier tubes and line outputs, where voltages exceeding one hundred volts are required, accurate measurement is necessary. A simple transistor testing circuit, as depicted in Figure 5-23a, can measure the breakdown voltage of crystal diodes and transistors, as well as the regulation characteristics of crystal regulators. In this circuit, when the diode is subjected to reverse voltage, the reverse current remains minimal. However, as the reverse voltage increases to a specific threshold, the reverse current surges rapidly, causing the tube to enter a reverse breakdown state, illustrated in Figure 5-23b. Once the tube is in breakdown, the current flowing through it is primarily determined by the external circuit. If the external circuit limits the current, it may lead to excessive current flow, risking damage to the tube. The reverse breakdown voltage of the transistor is characterized by the breakdown characteristics, indicating that the reverse current reaches a predetermined value at a specific reverse voltage. This predetermined value can be isolated from the transistor characteristics table under test conditions. In the circuit shown in Figure 5-23, a transformer steps down AC voltage from 220V to 250V, which is then rectified by a diode and filtered by a capacitor to yield a high DC voltage of 300V. A voltmeter is employed to measure the reverse breakdown voltage of the diode or transistor, while a crystal ammeter monitors the reverse current.
(1) For measuring the breakdown voltage BVceo of high-power tubes, the single-pole double-throw switch S is set to the "high-power" position. This allows for the measurement of the breakdown voltage of high-power diodes or transistors. For instance, when measuring the BVceo of the 3AD30 transistor, the ammeter should be set to the 50mA range, as illustrated in Figure 5-22c. Resistors R1 and RP1 serve as limiting resistors. The transistor characteristics table indicates that the test conditions for the 3AD30 BVceo require a reverse current of 20mA. By adjusting RP1, the ammeter pointer should align with 20mA, at which point the voltmeter reading indicates the collector-emitter reverse breakdown voltage of the tube. If the measured BVceo is obtained, the base-emitter resistors must be adjusted accordingly.
(2) For measuring the BVceo of small power tubes, the switch S is set to the "small power" position. This configuration allows for the measurement of the reverse breakdown voltage of low-power diodes or transistors. For example, to measure the BVceo of the 3DG6 transistor, the ammeter should be set to the 500µA range, as shown in Figure 5-23d. The resistors RP2 and foot-2 form a limiting resistor, and a high-resistance voltmeter is employed for accurate measurements. The transistor characteristics table specifies that the BVceo for the 3DG6 under test conditions requires a reverse current of 100µA. By adjusting RP2, the ammeter pointer should indicate 100µA, at which point the reading from the high-voltage resistance meter reflects the reverse breakdown voltage across the collector-emitter terminals of the tube.
(3) When measuring the voltage characteristics of a regulator, the switch S should be set to the "power" position. In addition to reading the Zener voltage from the voltmeter, adjusting RP1 allows for the measurement of the regulator's voltage characteristics at currents ranging from a few milliamperes to 20mA.
(4) Component selection is crucial for this circuit. A commercially available transformer should be chosen as a power transformer, and the rectifier diode must have a voltage rating exceeding 300V with a forward current rating greater than 100mA. When measuring high-power tubes, a standard voltmeter or multimeter is adequate. However, for low-power tubes, it is essential to utilize a voltmeter with high internal resistance, such as a 20kΩ per volt voltmeter or a simple transistor voltmeter, to ensure accurate measurements.In order to ensure that the transistor in the circuit to work properly, it is often the reverse breakdown voltage of the transistor to be measured. Especially for the requirements of the reverse breakdown voltage of the tube is relatively high, such as tubes OCL power amplifier of the differential amplifier, is greater than the reverse breakdown voltage requirements tens of volts. Available transistor withstand voltage test circuit testing. TV video amplifier tube output and line output, requiring more than a hundred volts, the need to measure up.
Figure 5-23a pressure test is a simple transistor circuit which is capable of measuring crystal diode, the breakdown voltage of the transistor buildings, but also to test crystal regulator regulation characteristics of the tube. Said hatch circuit: the diode is reverse voltage, reverse current is very small. But increasing reverse voltage to a certain value when the reverse current increases rapidly, the tube into the reverse breakdown state, as shown in Figure 5-23b.
After entering the tube to the breakdown state, the current through the tube, mainly depends on the external circuit, the external circuit if the current measure poured limited, the current will be large, there is danger of burn out of the tube. The reverse breakdown voltage of the transistor is reflected in the breakdown characteristics. It refers to the reverse current reverse voltage reaches a certain predetermined value. This anti predetermined value to the current can be isolated from the transistor characteristics table test conditions.
In the circuit of Figure 5-23, the transformer into the AC voltage 220V to 250V AC voltage through the diode rectifier and capacitor filter, to obtain 300V DC high voltage. When the load voltage is lower. Voltmeter used to measure the reverse breakdown voltage of diode or transistor, diode or crystal ammeter to monitor pension tube reverse current.
(1) measurement of high-power tube BVceo when single-pole double-throw switch S to position "high-power" at the high-power diode can be measured or crystal transistor anti Koh breakdown voltage. 3AD30 such as measuring the collector-emitter breakdown voltage BVceo, ammeter into gear with 50mA, the circuit shown in Figure 5-22c.
R1 and RP1 composition limiting resistor. From the transistor characteristics can be found in the table '. The test conditions 3AD30 BVceo anti currents to 20mA. Adjust RP1, ammeter pointer falls at 20mA. At this time, the voltage meter reading is made this tube collector -emitter reverse breakdown voltage. If the measured reverse breakdown voltage BVceo. Base emitter resistors an extremely indirect regulations. For example, the measured 3AD30 BVceo, to resistor 20fz so. (2) measurement of small power tube BVceo when single-pole double-throw switch S to position "small power" at the low-power diode can be measured or crystal tube reverse breakdown voltage.
3DG6 such as measuring the collector-emitter breakdown voltage, circuit ammeter selection 500riA file, the circuit shown in Fig. 5-23d, foot-2 and RP2 composition limiting resistor use high resistance voltmeter voltmeter. From the transistor characteristics can be found in the table, the BVceo 3DG6 test conditions reverse current lOOyA.
Adjust RP2 ammeter pointer falls 100VA place. At this time, the high-voltage resistance meter reading is this tube collector emitter reverse breakdown voltage poles. Regulators Features (3) the amount of rinse regulator regulator when measured, S also to position "power" place.
In addition to reading from the voltmeter Zener voltage outside, adjust RP1, it can also measure the voltage characteristics of the regulator in a few milliamperes to 20mA. (4) Component selection commercially available transformer power transformer. Available rectifier diode voltage is greater than 300V, the forward current is greater than 2CP lOOmA type of pipe.
When measuring high-power tube, with a simple voltmeter multimeter voltage profile on it. But when measuring low-power tube, be sure to use a high internal resistance voltmeter, such as 20kfl per volt voltmeter or use a simple transistor voltmeter, otherwise it is not measured out.
(1) For measuring the breakdown voltage BVceo of high-power tubes, the single-pole double-throw switch S is set to the "high-power" position. This allows for the measurement of the breakdown voltage of high-power diodes or transistors. For instance, when measuring the BVceo of the 3AD30 transistor, the ammeter should be set to the 50mA range, as illustrated in Figure 5-22c. Resistors R1 and RP1 serve as limiting resistors. The transistor characteristics table indicates that the test conditions for the 3AD30 BVceo require a reverse current of 20mA. By adjusting RP1, the ammeter pointer should align with 20mA, at which point the voltmeter reading indicates the collector-emitter reverse breakdown voltage of the tube. If the measured BVceo is obtained, the base-emitter resistors must be adjusted accordingly.
(2) For measuring the BVceo of small power tubes, the switch S is set to the "small power" position. This configuration allows for the measurement of the reverse breakdown voltage of low-power diodes or transistors. For example, to measure the BVceo of the 3DG6 transistor, the ammeter should be set to the 500µA range, as shown in Figure 5-23d. The resistors RP2 and foot-2 form a limiting resistor, and a high-resistance voltmeter is employed for accurate measurements. The transistor characteristics table specifies that the BVceo for the 3DG6 under test conditions requires a reverse current of 100µA. By adjusting RP2, the ammeter pointer should indicate 100µA, at which point the reading from the high-voltage resistance meter reflects the reverse breakdown voltage across the collector-emitter terminals of the tube.
(3) When measuring the voltage characteristics of a regulator, the switch S should be set to the "power" position. In addition to reading the Zener voltage from the voltmeter, adjusting RP1 allows for the measurement of the regulator's voltage characteristics at currents ranging from a few milliamperes to 20mA.
(4) Component selection is crucial for this circuit. A commercially available transformer should be chosen as a power transformer, and the rectifier diode must have a voltage rating exceeding 300V with a forward current rating greater than 100mA. When measuring high-power tubes, a standard voltmeter or multimeter is adequate. However, for low-power tubes, it is essential to utilize a voltmeter with high internal resistance, such as a 20kΩ per volt voltmeter or a simple transistor voltmeter, to ensure accurate measurements.In order to ensure that the transistor in the circuit to work properly, it is often the reverse breakdown voltage of the transistor to be measured. Especially for the requirements of the reverse breakdown voltage of the tube is relatively high, such as tubes OCL power amplifier of the differential amplifier, is greater than the reverse breakdown voltage requirements tens of volts. Available transistor withstand voltage test circuit testing. TV video amplifier tube output and line output, requiring more than a hundred volts, the need to measure up.
Figure 5-23a pressure test is a simple transistor circuit which is capable of measuring crystal diode, the breakdown voltage of the transistor buildings, but also to test crystal regulator regulation characteristics of the tube. Said hatch circuit: the diode is reverse voltage, reverse current is very small. But increasing reverse voltage to a certain value when the reverse current increases rapidly, the tube into the reverse breakdown state, as shown in Figure 5-23b.
After entering the tube to the breakdown state, the current through the tube, mainly depends on the external circuit, the external circuit if the current measure poured limited, the current will be large, there is danger of burn out of the tube. The reverse breakdown voltage of the transistor is reflected in the breakdown characteristics. It refers to the reverse current reverse voltage reaches a certain predetermined value. This anti predetermined value to the current can be isolated from the transistor characteristics table test conditions.
In the circuit of Figure 5-23, the transformer into the AC voltage 220V to 250V AC voltage through the diode rectifier and capacitor filter, to obtain 300V DC high voltage. When the load voltage is lower. Voltmeter used to measure the reverse breakdown voltage of diode or transistor, diode or crystal ammeter to monitor pension tube reverse current.
(1) measurement of high-power tube BVceo when single-pole double-throw switch S to position "high-power" at the high-power diode can be measured or crystal transistor anti Koh breakdown voltage. 3AD30 such as measuring the collector-emitter breakdown voltage BVceo, ammeter into gear with 50mA, the circuit shown in Figure 5-22c.
R1 and RP1 composition limiting resistor. From the transistor characteristics can be found in the table '. The test conditions 3AD30 BVceo anti currents to 20mA. Adjust RP1, ammeter pointer falls at 20mA. At this time, the voltage meter reading is made this tube collector -emitter reverse breakdown voltage. If the measured reverse breakdown voltage BVceo. Base emitter resistors an extremely indirect regulations. For example, the measured 3AD30 BVceo, to resistor 20fz so. (2) measurement of small power tube BVceo when single-pole double-throw switch S to position "small power" at the low-power diode can be measured or crystal tube reverse breakdown voltage.
3DG6 such as measuring the collector-emitter breakdown voltage, circuit ammeter selection 500riA file, the circuit shown in Fig. 5-23d, foot-2 and RP2 composition limiting resistor use high resistance voltmeter voltmeter. From the transistor characteristics can be found in the table, the BVceo 3DG6 test conditions reverse current lOOyA.
Adjust RP2 ammeter pointer falls 100VA place. At this time, the high-voltage resistance meter reading is this tube collector emitter reverse breakdown voltage poles. Regulators Features (3) the amount of rinse regulator regulator when measured, S also to position "power" place.
In addition to reading from the voltmeter Zener voltage outside, adjust RP1, it can also measure the voltage characteristics of the regulator in a few milliamperes to 20mA. (4) Component selection commercially available transformer power transformer. Available rectifier diode voltage is greater than 300V, the forward current is greater than 2CP lOOmA type of pipe.
When measuring high-power tube, with a simple voltmeter multimeter voltage profile on it. But when measuring low-power tube, be sure to use a high internal resistance voltmeter, such as 20kfl per volt voltmeter or use a simple transistor voltmeter, otherwise it is not measured out.