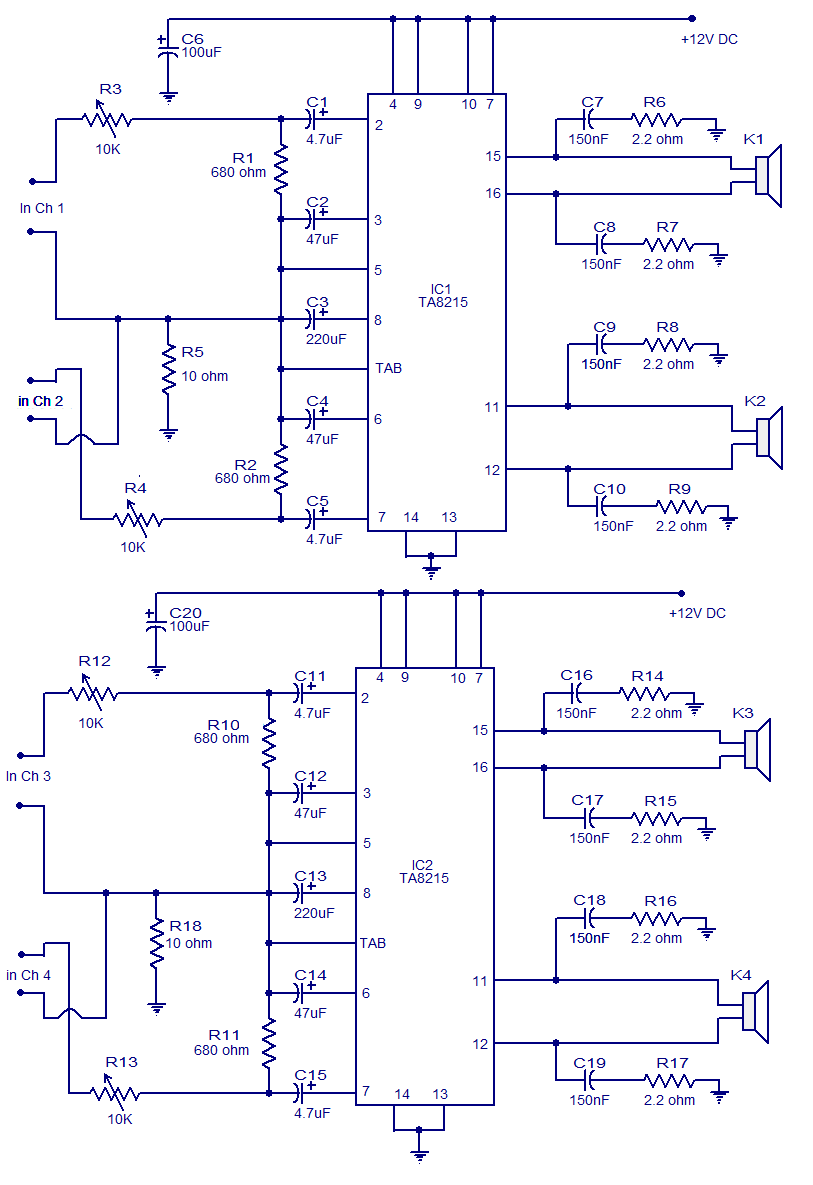
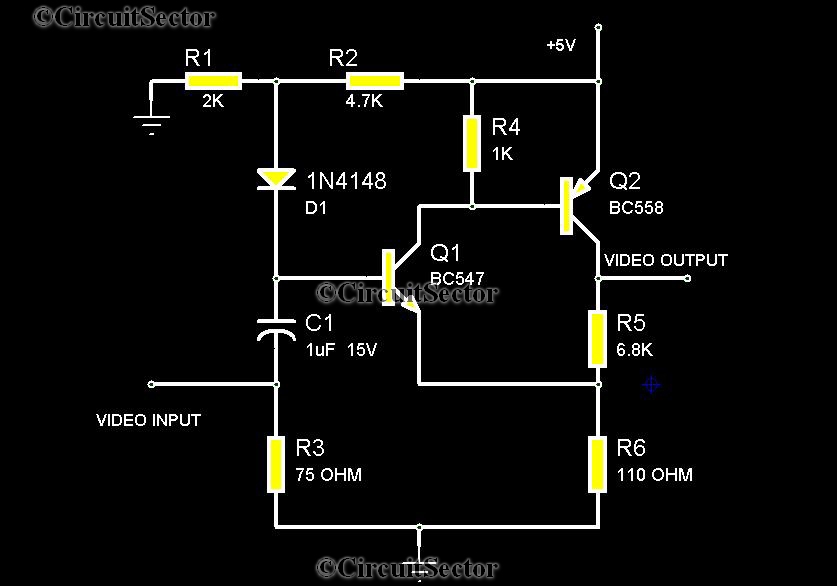
Transistored 10W Audio Amplifier
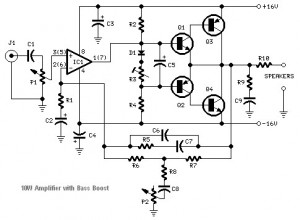
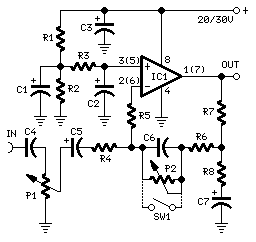
This audio amplifier circuit is based on the operational amplifier NE5532 and utilizes a pair of power transistors, TIP41A and TIP42A. It is capable of delivering up to 10W of audio power output into an 8-ohm speaker. The design is related to an 18 Watt Audio Amplifier and was created primarily to address the needs of users who were unable to find the TLE2141C chip. The circuit operates using the widely available NE5532 Dual IC; however, the output capability is limited to approximately 9.5 to 11.5W due to the voltage supply rails, which cannot exceed ±18V. Amplifiers of this type are typically used to drive small loudspeaker cabinets, which may result in a compromise in the bass frequency range. To mitigate this issue without sacrificing quality, a bass-boost control was integrated into the feedback loop of the amplifier. This bass lift curve can achieve a maximum of +16.4dB at 50Hz. Even with the bass control set to its minimum position, the amplifier's frequency response demonstrates a gentle increase: +0.8dB at 400Hz, +4.7dB at 100Hz, and +6dB at 50Hz (referenced to 1kHz). Proper grounding is essential to eliminate hum and ground loops. The ground connections for J1, P1, C2, C3, and C4 should be connected to the same point, while C9 should be connected to the output ground. Additionally, the input and output grounds must be separately connected to the power supply ground.
This audio amplifier circuit employs the NE5532 operational amplifier, known for its low noise and high performance, making it suitable for audio applications. The TIP41A and TIP42A power transistors are configured in a push-pull arrangement, which enhances the circuit's efficiency and output power capabilities. The design allows for a maximum output of 10W into an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for driving small loudspeakers effectively.
The inclusion of a bass-boost control in the feedback loop addresses the inherent limitations of the amplifier concerning low-frequency response. By allowing for an increase of up to +16.4dB at 50Hz, the circuit compensates for the typical roll-off that occurs in small speaker systems. This adjustment ensures a more balanced audio output, particularly for bass-heavy music genres.
To maintain optimal performance, careful attention must be paid to the grounding scheme. The ground connections for various components, including the input and output stages, should be unified at a single point to minimize ground loops and hum. This practice is crucial in audio applications where noise can significantly impact sound quality.
The circuit's design thus balances performance and usability, making it an excellent choice for audio enthusiasts seeking a compact and effective amplifier solution.Build based operational amplifier NE5532 and a couple of power transistor TIP41A / TIP42A, this audio amplifier circuit has capability to deliver up to 10W audio power output into 8 ohm speaker. This circuit is related to the 18 Watt Audio Amplifier, and was designed mainly to satisfy the requests of correspondents unable to locate the TLE2141C c
hip. It works with the widespread NE5532 Dual IC but, certainly, its capability output is going to be comprised around the 9. 5 11. 5W range, because the voltage supply rails can not exceed ±18V. As amplifiers of this variety are usually applied to drive small loudspeaker cabinets, the bass frequency range is rather sacrificed.
As a result a bass-boost manage was inserted within the feedback loop of the amplifier, so as to overcome this issue with out top quality losses. The bass lift curve can reach a maximum of +16. 4dB @ 50Hz. In any case, even when the bass manage is rotated totally counterclockwise, the amplifier frequency response shows a gentle raising curve: +0.
8dB @ 400Hz, +4. 7dB @ 100Hz and +6dB @ 50Hz (referred to 1KHz). A right grounding is extremely necessary to eradicate hum and ground loops. Connect for the identical point the ground sides of J1, P1, C2, C3 &C4. Connect C9 towards the output ground. Then connect separately the input and output grounds to the power supply ground. 🔗 External reference
This audio amplifier circuit employs the NE5532 operational amplifier, known for its low noise and high performance, making it suitable for audio applications. The TIP41A and TIP42A power transistors are configured in a push-pull arrangement, which enhances the circuit's efficiency and output power capabilities. The design allows for a maximum output of 10W into an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for driving small loudspeakers effectively.
The inclusion of a bass-boost control in the feedback loop addresses the inherent limitations of the amplifier concerning low-frequency response. By allowing for an increase of up to +16.4dB at 50Hz, the circuit compensates for the typical roll-off that occurs in small speaker systems. This adjustment ensures a more balanced audio output, particularly for bass-heavy music genres.
To maintain optimal performance, careful attention must be paid to the grounding scheme. The ground connections for various components, including the input and output stages, should be unified at a single point to minimize ground loops and hum. This practice is crucial in audio applications where noise can significantly impact sound quality.
The circuit's design thus balances performance and usability, making it an excellent choice for audio enthusiasts seeking a compact and effective amplifier solution.Build based operational amplifier NE5532 and a couple of power transistor TIP41A / TIP42A, this audio amplifier circuit has capability to deliver up to 10W audio power output into 8 ohm speaker. This circuit is related to the 18 Watt Audio Amplifier, and was designed mainly to satisfy the requests of correspondents unable to locate the TLE2141C c
hip. It works with the widespread NE5532 Dual IC but, certainly, its capability output is going to be comprised around the 9. 5 11. 5W range, because the voltage supply rails can not exceed ±18V. As amplifiers of this variety are usually applied to drive small loudspeaker cabinets, the bass frequency range is rather sacrificed.
As a result a bass-boost manage was inserted within the feedback loop of the amplifier, so as to overcome this issue with out top quality losses. The bass lift curve can reach a maximum of +16. 4dB @ 50Hz. In any case, even when the bass manage is rotated totally counterclockwise, the amplifier frequency response shows a gentle raising curve: +0.
8dB @ 400Hz, +4. 7dB @ 100Hz and +6dB @ 50Hz (referred to 1KHz). A right grounding is extremely necessary to eradicate hum and ground loops. Connect for the identical point the ground sides of J1, P1, C2, C3 &C4. Connect C9 towards the output ground. Then connect separately the input and output grounds to the power supply ground. 🔗 External reference