Video Amplifier Circuit for Camera PCB
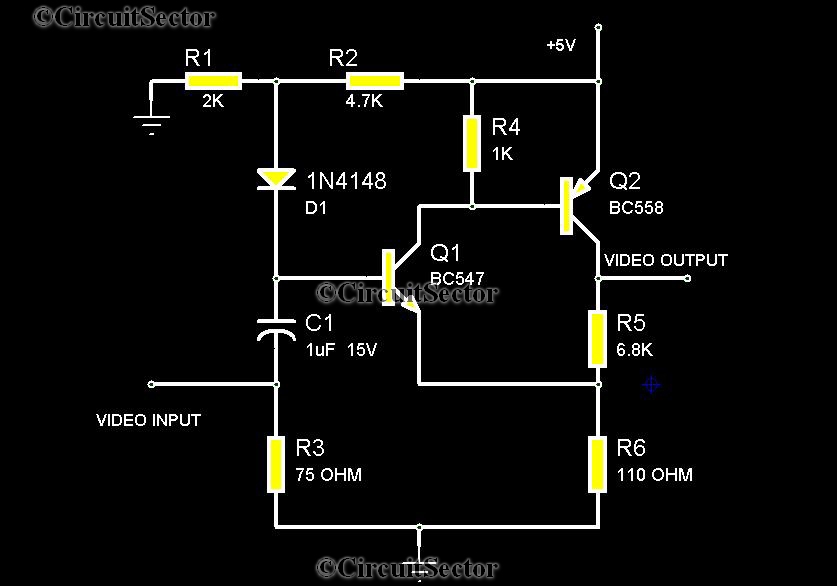
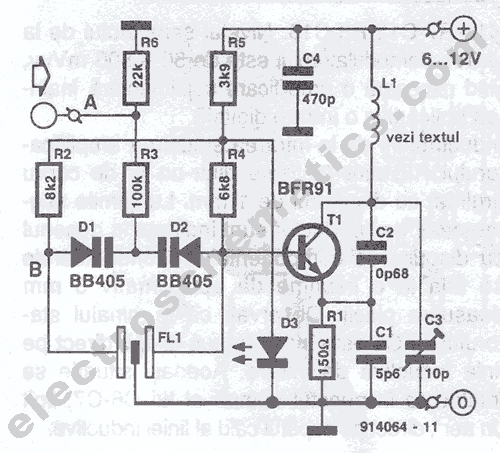
There are instances when it is necessary to view video clips captured by a digital camera on a television. This can be accomplished by connecting the camera's video output to the television's video input. However, a direct connection is not feasible because the signal requires amplification before it can be transmitted from the camera to the television. The video amplifier schematic circuit illustrated is a simple PAL video amplifier, designed to achieve a 3 dB bandwidth of 5.5 MHz. This circuit enables the connection of the camera to the television, functioning as a low-level transistorized video amplifier stage that accepts a 1V (peak-to-peak) input signal and outputs a 2V (peak-to-peak) signal.
The described video amplifier circuit is essential for enhancing the video signal quality when interfacing a digital camera with a television. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including transistors, resistors, and capacitors, which work together to amplify the low-level video signal generated by the camera.
The transistor serves as the primary amplification device. In this configuration, it is crucial to select a transistor capable of handling the frequency range associated with video signals, particularly for PAL standards. The circuit's design should ensure that the transistor operates within its linear region to prevent distortion of the video signal.
Resistors are employed to set the biasing conditions for the transistor, allowing it to operate effectively within the desired bandwidth. Additionally, feedback resistors may be included to stabilize the gain of the amplifier and improve linearity. Capacitors are used for coupling and decoupling purposes, ensuring that DC bias levels do not affect the AC video signal while maintaining the integrity of the frequency response.
The 3 dB bandwidth of 5.5 MHz indicates that the amplifier can effectively handle video signals within this frequency range without significant attenuation. This bandwidth is suitable for standard PAL video signals, which typically operate within a frequency range that includes the necessary components for clear image reproduction.
Overall, this video amplifier circuit is a practical solution for connecting a digital camera to a television, facilitating the viewing of captured video clips with enhanced signal strength and clarity. Proper implementation of the circuit will ensure reliable performance and high-quality video output.There are occasions when you want to view your video clips taken in your digital camera on your TV. You can do so by interfacing the camera video output to video input of your TV. But this times you cant connect directly as it needs some amplification before the signal reaches from camera to television. The video amplifier schematic circuit shown in the figure is a simple PAL video amp, expected to have a 3db bandwidth of 5. 5MHz. You can connect your camera to TV through this circuit. So this is a low level transistorized video amplifier stage that accepts 1V (p-p) and outputs 2V(p-p) signal. 🔗 External reference
The described video amplifier circuit is essential for enhancing the video signal quality when interfacing a digital camera with a television. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including transistors, resistors, and capacitors, which work together to amplify the low-level video signal generated by the camera.
The transistor serves as the primary amplification device. In this configuration, it is crucial to select a transistor capable of handling the frequency range associated with video signals, particularly for PAL standards. The circuit's design should ensure that the transistor operates within its linear region to prevent distortion of the video signal.
Resistors are employed to set the biasing conditions for the transistor, allowing it to operate effectively within the desired bandwidth. Additionally, feedback resistors may be included to stabilize the gain of the amplifier and improve linearity. Capacitors are used for coupling and decoupling purposes, ensuring that DC bias levels do not affect the AC video signal while maintaining the integrity of the frequency response.
The 3 dB bandwidth of 5.5 MHz indicates that the amplifier can effectively handle video signals within this frequency range without significant attenuation. This bandwidth is suitable for standard PAL video signals, which typically operate within a frequency range that includes the necessary components for clear image reproduction.
Overall, this video amplifier circuit is a practical solution for connecting a digital camera to a television, facilitating the viewing of captured video clips with enhanced signal strength and clarity. Proper implementation of the circuit will ensure reliable performance and high-quality video output.There are occasions when you want to view your video clips taken in your digital camera on your TV. You can do so by interfacing the camera video output to video input of your TV. But this times you cant connect directly as it needs some amplification before the signal reaches from camera to television. The video amplifier schematic circuit shown in the figure is a simple PAL video amp, expected to have a 3db bandwidth of 5. 5MHz. You can connect your camera to TV through this circuit. So this is a low level transistorized video amplifier stage that accepts 1V (p-p) and outputs 2V(p-p) signal. 🔗 External reference