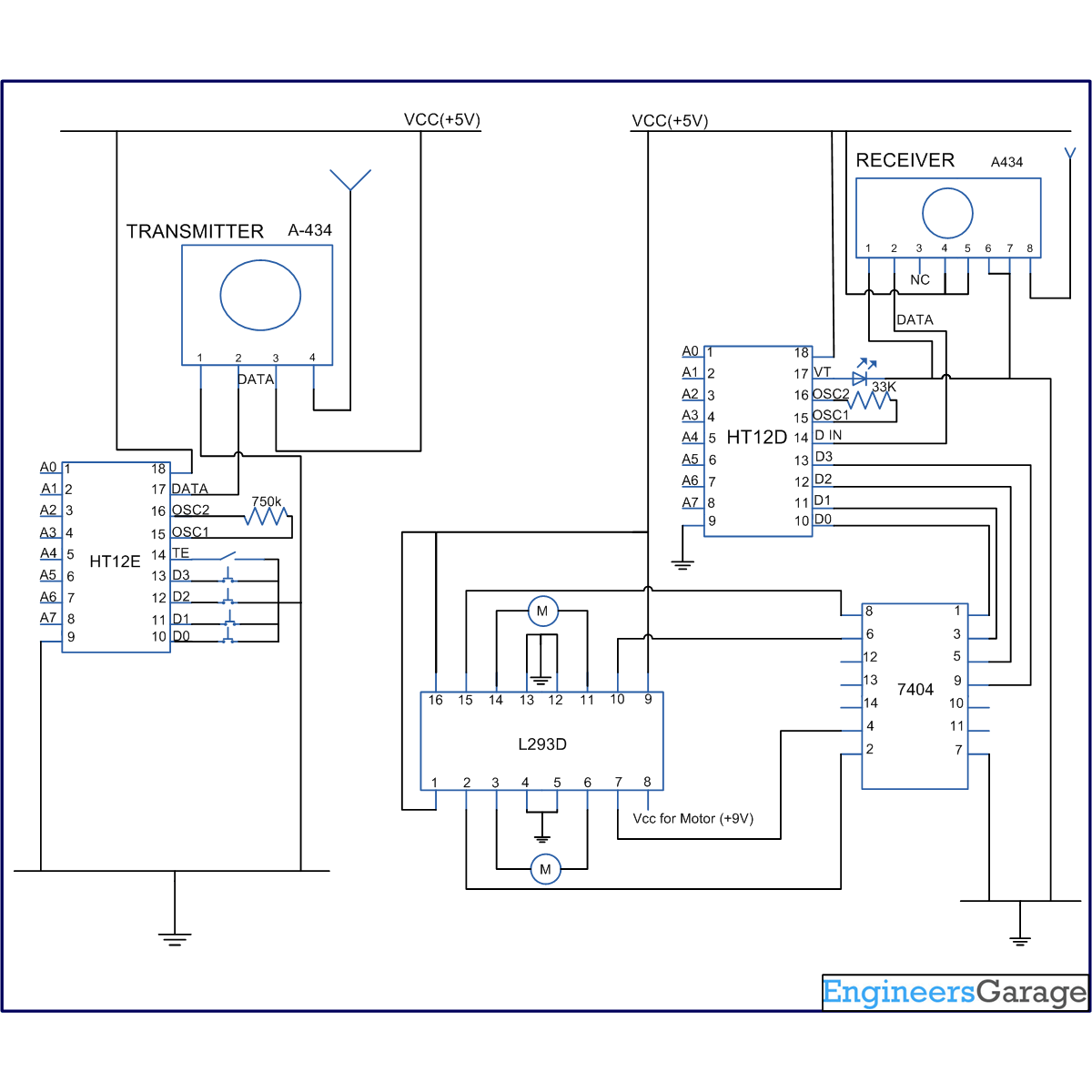
TRIAC DIAC REVERSING SERVO CONTROL

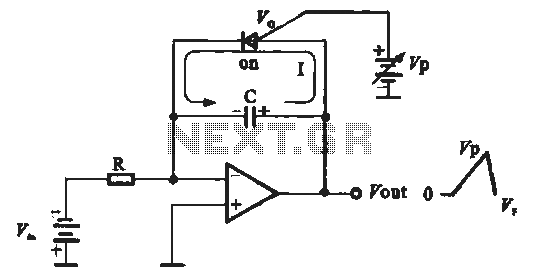
Varies the speed and direction of a 5-amp reversible series AC motor according to a DC control signal. The polarity of the control signal determines the direction of rotation. A gain potentiometer adjusts the slope of the speed versus control voltage curve.
The circuit described operates a 5-amp reversible series AC motor by utilizing a DC control signal to modulate both speed and direction. The key component in this system is the bidirectional static switch, which allows for the control of AC power to the motor based on the polarity of the incoming DC signal. When the control signal is positive, the motor will rotate in one direction, while a negative signal reverses the rotation.
To achieve variable speed control, a gain potentiometer is integrated into the circuit. This potentiometer alters the slope of the speed versus control voltage curve, providing fine-tuning of the motor’s response to the control signal. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can set how quickly the motor responds to changes in the control voltage, allowing for smoother acceleration and deceleration.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against back EMF generated by the motor, as well as capacitors to filter noise from the control signals. Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered as well, especially when operating at higher currents, to ensure reliability and longevity of the components involved.
Overall, this system provides a versatile solution for applications requiring precise control of AC motor speed and direction, making it suitable for various industrial and automation tasks.Varies speed and direction of 5-amp reversible series ac motor in accordance with d-c control signal. Polarity of control signal determines direction of rotation. Gain potentiometer adjusts slope of speed versus control voltage curve. -M. P. Southworth, Bidirectional Static Switch Simplifies Ac Control, Control Engineering, March 1964, p 75-76.
🔗 External reference
The circuit described operates a 5-amp reversible series AC motor by utilizing a DC control signal to modulate both speed and direction. The key component in this system is the bidirectional static switch, which allows for the control of AC power to the motor based on the polarity of the incoming DC signal. When the control signal is positive, the motor will rotate in one direction, while a negative signal reverses the rotation.
To achieve variable speed control, a gain potentiometer is integrated into the circuit. This potentiometer alters the slope of the speed versus control voltage curve, providing fine-tuning of the motor’s response to the control signal. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can set how quickly the motor responds to changes in the control voltage, allowing for smoother acceleration and deceleration.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against back EMF generated by the motor, as well as capacitors to filter noise from the control signals. Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered as well, especially when operating at higher currents, to ensure reliability and longevity of the components involved.
Overall, this system provides a versatile solution for applications requiring precise control of AC motor speed and direction, making it suitable for various industrial and automation tasks.Varies speed and direction of 5-amp reversible series ac motor in accordance with d-c control signal. Polarity of control signal determines direction of rotation. Gain potentiometer adjusts slope of speed versus control voltage curve. -M. P. Southworth, Bidirectional Static Switch Simplifies Ac Control, Control Engineering, March 1964, p 75-76.
🔗 External reference