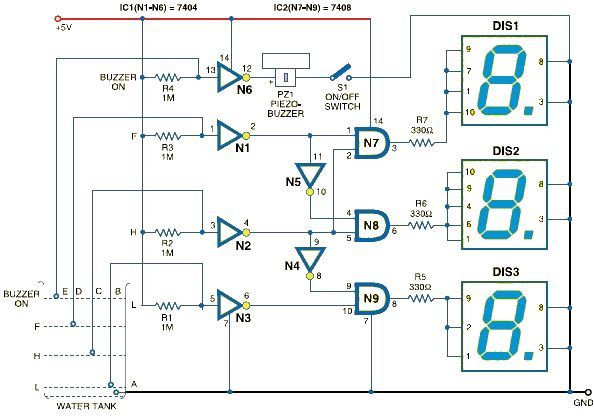
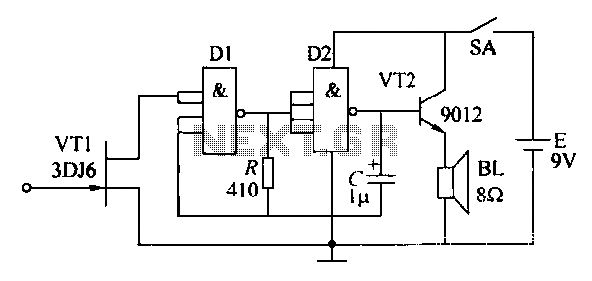
Infrared detector circuit using PID20
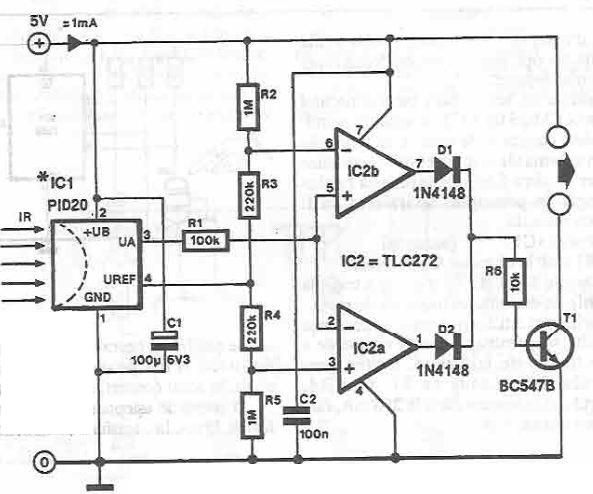
This infrared detector circuit is designed using the PID20 integrated circuit manufactured by Siemens, which converts thermal radiation into electrical impulses. It includes an operational amplifier and several electronic components. The output signal at pin 3 is compared with a reference voltage equal to half the supply voltage, which is derived from the voltage divider formed by resistors R2, R3, R4, and R5. When an object warmer than the surrounding environment approaches, or when an object colder than the environment is removed, the output voltage increases. The variation of the sensor output is compared by IC2a and IC2b, which are set to monitor voltages of 0.5 V below and above the reference voltage, respectively. Depending on the output, one of the comparators will activate T1.
The infrared detector circuit leverages the PID20 integrated circuit, which is adept at detecting infrared radiation and converting it into corresponding electrical signals. This circuit operates by establishing a reference voltage through a voltage divider created with resistors R2, R3, R4, and R5. The reference voltage is crucial as it provides a baseline for comparison against the output signal generated by the PID20.
When an object with a temperature higher than the ambient environment comes within proximity of the sensor, the output signal at pin 3 of the PID20 increases. Conversely, if an object with a lower temperature is removed from the vicinity, the output signal also increases. This dual behavior allows the circuit to effectively detect both the approach of warmer objects and the retreat of cooler objects.
The operational amplifiers IC2a and IC2b play a critical role in this circuit. They are configured to compare the output signal from the PID20 against the established reference voltage. IC2a monitors for signals that fall below the reference voltage by 0.5 V, while IC2b checks for signals that exceed the reference voltage by the same margin. This arrangement ensures that the circuit can accurately detect and respond to variations in temperature.
The output from these comparators is used to control a transistor, T1, which acts as a switch or relay in the circuit. Depending on which comparator is activated, T1 will either turn on or off, allowing the circuit to trigger an external device or alert system when a temperature change is detected. This functionality is essential for applications such as security systems, automatic lighting, or temperature monitoring systems, where detection of thermal changes can indicate the presence of people or objects.
Overall, this infrared detector circuit is a robust and efficient design for thermal detection applications, utilizing well-established electronic components and principles to achieve reliable performance.This infrared detector circuit is designed using the PID20 integrated circuit manufactured by Siemens (which converts thermal radiation into electrical impulses), an operational amplifier and a few electronic components. The output signal at pin 3 is compared with a reference voltage equal to half the supply voltage. Reference voltage is taken fro m the voltage divider R2-R3-R4-R5. When approaching an object warmer than the surrounding environment, or to remove an object colder than the environment, the output voltage increases. Variation of the sensor output will be compared, the IC2a and IC2b, located voltage of 0. 5 V under and over voltage reference respectively. Depending on the output, one of the comparators basculate and activates T1. 🔗 External reference
The infrared detector circuit leverages the PID20 integrated circuit, which is adept at detecting infrared radiation and converting it into corresponding electrical signals. This circuit operates by establishing a reference voltage through a voltage divider created with resistors R2, R3, R4, and R5. The reference voltage is crucial as it provides a baseline for comparison against the output signal generated by the PID20.
When an object with a temperature higher than the ambient environment comes within proximity of the sensor, the output signal at pin 3 of the PID20 increases. Conversely, if an object with a lower temperature is removed from the vicinity, the output signal also increases. This dual behavior allows the circuit to effectively detect both the approach of warmer objects and the retreat of cooler objects.
The operational amplifiers IC2a and IC2b play a critical role in this circuit. They are configured to compare the output signal from the PID20 against the established reference voltage. IC2a monitors for signals that fall below the reference voltage by 0.5 V, while IC2b checks for signals that exceed the reference voltage by the same margin. This arrangement ensures that the circuit can accurately detect and respond to variations in temperature.
The output from these comparators is used to control a transistor, T1, which acts as a switch or relay in the circuit. Depending on which comparator is activated, T1 will either turn on or off, allowing the circuit to trigger an external device or alert system when a temperature change is detected. This functionality is essential for applications such as security systems, automatic lighting, or temperature monitoring systems, where detection of thermal changes can indicate the presence of people or objects.
Overall, this infrared detector circuit is a robust and efficient design for thermal detection applications, utilizing well-established electronic components and principles to achieve reliable performance.This infrared detector circuit is designed using the PID20 integrated circuit manufactured by Siemens (which converts thermal radiation into electrical impulses), an operational amplifier and a few electronic components. The output signal at pin 3 is compared with a reference voltage equal to half the supply voltage. Reference voltage is taken fro m the voltage divider R2-R3-R4-R5. When approaching an object warmer than the surrounding environment, or to remove an object colder than the environment, the output voltage increases. Variation of the sensor output will be compared, the IC2a and IC2b, located voltage of 0. 5 V under and over voltage reference respectively. Depending on the output, one of the comparators basculate and activates T1. 🔗 External reference