Tube Power Amplifier with EL34 - 35W circuit
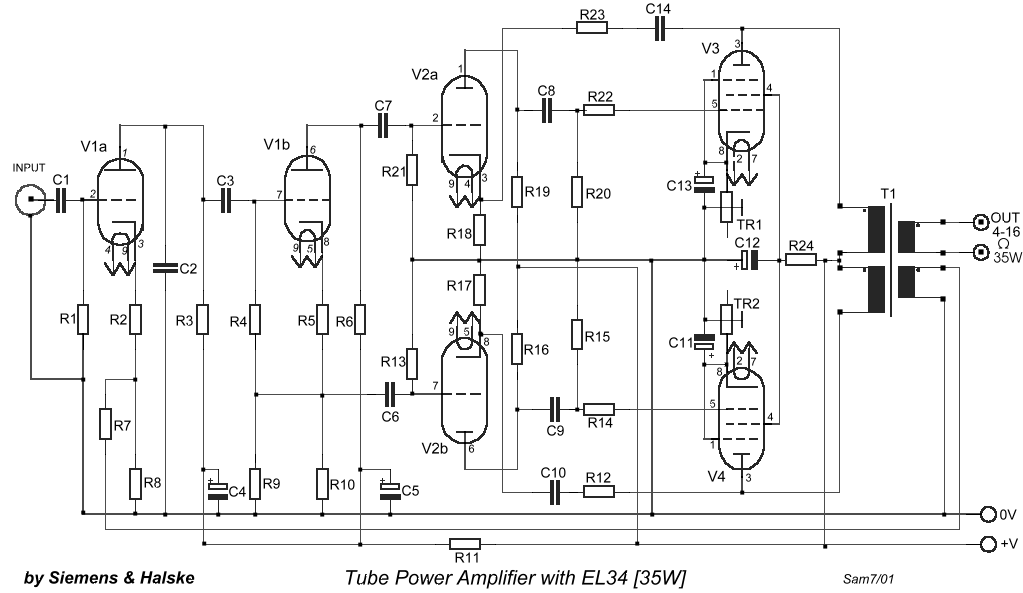
This is a classic design of a 35 W final amplifier utilizing two EL34 tubes in a push-pull configuration, developed by Siemens and Halske. The design dates back to March 24, 1953, and is identified by the code SV410/1. The amplifier was operational from 1954 until 1989, typically functioning for an average of 15 hours per day.
The described amplifier features a push-pull topology, which is well-known for its efficiency in audio amplification. The use of two EL34 vacuum tubes allows for a robust output of 35 watts, making it suitable for driving speakers in various audio applications. The push-pull configuration provides advantages such as reduced distortion and improved linearity, which are crucial for high-fidelity sound reproduction.
The circuit likely includes a power supply section designed to provide the necessary high voltage for the EL34 tubes, as well as filament voltage for their operation. The output stage would typically incorporate an output transformer, which matches the high-impedance output of the tubes to the low-impedance load of the speakers. Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be implemented to further enhance performance by stabilizing gain and reducing distortion.
Given the long operational lifespan of the amplifier, it is essential to consider the durability and reliability of components used in the design. High-quality capacitors and resistors would be necessary to maintain performance over time, especially under continuous use for 15 hours daily. The original design from 1953 reflects the engineering standards of the era while providing a foundation for audio amplification that remains appreciated by enthusiasts today.It`s a classic designing of final amplifier 35 W, with two EL34 in push-pull, from the Siemens and Halske, with year of designing 24/3/1953 and code SV410/1. The amplifier it worked from 1954 until 1989, whenever it came also out except operation, with mean of operation 15 hours per day..
🔗 External reference
The described amplifier features a push-pull topology, which is well-known for its efficiency in audio amplification. The use of two EL34 vacuum tubes allows for a robust output of 35 watts, making it suitable for driving speakers in various audio applications. The push-pull configuration provides advantages such as reduced distortion and improved linearity, which are crucial for high-fidelity sound reproduction.
The circuit likely includes a power supply section designed to provide the necessary high voltage for the EL34 tubes, as well as filament voltage for their operation. The output stage would typically incorporate an output transformer, which matches the high-impedance output of the tubes to the low-impedance load of the speakers. Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be implemented to further enhance performance by stabilizing gain and reducing distortion.
Given the long operational lifespan of the amplifier, it is essential to consider the durability and reliability of components used in the design. High-quality capacitors and resistors would be necessary to maintain performance over time, especially under continuous use for 15 hours daily. The original design from 1953 reflects the engineering standards of the era while providing a foundation for audio amplification that remains appreciated by enthusiasts today.It`s a classic designing of final amplifier 35 W, with two EL34 in push-pull, from the Siemens and Halske, with year of designing 24/3/1953 and code SV410/1. The amplifier it worked from 1954 until 1989, whenever it came also out except operation, with mean of operation 15 hours per day..
🔗 External reference