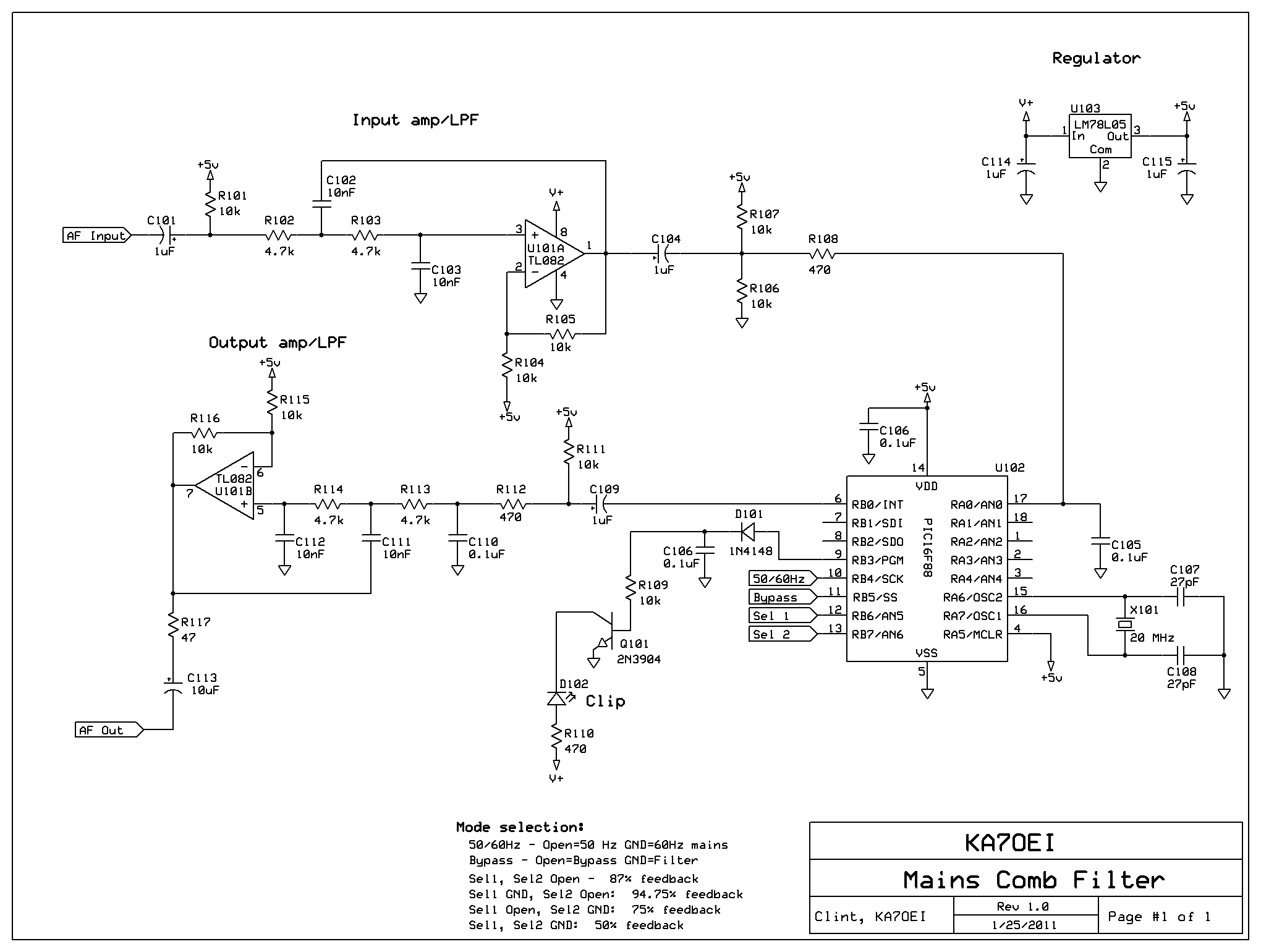
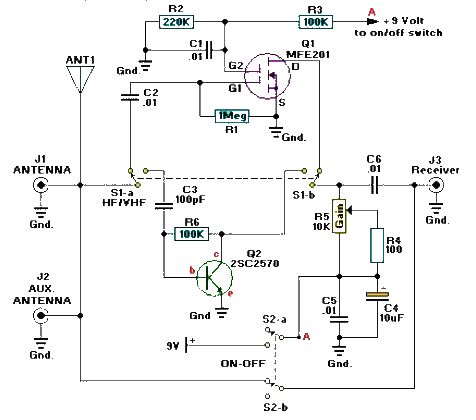
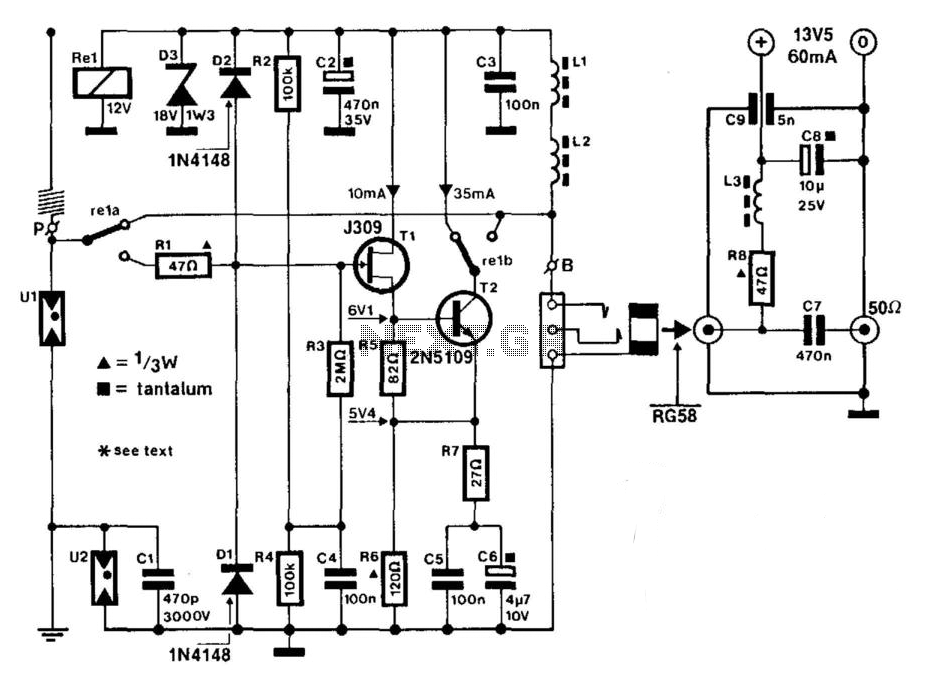
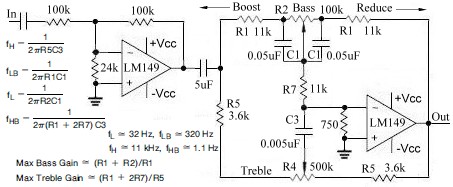
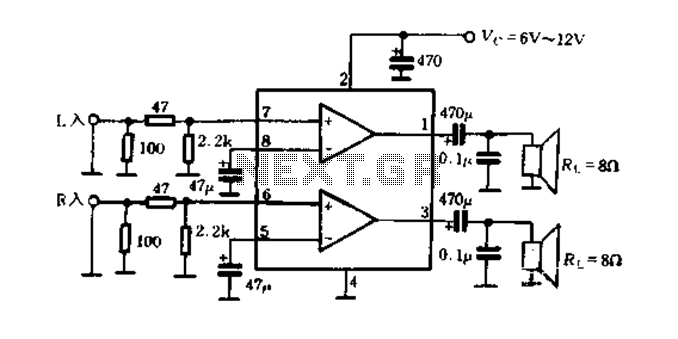
Tunable active filter

The high-pass and low-pass outputs cover the range of 300 Hz to 3000 Hz. The potentiometers must have a reverse log taper. The fixed-frequency active filter is summed in the fourth operational amplifier to provide a notch center frequency of 1 kHz, with a Q factor of 50.
The described circuit features a fixed-frequency active filter designed to manipulate audio signals by selectively allowing or attenuating certain frequency ranges. The high-pass and low-pass outputs are configured to operate within the frequency range of 300 Hz to 3000 Hz, which is typical for audio processing applications, ensuring that both low and high frequencies can be effectively managed.
The use of potentiometers with a reverse log taper is critical in this design. This type of taper allows for more precise control over the attenuation and gain of the audio signals at lower levels, making it particularly suitable for audio applications where fine adjustments are necessary.
The circuit includes a fourth operational amplifier (op-amp), which serves the purpose of summing the outputs of the high-pass and low-pass filters. This op-amp configuration is essential for creating a notch filter that is centered at a frequency of 1 kHz. The Q factor, which is set at 50, indicates a narrow bandwidth around the center frequency, allowing for selective attenuation of signals at 1 kHz while preserving signals outside this frequency. This characteristic is beneficial in applications such as feedback suppression in audio systems or in environments with specific noise frequencies that need to be minimized.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for audio signal processing, providing both flexibility and precision in frequency management.The high-pass and low-pass outputs cov- output. The potentiometers must have a re-ering the range of 300 Hz to 3000 Hz have been verse log taper Fixed-frequency active filter summed in the fourth op amp to provide a notch center frequency is 1 kHz, with a Q of 50. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit features a fixed-frequency active filter designed to manipulate audio signals by selectively allowing or attenuating certain frequency ranges. The high-pass and low-pass outputs are configured to operate within the frequency range of 300 Hz to 3000 Hz, which is typical for audio processing applications, ensuring that both low and high frequencies can be effectively managed.
The use of potentiometers with a reverse log taper is critical in this design. This type of taper allows for more precise control over the attenuation and gain of the audio signals at lower levels, making it particularly suitable for audio applications where fine adjustments are necessary.
The circuit includes a fourth operational amplifier (op-amp), which serves the purpose of summing the outputs of the high-pass and low-pass filters. This op-amp configuration is essential for creating a notch filter that is centered at a frequency of 1 kHz. The Q factor, which is set at 50, indicates a narrow bandwidth around the center frequency, allowing for selective attenuation of signals at 1 kHz while preserving signals outside this frequency. This characteristic is beneficial in applications such as feedback suppression in audio systems or in environments with specific noise frequencies that need to be minimized.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for audio signal processing, providing both flexibility and precision in frequency management.The high-pass and low-pass outputs cov- output. The potentiometers must have a re-ering the range of 300 Hz to 3000 Hz have been verse log taper Fixed-frequency active filter summed in the fourth op amp to provide a notch center frequency is 1 kHz, with a Q of 50. 🔗 External reference