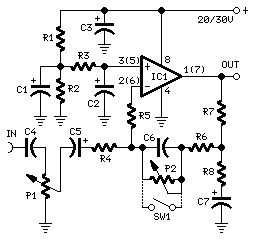
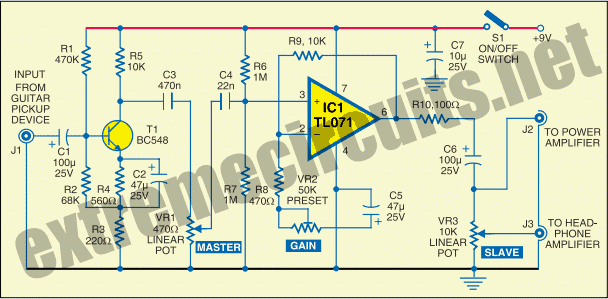
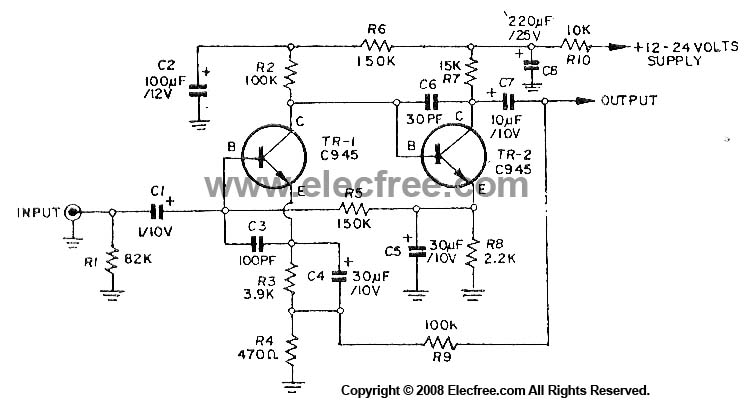
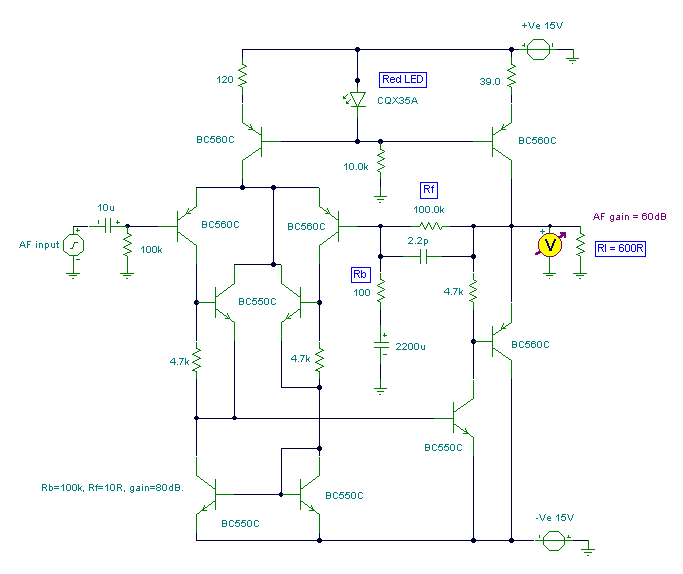
Two-meter preamplifier
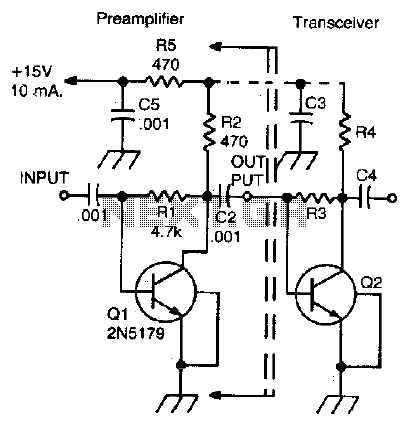
This simple, inexpensive, wideband RF amplifier provides 14 dB gain on two meters without the use of tuned circuits.
The RF amplifier described operates within the two-meter band, which typically spans frequencies from 144 to 148 MHz. It is designed to amplify radio frequency signals with a gain of 14 dB, making it suitable for applications such as amateur radio, signal boosting, and various communication systems. The term "wideband" indicates that the amplifier can operate effectively over a broad range of frequencies without requiring tuned circuits, which are commonly used in narrowband applications to select specific frequencies.
Key components of this RF amplifier may include transistors or integrated circuits that are capable of handling RF signals efficiently. The absence of tuned circuits simplifies the design, reducing component count and overall cost while enhancing reliability. The amplifier's performance can be further optimized through careful selection of passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, that determine the input and output impedance, stability, and frequency response.
The circuit layout should be designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance at RF frequencies. Proper grounding techniques and the use of short, direct traces are essential to maintain signal integrity. Additionally, considerations for thermal management may be necessary to ensure the amplifier operates within its specified temperature range, as RF amplifiers can generate heat during operation.
Overall, this RF amplifier represents a practical solution for applications requiring moderate gain across a wide frequency range, offering an efficient and cost-effective means of enhancing signal strength in various RF communication systems.This simple, inexpensive, wideband rf amplifier provides 14 dB gain on two meters Without the use of tuned circuits.
The RF amplifier described operates within the two-meter band, which typically spans frequencies from 144 to 148 MHz. It is designed to amplify radio frequency signals with a gain of 14 dB, making it suitable for applications such as amateur radio, signal boosting, and various communication systems. The term "wideband" indicates that the amplifier can operate effectively over a broad range of frequencies without requiring tuned circuits, which are commonly used in narrowband applications to select specific frequencies.
Key components of this RF amplifier may include transistors or integrated circuits that are capable of handling RF signals efficiently. The absence of tuned circuits simplifies the design, reducing component count and overall cost while enhancing reliability. The amplifier's performance can be further optimized through careful selection of passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, that determine the input and output impedance, stability, and frequency response.
The circuit layout should be designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance at RF frequencies. Proper grounding techniques and the use of short, direct traces are essential to maintain signal integrity. Additionally, considerations for thermal management may be necessary to ensure the amplifier operates within its specified temperature range, as RF amplifiers can generate heat during operation.
Overall, this RF amplifier represents a practical solution for applications requiring moderate gain across a wide frequency range, offering an efficient and cost-effective means of enhancing signal strength in various RF communication systems.This simple, inexpensive, wideband rf amplifier provides 14 dB gain on two meters Without the use of tuned circuits.