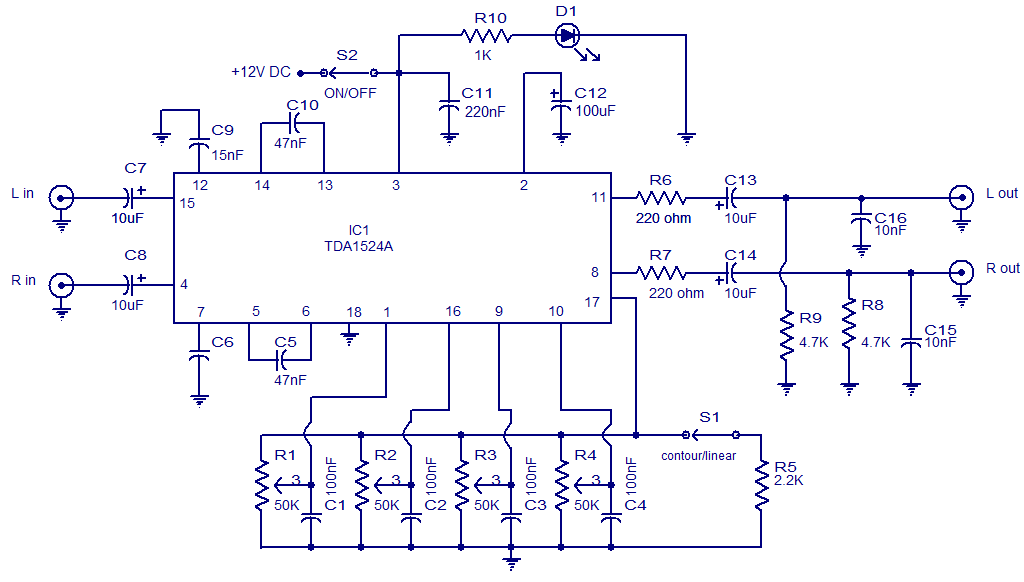
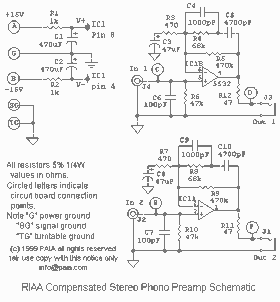
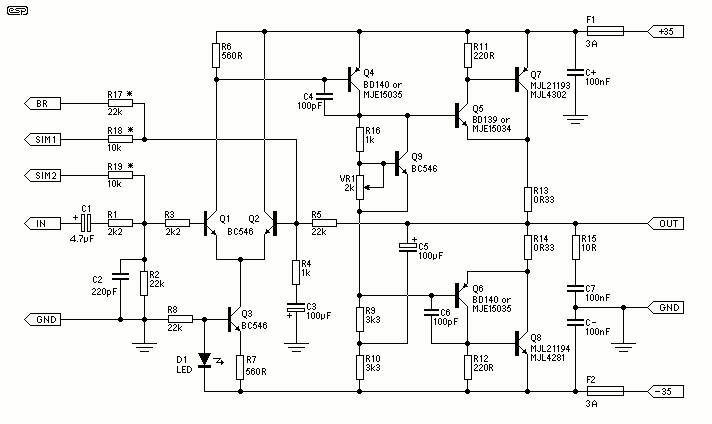
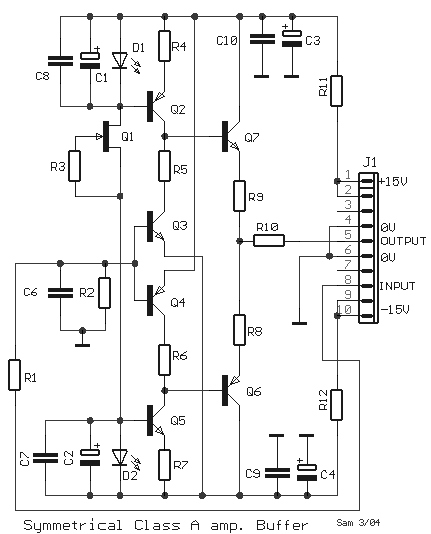
Hi-Fi Phono Preamplifier with RIAA Specification
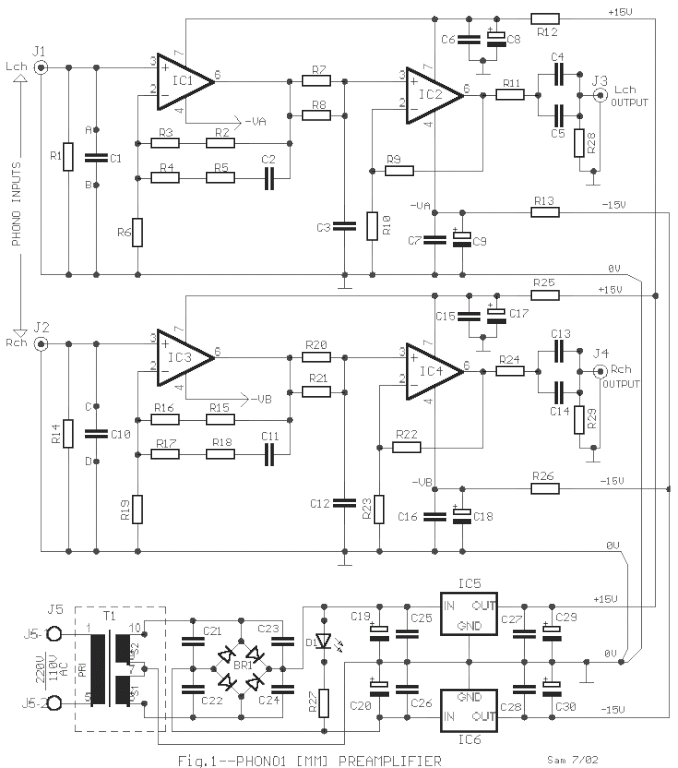
The circuit was designed according to the RIAA implementation of a Hi-Fi phono preamplifier for the purpose of reproducing audio from a moving magnet cartridge.
The RIAA (Recording Industry Association of America) equalization curve is essential for the accurate playback of audio from vinyl records, as it compensates for the frequency response characteristics of the recording process. The Hi-Fi phono preamplifier serves to amplify the low-level signals produced by moving magnet cartridges, which typically output a signal in the range of millivolts.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: an input stage for initial signal amplification, an RIAA equalization stage to apply the necessary frequency response adjustments, and a final output stage to drive the line-level output. The input stage often employs a low-noise operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a non-inverting or inverting amplifier configuration, which helps to provide the necessary gain while maintaining low distortion.
The RIAA equalization stage is implemented using passive components such as resistors and capacitors, which create a filter network that shapes the frequency response according to the RIAA standard. This network is crucial for ensuring that the playback sound closely matches the original recording, as it compensates for the high-frequency roll-off and low-frequency boost that occurs during the vinyl mastering process.
The output stage of the preamplifier is designed to provide a suitable output level for standard audio equipment, typically configured to drive a 10k ohm load. This stage may also include additional filtering to eliminate any unwanted noise or interference before the signal is sent to the line input of an amplifier or audio receiver.
Overall, the Hi-Fi phono preamplifier circuit is a critical component in the vinyl playback chain, ensuring that the audio signal is accurately reproduced with fidelity and clarity. Proper design and implementation of the circuit are essential for achieving high-quality audio reproduction from moving magnet cartridges.The circuit was designed according to the RIAA implementation of Hi-Fi phono preamplifier for the purpose of reproducing an audio from a moving magnet car.. 🔗 External reference
The RIAA (Recording Industry Association of America) equalization curve is essential for the accurate playback of audio from vinyl records, as it compensates for the frequency response characteristics of the recording process. The Hi-Fi phono preamplifier serves to amplify the low-level signals produced by moving magnet cartridges, which typically output a signal in the range of millivolts.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: an input stage for initial signal amplification, an RIAA equalization stage to apply the necessary frequency response adjustments, and a final output stage to drive the line-level output. The input stage often employs a low-noise operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a non-inverting or inverting amplifier configuration, which helps to provide the necessary gain while maintaining low distortion.
The RIAA equalization stage is implemented using passive components such as resistors and capacitors, which create a filter network that shapes the frequency response according to the RIAA standard. This network is crucial for ensuring that the playback sound closely matches the original recording, as it compensates for the high-frequency roll-off and low-frequency boost that occurs during the vinyl mastering process.
The output stage of the preamplifier is designed to provide a suitable output level for standard audio equipment, typically configured to drive a 10k ohm load. This stage may also include additional filtering to eliminate any unwanted noise or interference before the signal is sent to the line input of an amplifier or audio receiver.
Overall, the Hi-Fi phono preamplifier circuit is a critical component in the vinyl playback chain, ensuring that the audio signal is accurately reproduced with fidelity and clarity. Proper design and implementation of the circuit are essential for achieving high-quality audio reproduction from moving magnet cartridges.The circuit was designed according to the RIAA implementation of Hi-Fi phono preamplifier for the purpose of reproducing an audio from a moving magnet car.. 🔗 External reference