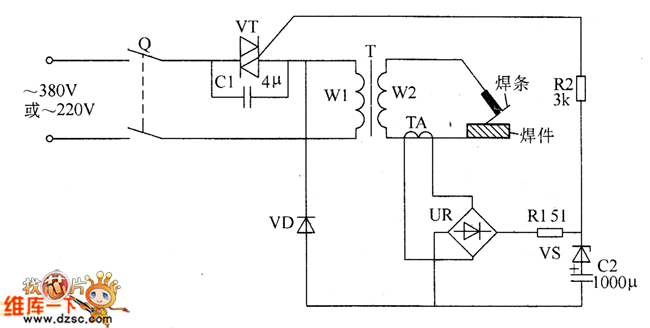
Two mode night light circuit - WorkingCircuit DIagram
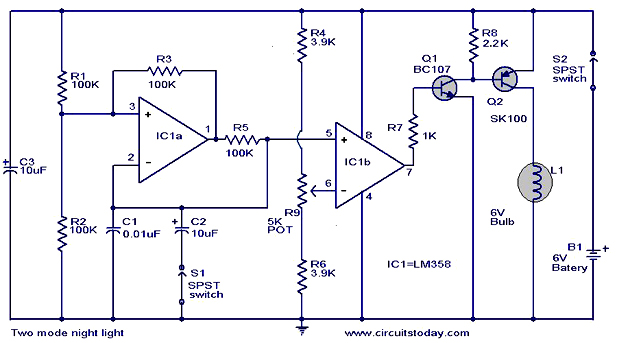
The operation and circuit diagram of a two-mode night light circuit are provided below.
The two-mode night light circuit is designed to operate in two distinct lighting modes, typically offering a choice between a standard brightness setting and a dimmer, energy-saving mode. This circuit can be particularly useful in environments such as bedrooms or hallways, where a soft light is preferred during nighttime hours.
The core components of the circuit include a light-emitting diode (LED) for illumination, a resistor to limit the current flowing through the LED, and a switch mechanism that allows the user to toggle between the two modes. Additionally, a transistor may be used to amplify the control signal from the switch, enabling the circuit to handle the different brightness levels effectively.
In the standard mode, the LED is powered directly, providing maximum brightness. In the dim mode, the circuit could utilize a resistor in series with the LED to reduce the current, resulting in a lower light output. Alternatively, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) approach could be employed to control the brightness dynamically, allowing for a more efficient power usage.
The schematic diagram typically illustrates the arrangement of these components, with clear indications of the power supply connections, the orientation of the LED, and the placement of the switch. Proper attention to the values of the resistors and the specifications of the LED is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the circuit.
In summary, the two-mode night light circuit is a practical solution for providing adjustable lighting in low-light environments, combining functionality with energy efficiency.The working and circuit diagram of a two mode night light circuit is given below.. 🔗 External reference
The two-mode night light circuit is designed to operate in two distinct lighting modes, typically offering a choice between a standard brightness setting and a dimmer, energy-saving mode. This circuit can be particularly useful in environments such as bedrooms or hallways, where a soft light is preferred during nighttime hours.
The core components of the circuit include a light-emitting diode (LED) for illumination, a resistor to limit the current flowing through the LED, and a switch mechanism that allows the user to toggle between the two modes. Additionally, a transistor may be used to amplify the control signal from the switch, enabling the circuit to handle the different brightness levels effectively.
In the standard mode, the LED is powered directly, providing maximum brightness. In the dim mode, the circuit could utilize a resistor in series with the LED to reduce the current, resulting in a lower light output. Alternatively, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) approach could be employed to control the brightness dynamically, allowing for a more efficient power usage.
The schematic diagram typically illustrates the arrangement of these components, with clear indications of the power supply connections, the orientation of the LED, and the placement of the switch. Proper attention to the values of the resistors and the specifications of the LED is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the circuit.
In summary, the two-mode night light circuit is a practical solution for providing adjustable lighting in low-light environments, combining functionality with energy efficiency.The working and circuit diagram of a two mode night light circuit is given below.. 🔗 External reference