ULINKpro Interface Schematic
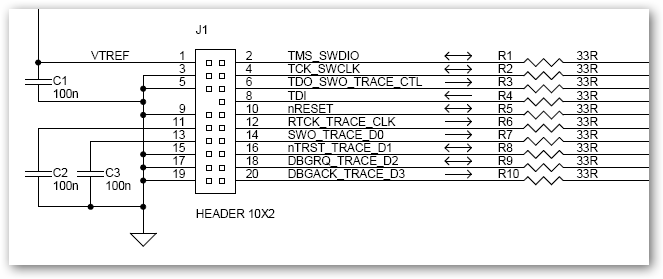
This interface schematic illustrates the JTAG, Serial Wire, and ETM interface circuits of ULINKpro. It can be utilized to analyze potential issues with the target hardware.
The schematic represents the interconnections and functionalities of the JTAG (Joint Test Action Group), Serial Wire Debug (SWD), and Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) interfaces, which are essential for debugging and programming ARM-based microcontrollers.
The JTAG interface provides a standard method for accessing the debugging features of a microcontroller, allowing for boundary scan testing and in-system programming. It typically consists of a series of pins, including TCK (Test Clock), TMS (Test Mode Select), TDI (Test Data In), and TDO (Test Data Out), facilitating communication between the debugger and the target device.
The Serial Wire Debug interface is a more efficient alternative to JTAG, utilizing fewer pins while maintaining robust debugging capabilities. It employs a two-wire protocol, consisting of SWDIO (Serial Wire Debug Input/Output) and SWCLK (Serial Wire Clock), allowing for a simpler connection to the target hardware.
The Embedded Trace Macrocell interface is designed for real-time tracing of program execution, enabling developers to gather performance metrics and analyze code behavior without significantly impacting system performance. This interface provides a means to capture data such as instruction execution and data accesses.
Overall, the schematic serves as a vital tool for engineers to troubleshoot and optimize the performance of ARM-based systems, ensuring that the necessary interfaces are correctly implemented and functioning as intended.This interface schematic shows the JTAG, Serial Wire, and ETM interface circuits of ULINKpro. Use this schematic to analyze potential problems with the target hardware. ARM websites use two types of cookie: (1) those that enable the site to function and perform as required; and (2) analytical cookies which anonymously track visitors only while usi ng the site. If you are not happy with this use of these cookies please review our Privacy Policy to learn how they can be disabled. By disabling cookies some features of the site will not work. 🔗 External reference
The schematic represents the interconnections and functionalities of the JTAG (Joint Test Action Group), Serial Wire Debug (SWD), and Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) interfaces, which are essential for debugging and programming ARM-based microcontrollers.
The JTAG interface provides a standard method for accessing the debugging features of a microcontroller, allowing for boundary scan testing and in-system programming. It typically consists of a series of pins, including TCK (Test Clock), TMS (Test Mode Select), TDI (Test Data In), and TDO (Test Data Out), facilitating communication between the debugger and the target device.
The Serial Wire Debug interface is a more efficient alternative to JTAG, utilizing fewer pins while maintaining robust debugging capabilities. It employs a two-wire protocol, consisting of SWDIO (Serial Wire Debug Input/Output) and SWCLK (Serial Wire Clock), allowing for a simpler connection to the target hardware.
The Embedded Trace Macrocell interface is designed for real-time tracing of program execution, enabling developers to gather performance metrics and analyze code behavior without significantly impacting system performance. This interface provides a means to capture data such as instruction execution and data accesses.
Overall, the schematic serves as a vital tool for engineers to troubleshoot and optimize the performance of ARM-based systems, ensuring that the necessary interfaces are correctly implemented and functioning as intended.This interface schematic shows the JTAG, Serial Wire, and ETM interface circuits of ULINKpro. Use this schematic to analyze potential problems with the target hardware. ARM websites use two types of cookie: (1) those that enable the site to function and perform as required; and (2) analytical cookies which anonymously track visitors only while usi ng the site. If you are not happy with this use of these cookies please review our Privacy Policy to learn how they can be disabled. By disabling cookies some features of the site will not work. 🔗 External reference