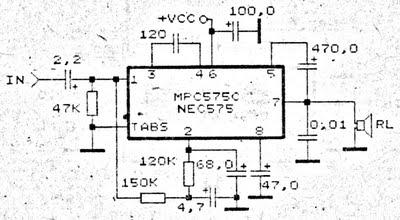
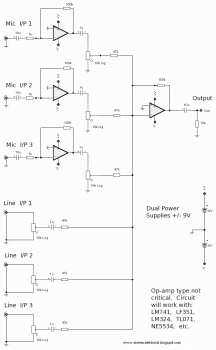
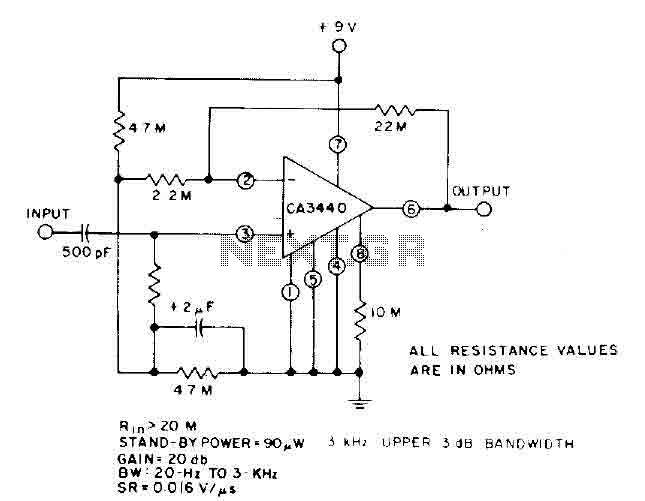
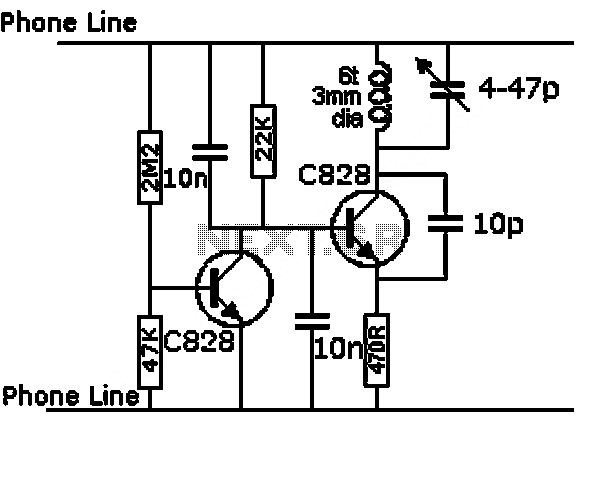
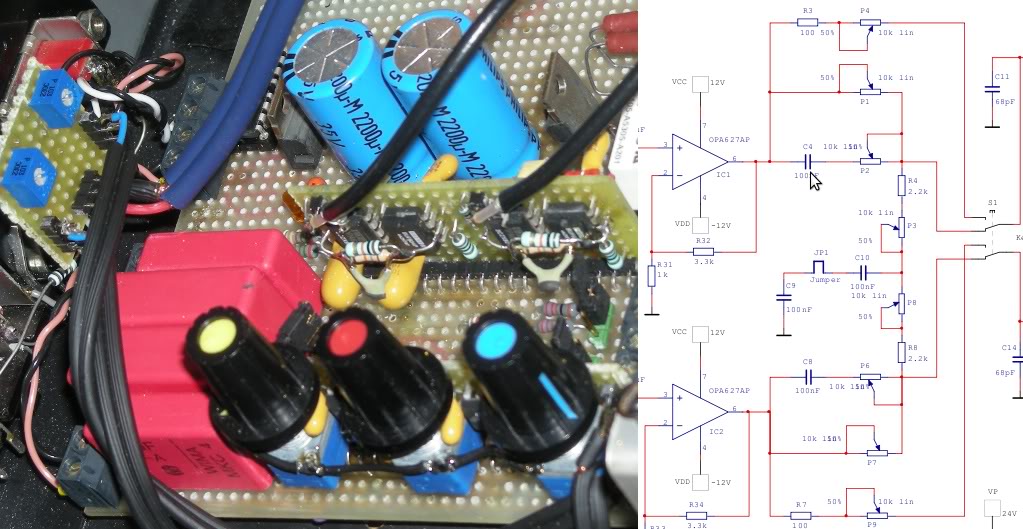
Ultra-high gain audio amplifier

Sometimes referred to as the JFET µ-amp, this circuit offers a very low power, high gain amplification function. As the drain current decreases, the µ of a JFET increases, meaning that the lower the drain current, the greater the gain achieved. However, it is important to note that the input dynamic range is compromised as the gain increases.
The JFET µ-amp circuit utilizes a Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) to achieve its amplification characteristics. The JFET operates by controlling the current flow through a semiconductor channel via an electric field created by the gate voltage. This configuration allows for high input impedance and low output impedance, making it suitable for various applications where signal integrity is critical.
The gain of the JFET amplifier can be adjusted by varying the drain current. A lower drain current results in a higher transconductance (µ), which directly translates to increased voltage gain. However, this increase in gain comes at the cost of input dynamic range, as the circuit may become more sensitive to noise and distortion at higher gain levels.
In practical applications, the JFET µ-amp is often used in sensor signal conditioning, audio amplification, and other low-power applications where high gain is required without introducing significant power consumption. The circuit design typically includes biasing resistors to stabilize the operating point of the JFET, ensuring consistent performance across varying temperatures and supply voltages.
Overall, the JFET µ-amp circuit is a versatile and efficient solution for applications requiring high gain with minimal power usage, though careful consideration must be given to the trade-offs in input dynamic range as gain is maximized.Sometimes called the JFET µ-amp, this circuit provides a very low power, high gain amplifying function. Since µ of a JFET increases as drain current decreases, the lower drain current is, the more gain you get
Input dynamic range is sacrificed with increasing gain, however. 🔗 External reference
The JFET µ-amp circuit utilizes a Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) to achieve its amplification characteristics. The JFET operates by controlling the current flow through a semiconductor channel via an electric field created by the gate voltage. This configuration allows for high input impedance and low output impedance, making it suitable for various applications where signal integrity is critical.
The gain of the JFET amplifier can be adjusted by varying the drain current. A lower drain current results in a higher transconductance (µ), which directly translates to increased voltage gain. However, this increase in gain comes at the cost of input dynamic range, as the circuit may become more sensitive to noise and distortion at higher gain levels.
In practical applications, the JFET µ-amp is often used in sensor signal conditioning, audio amplification, and other low-power applications where high gain is required without introducing significant power consumption. The circuit design typically includes biasing resistors to stabilize the operating point of the JFET, ensuring consistent performance across varying temperatures and supply voltages.
Overall, the JFET µ-amp circuit is a versatile and efficient solution for applications requiring high gain with minimal power usage, though careful consideration must be given to the trade-offs in input dynamic range as gain is maximized.Sometimes called the JFET µ-amp, this circuit provides a very low power, high gain amplifying function. Since µ of a JFET increases as drain current decreases, the lower drain current is, the more gain you get
Input dynamic range is sacrificed with increasing gain, however. 🔗 External reference