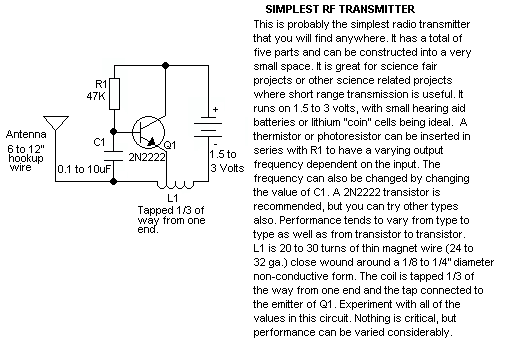
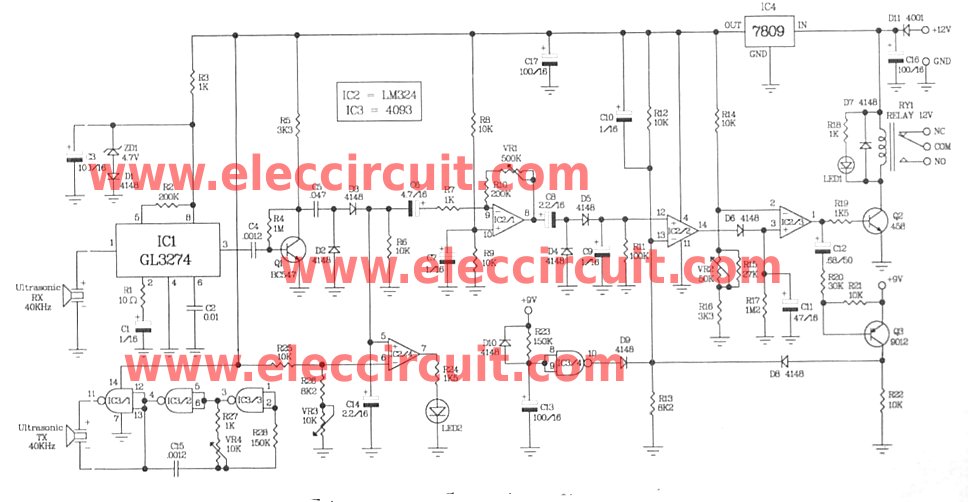
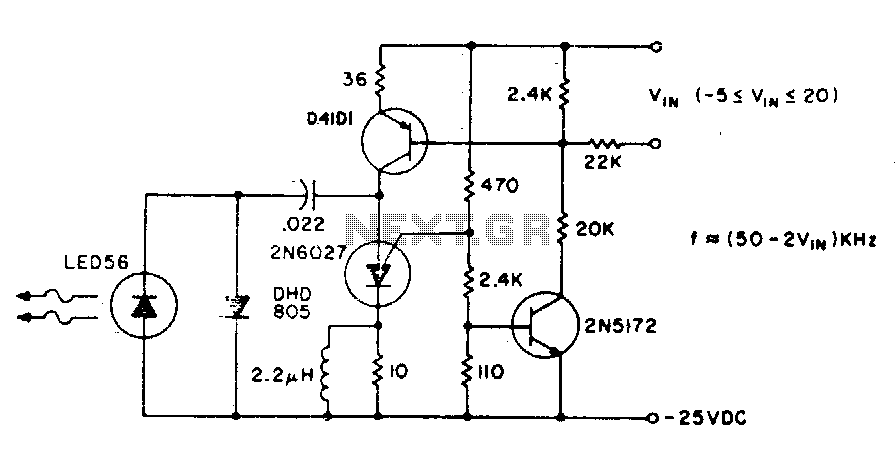
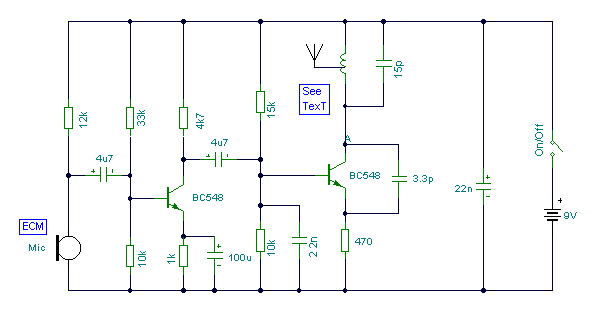
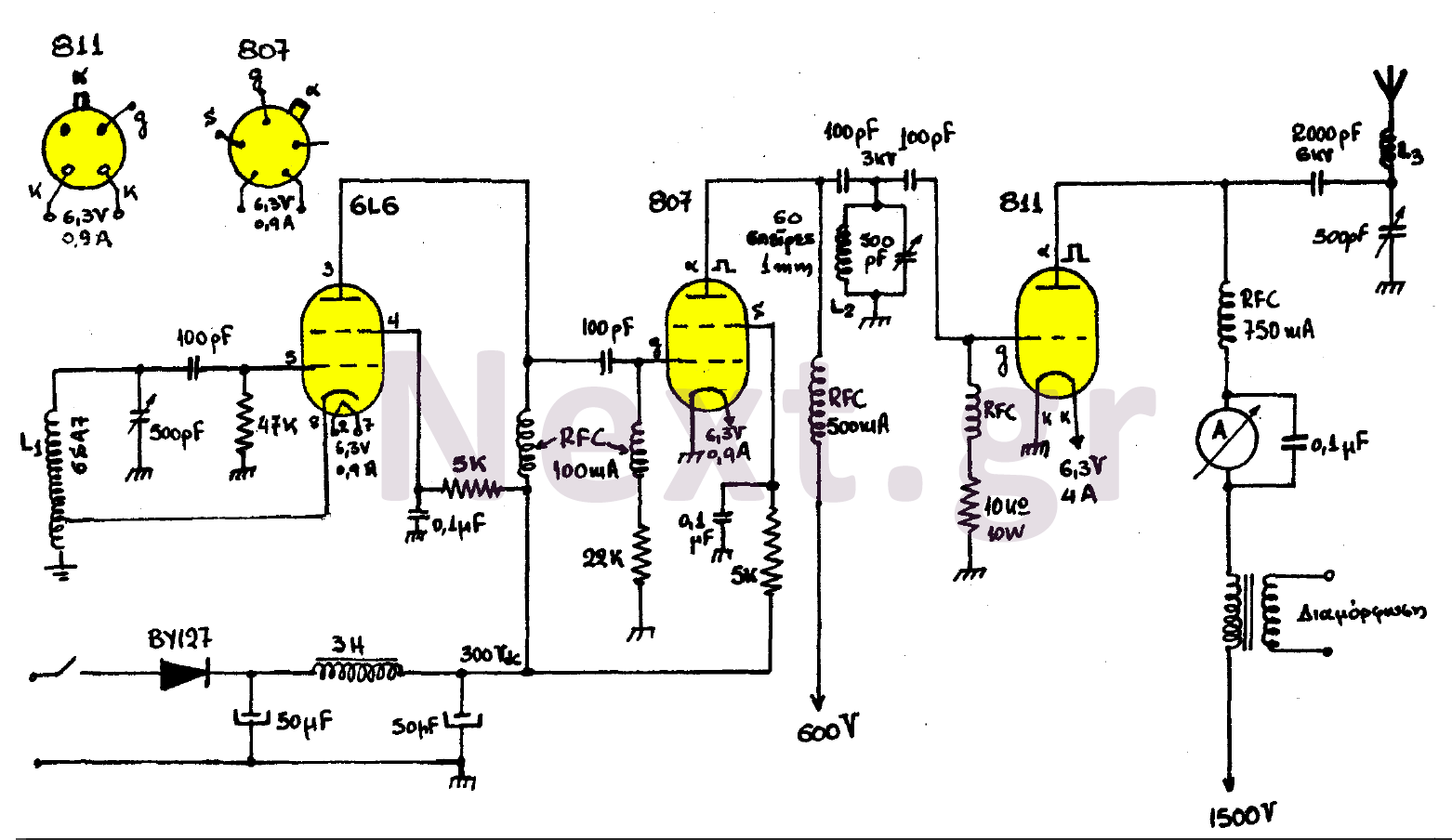
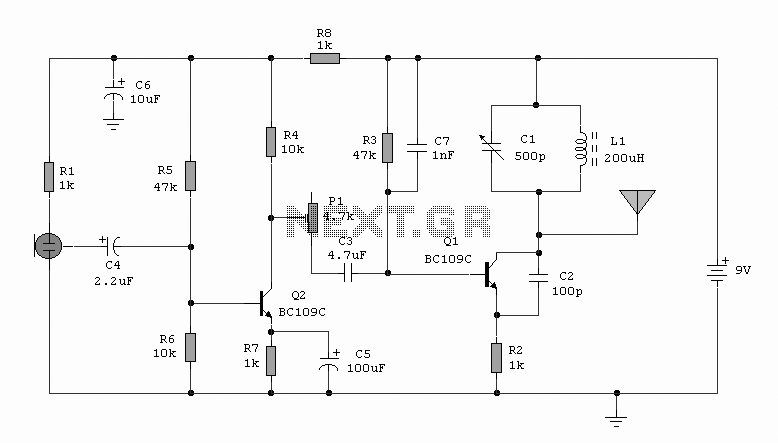
ultrasonic transmitter
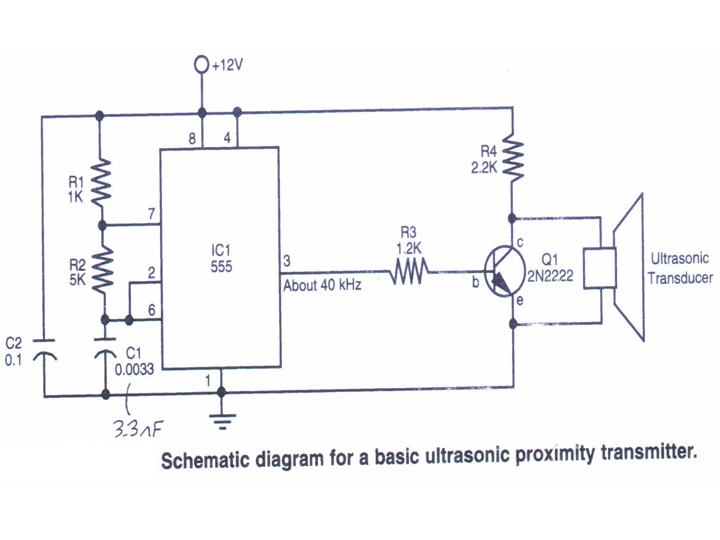
This section provides step-by-step instructions along with images for constructing an Ultrasonic Proximity Transmitter. Due to the simplicity of the circuit, only a schematic for the sensor is presented here. The objective of this tutorial is to assist others in building an ultrasonic proximity transmitter, which, when combined with an ultrasonic receiver, will serve as the eyes of a robot. Complete construction details and photos are included in this tutorial for the sensor. Once the concepts are conveyed, the reader should be able to build their own sensor.
The Ultrasonic Proximity Transmitter is designed to emit ultrasonic waves that can be detected by an ultrasonic receiver. This basic circuit typically consists of a few key components: an ultrasonic transducer, a microcontroller or oscillator circuit, and necessary passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The transducer converts electrical signals into ultrasonic sound waves, which propagate through the air.
The schematic representation of the circuit will include the ultrasonic transducer connected to a microcontroller. The microcontroller generates a square wave signal, which is fed to the transducer. This signal determines the frequency of the emitted ultrasonic waves, commonly around 40 kHz for proximity sensing applications.
In addition to the transducer and microcontroller, the circuit may incorporate a power supply section to ensure stable operation. This can be achieved using a battery or a regulated power supply. Decoupling capacitors are often included to filter out noise and provide a stable voltage to the microcontroller.
The construction process involves carefully assembling the components on a breadboard or PCB, following the schematic. The tutorial provides detailed images to guide through each step of the assembly, ensuring that connections are made correctly and securely.
Once the assembly is complete, the device can be tested by measuring the distance to an object using the time it takes for the emitted ultrasonic waves to reflect back to the transducer. This functionality allows the ultrasonic proximity transmitter to be integrated into robotic systems, enabling them to navigate and avoid obstacles effectively.
Overall, this project not only demonstrates the principles of ultrasonic sensing but also provides a practical application in robotics, enhancing the capabilities of autonomous systems.This section gives step-by-step instructions along with photos to the construction of Ultrasonic Proximity Transmitter. Because this is a very simple circuit, only a schematic for the sensor is shown here: (For the PDF format click here.
) This tutorial`s objective was to help others built a ultrasonic proximity transmitter which combined with a ul trasonic receiver will be used as the eyes of a robot. Complete construction details and photos are included in this tutorial for the sensor. Once the concepts are conveyed the reader should be able to build their own sensor. 🔗 External reference
The Ultrasonic Proximity Transmitter is designed to emit ultrasonic waves that can be detected by an ultrasonic receiver. This basic circuit typically consists of a few key components: an ultrasonic transducer, a microcontroller or oscillator circuit, and necessary passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The transducer converts electrical signals into ultrasonic sound waves, which propagate through the air.
The schematic representation of the circuit will include the ultrasonic transducer connected to a microcontroller. The microcontroller generates a square wave signal, which is fed to the transducer. This signal determines the frequency of the emitted ultrasonic waves, commonly around 40 kHz for proximity sensing applications.
In addition to the transducer and microcontroller, the circuit may incorporate a power supply section to ensure stable operation. This can be achieved using a battery or a regulated power supply. Decoupling capacitors are often included to filter out noise and provide a stable voltage to the microcontroller.
The construction process involves carefully assembling the components on a breadboard or PCB, following the schematic. The tutorial provides detailed images to guide through each step of the assembly, ensuring that connections are made correctly and securely.
Once the assembly is complete, the device can be tested by measuring the distance to an object using the time it takes for the emitted ultrasonic waves to reflect back to the transducer. This functionality allows the ultrasonic proximity transmitter to be integrated into robotic systems, enabling them to navigate and avoid obstacles effectively.
Overall, this project not only demonstrates the principles of ultrasonic sensing but also provides a practical application in robotics, enhancing the capabilities of autonomous systems.This section gives step-by-step instructions along with photos to the construction of Ultrasonic Proximity Transmitter. Because this is a very simple circuit, only a schematic for the sensor is shown here: (For the PDF format click here.
) This tutorial`s objective was to help others built a ultrasonic proximity transmitter which combined with a ul trasonic receiver will be used as the eyes of a robot. Complete construction details and photos are included in this tutorial for the sensor. Once the concepts are conveyed the reader should be able to build their own sensor. 🔗 External reference