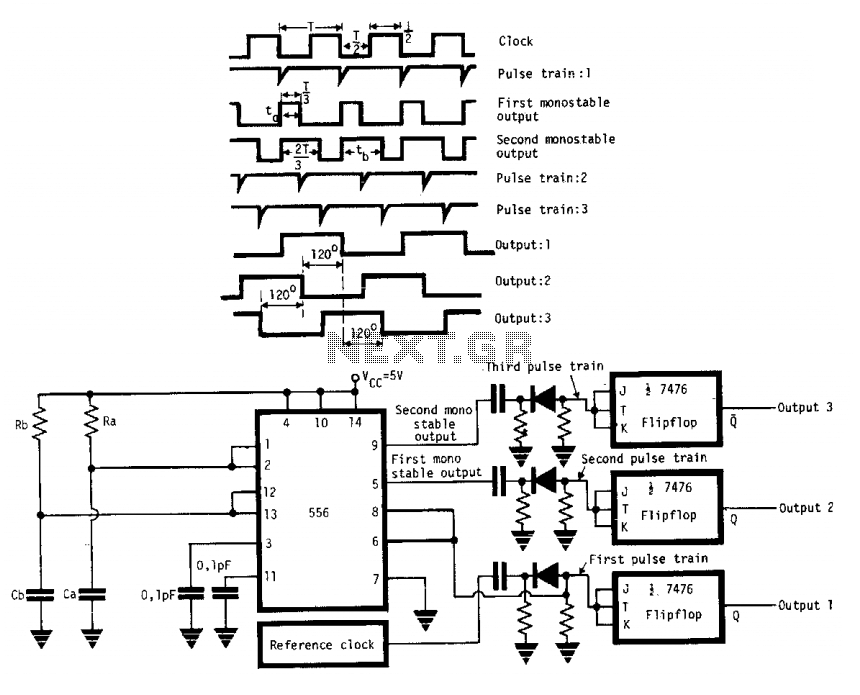
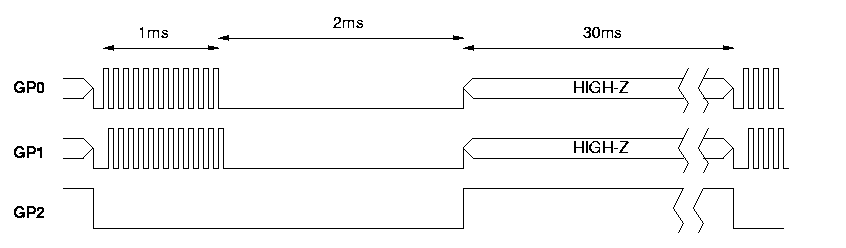
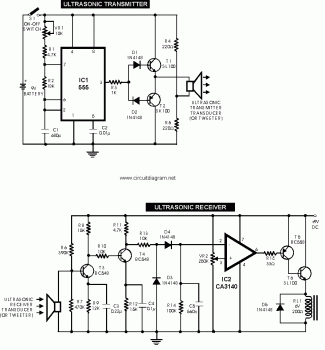
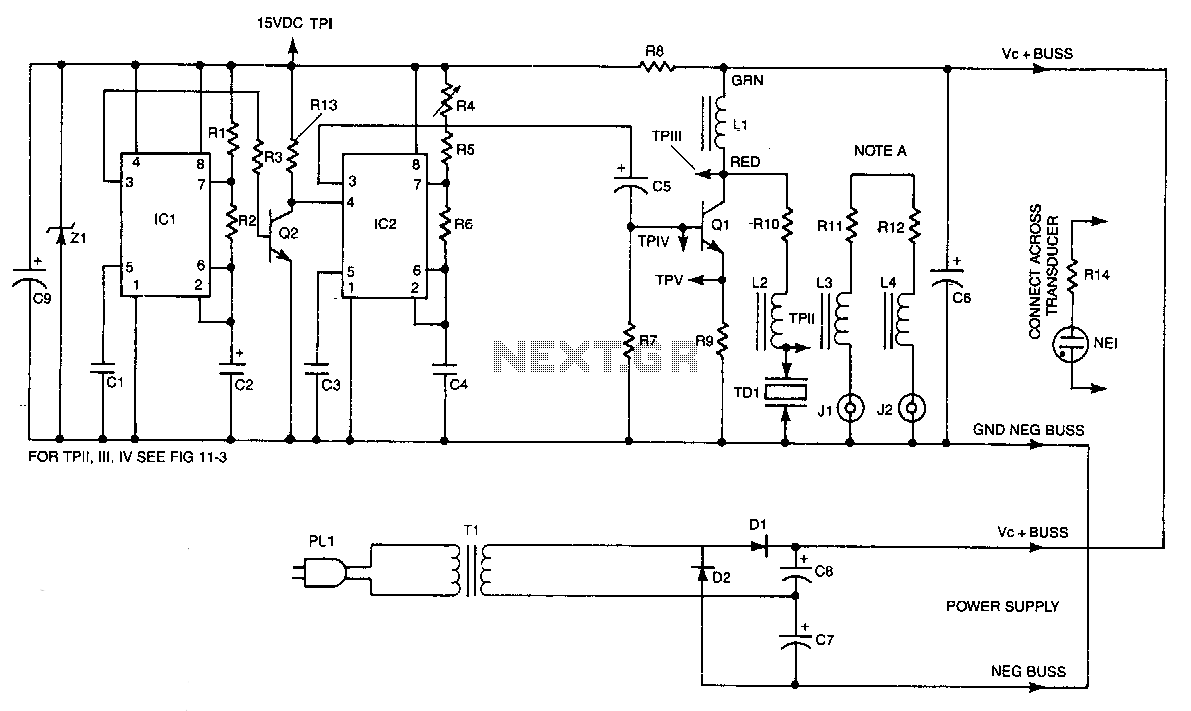
Ultrasonic waves
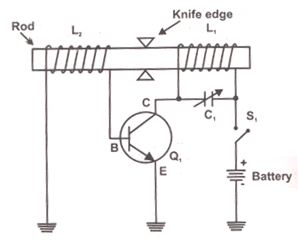
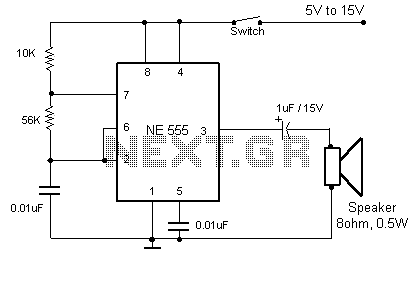
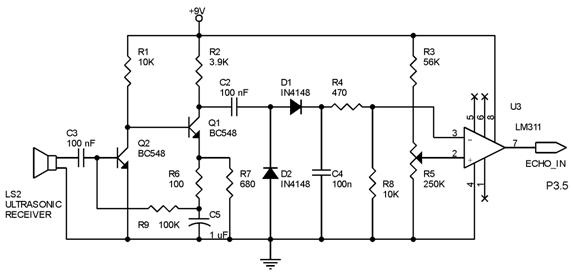
Frequencies that exceed the limits of human hearing are referred to as ultrasonic waves or frequencies. These ultrasonic waves can be generated using various components, including piezoelectric cells, magnetostrictive oscillators, piezoelectric oscillators, and Hartley oscillators with piezoelectric cells.
Ultrasonic waves are sound waves with frequencies above 20 kHz, which is the upper limit of human hearing. These waves have various applications in fields such as medical imaging, industrial non-destructive testing, and ultrasonic cleaning. The generation of ultrasonic waves typically involves the use of piezoelectric materials, which convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations and vice versa.
A piezoelectric cell operates by applying an electrical voltage across a piezoelectric material, causing it to deform and produce sound waves. In contrast, magnetostrictive oscillators utilize the magnetostrictive effect, where certain materials change shape in the presence of a magnetic field, to generate ultrasonic frequencies.
The Hartley oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that can be configured to produce ultrasonic frequencies by incorporating a piezoelectric element in its feedback loop. This configuration allows for stable oscillation at high frequencies, making it suitable for applications requiring precise ultrasonic signals.
In summary, ultrasonic wave generation can be achieved through various methods and components, each with its unique characteristics and advantages, facilitating a wide array of applications in technology and industry.The frequencies which are above to the limits of hearing are called Ultrasonic waves or frequencies, ultrasonic waves, piezo electic cell, Magneto Striation OSC, Piezo Electric OSC, Hartley OSC with piezo Cell.. 🔗 External reference
Ultrasonic waves are sound waves with frequencies above 20 kHz, which is the upper limit of human hearing. These waves have various applications in fields such as medical imaging, industrial non-destructive testing, and ultrasonic cleaning. The generation of ultrasonic waves typically involves the use of piezoelectric materials, which convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations and vice versa.
A piezoelectric cell operates by applying an electrical voltage across a piezoelectric material, causing it to deform and produce sound waves. In contrast, magnetostrictive oscillators utilize the magnetostrictive effect, where certain materials change shape in the presence of a magnetic field, to generate ultrasonic frequencies.
The Hartley oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that can be configured to produce ultrasonic frequencies by incorporating a piezoelectric element in its feedback loop. This configuration allows for stable oscillation at high frequencies, making it suitable for applications requiring precise ultrasonic signals.
In summary, ultrasonic wave generation can be achieved through various methods and components, each with its unique characteristics and advantages, facilitating a wide array of applications in technology and industry.The frequencies which are above to the limits of hearing are called Ultrasonic waves or frequencies, ultrasonic waves, piezo electic cell, Magneto Striation OSC, Piezo Electric OSC, Hartley OSC with piezo Cell.. 🔗 External reference