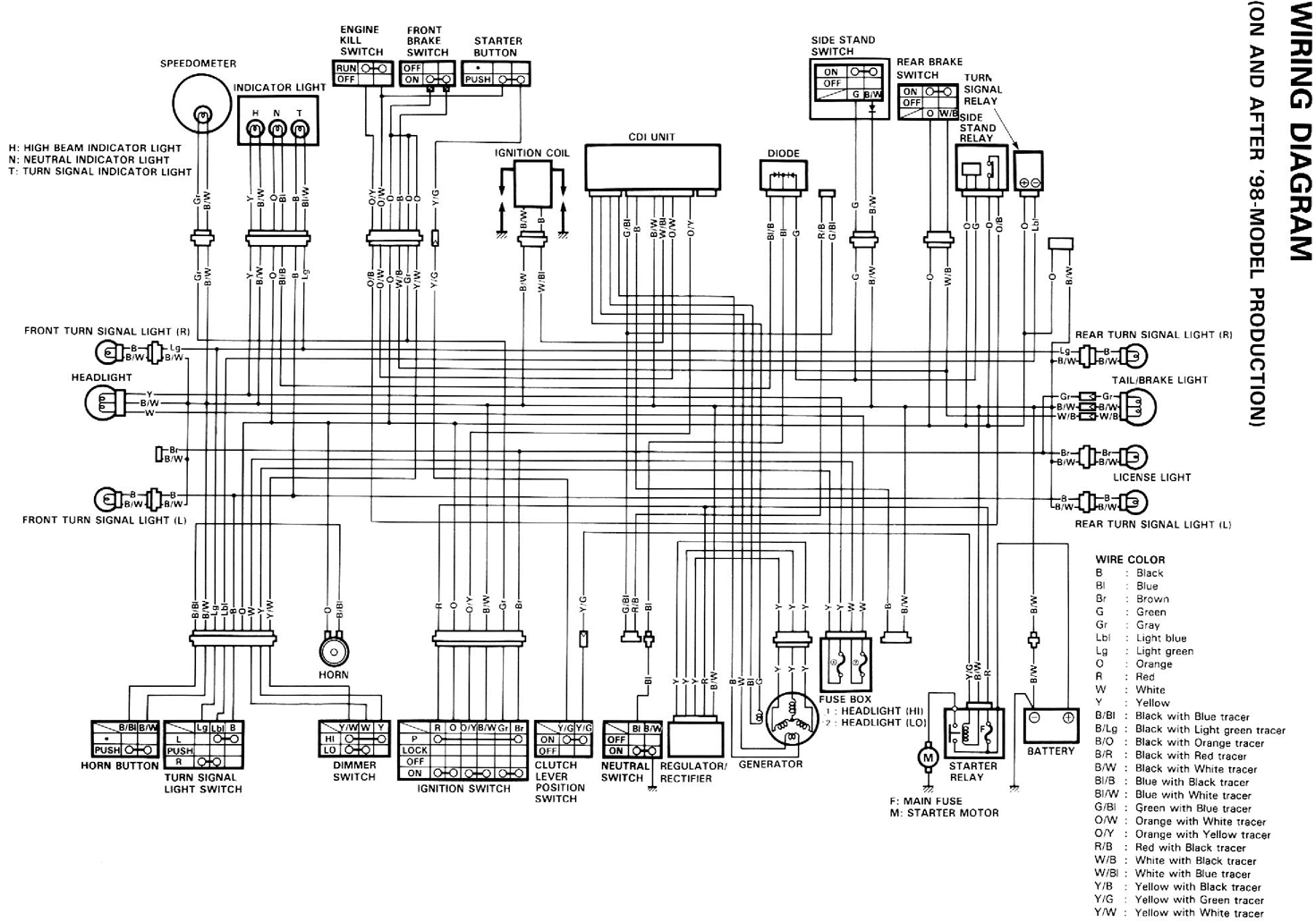
LM909 radio telecontrol receiving decoding circuit diagram
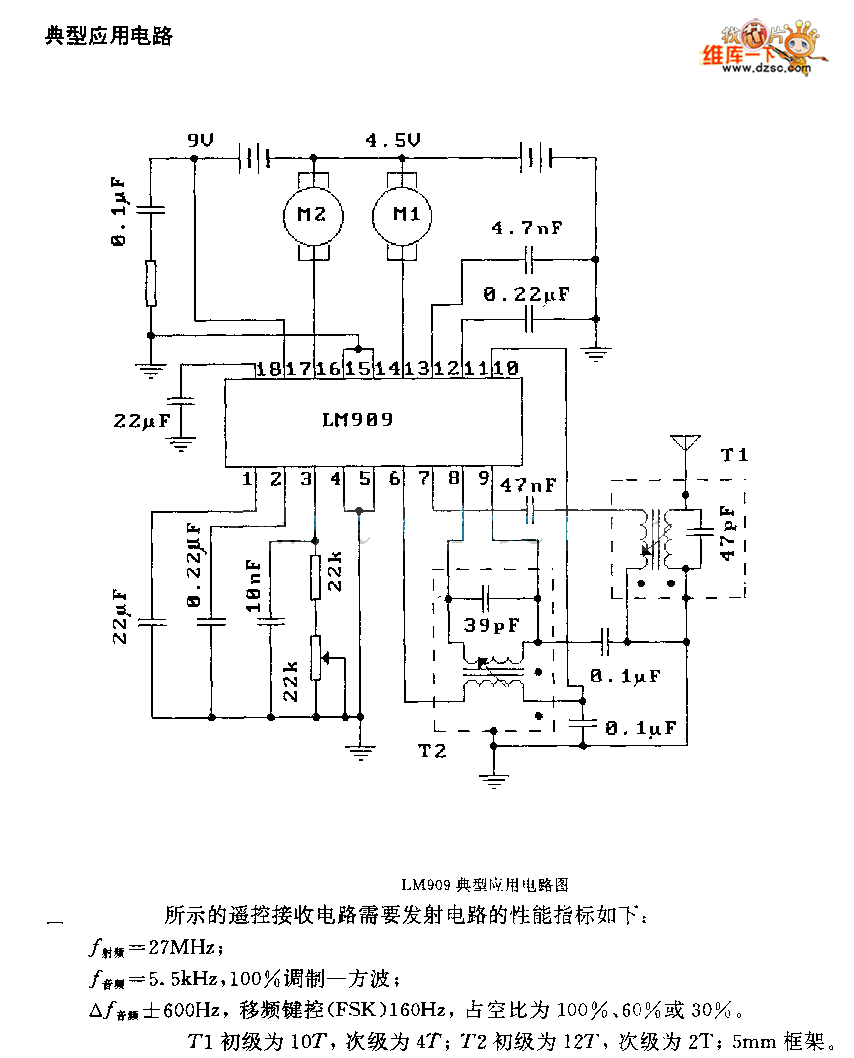
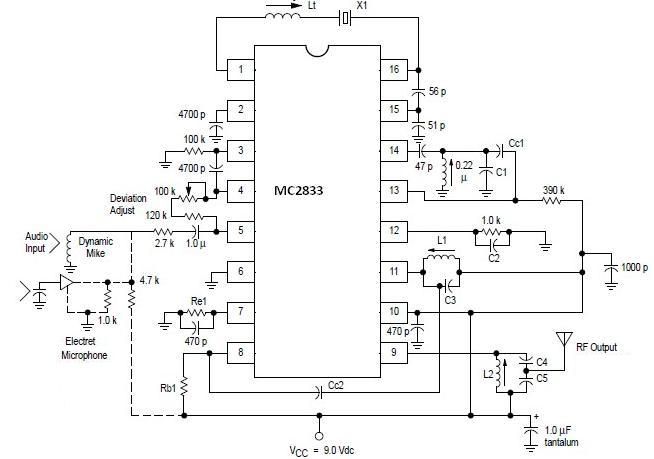
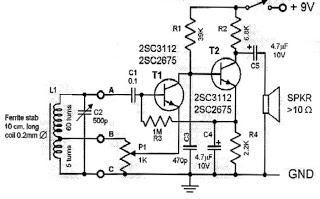
The performance indices of the telecontrol receiving decoding circuit are as follows: radio frequency (f) = 27 MHz, audio frequency (f) = 5.5 kHz, 100% modulation in square-wave form; radio frequency deviation is ±600 Hz, and the frequency shift keying (FSK) is 160 Hz. The duty factor can be set to 100%, 60%, or 30%. The primary winding of transformer T1 consists of 10 turns, while the secondary has 4 turns. Transformer T2 has a primary winding of 12 turns.
The telecontrol receiving decoding circuit is designed to operate at a radio frequency of 27 MHz, which is a common frequency for remote control applications. The audio frequency of 5.5 kHz indicates the frequency at which the audio signal is processed, allowing for effective communication between the transmitter and receiver. The circuit utilizes a square-wave modulation technique, achieving 100% modulation depth, which ensures that the transmitted signal maintains its integrity and is easily distinguishable from noise.
The circuit's frequency deviation of ±600 Hz indicates the range within which the carrier frequency can shift during operation, allowing for reliable signal detection. The use of frequency shift keying (FSK) at 160 Hz enables the transmission of binary data by shifting between two frequencies, which is essential for digital communication in telecontrol systems.
The duty factor, adjustable to 100%, 60%, or 30%, allows for variations in the on/off time of the transmitted signal, impacting the power consumption and responsiveness of the circuit. This flexibility is crucial for optimizing performance based on specific application requirements.
Transformers T1 and T2 play a vital role in the circuit's operation. T1, with a primary winding of 10 turns and a secondary winding of 4 turns, is likely used for impedance matching and signal coupling. The turns ratio of 2.5:1 suggests that the transformer steps down the voltage from the primary to the secondary side, which can be advantageous for interfacing with low-voltage circuits. T2, with a primary winding of 12 turns, serves a similar function, potentially providing additional signal conditioning or isolation.
Overall, the telecontrol receiving decoding circuit is engineered to ensure reliable communication and efficient signal processing, making it suitable for applications in remote control systems, wireless data transmission, and other related fields.The telecontrol receiving decoding circuit`s performance index shown as the chart are as follow: f radio frequency =27MHz, f audio frequency =5.5KHz, 100% modulation - square-wave; f radio frequency=±600Hz, and the frequency shift keying (FSK) is 160Hz, and the dutyfactor is 100%, 60% or 30%, T1`s primary is 10T, secondary is 4T; T2`s primary is 12T, second.. 🔗 External reference
The telecontrol receiving decoding circuit is designed to operate at a radio frequency of 27 MHz, which is a common frequency for remote control applications. The audio frequency of 5.5 kHz indicates the frequency at which the audio signal is processed, allowing for effective communication between the transmitter and receiver. The circuit utilizes a square-wave modulation technique, achieving 100% modulation depth, which ensures that the transmitted signal maintains its integrity and is easily distinguishable from noise.
The circuit's frequency deviation of ±600 Hz indicates the range within which the carrier frequency can shift during operation, allowing for reliable signal detection. The use of frequency shift keying (FSK) at 160 Hz enables the transmission of binary data by shifting between two frequencies, which is essential for digital communication in telecontrol systems.
The duty factor, adjustable to 100%, 60%, or 30%, allows for variations in the on/off time of the transmitted signal, impacting the power consumption and responsiveness of the circuit. This flexibility is crucial for optimizing performance based on specific application requirements.
Transformers T1 and T2 play a vital role in the circuit's operation. T1, with a primary winding of 10 turns and a secondary winding of 4 turns, is likely used for impedance matching and signal coupling. The turns ratio of 2.5:1 suggests that the transformer steps down the voltage from the primary to the secondary side, which can be advantageous for interfacing with low-voltage circuits. T2, with a primary winding of 12 turns, serves a similar function, potentially providing additional signal conditioning or isolation.
Overall, the telecontrol receiving decoding circuit is engineered to ensure reliable communication and efficient signal processing, making it suitable for applications in remote control systems, wireless data transmission, and other related fields.The telecontrol receiving decoding circuit`s performance index shown as the chart are as follow: f radio frequency =27MHz, f audio frequency =5.5KHz, 100% modulation - square-wave; f radio frequency=±600Hz, and the frequency shift keying (FSK) is 160Hz, and the dutyfactor is 100%, 60% or 30%, T1`s primary is 10T, secondary is 4T; T2`s primary is 12T, second.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713