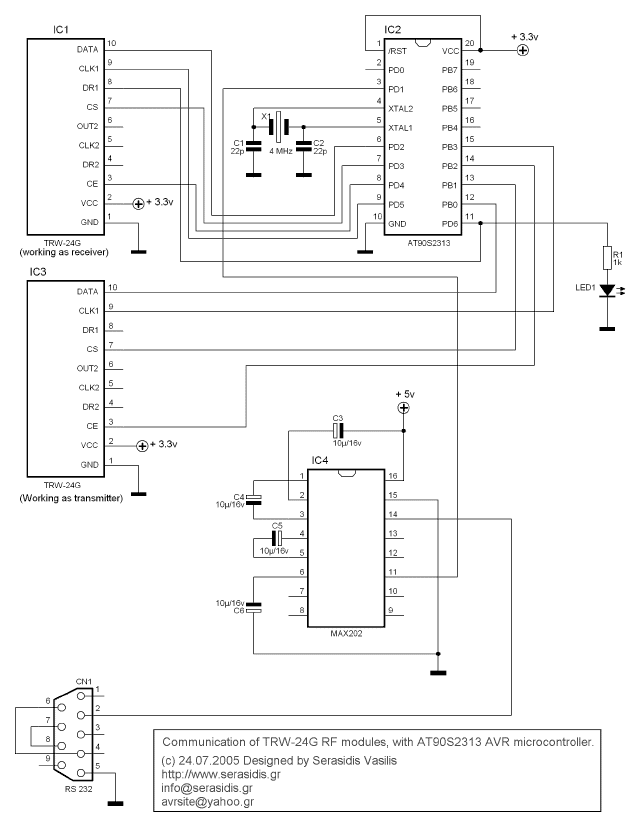
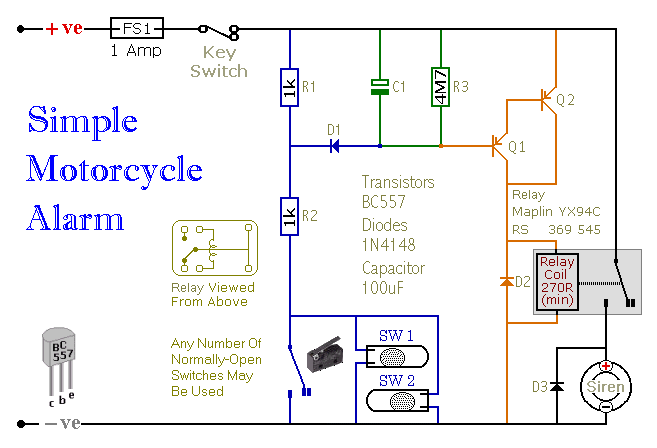
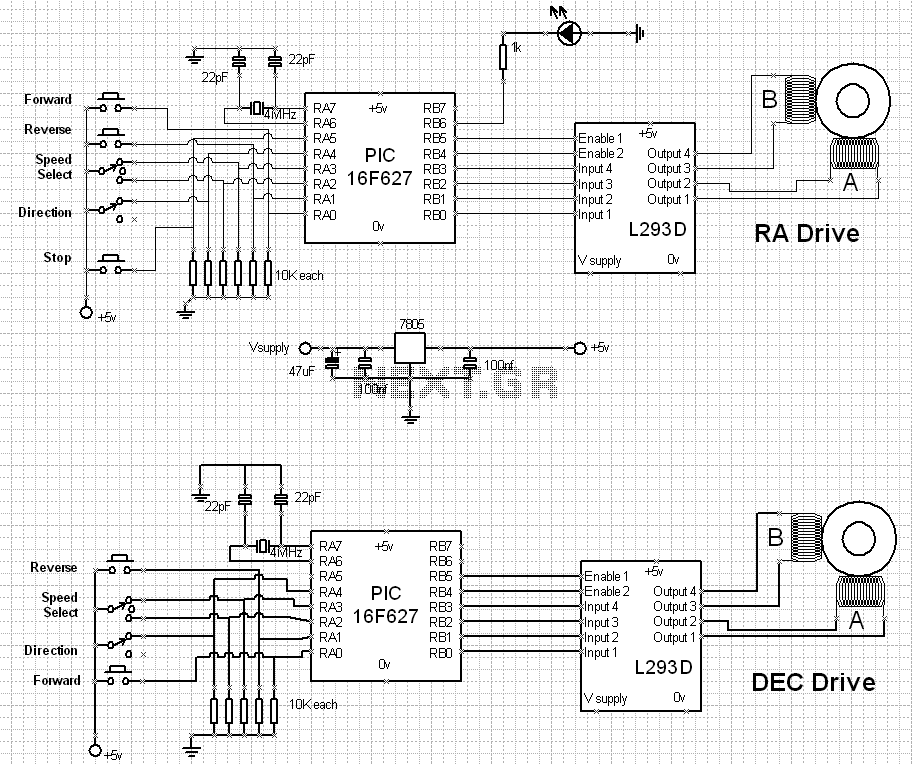
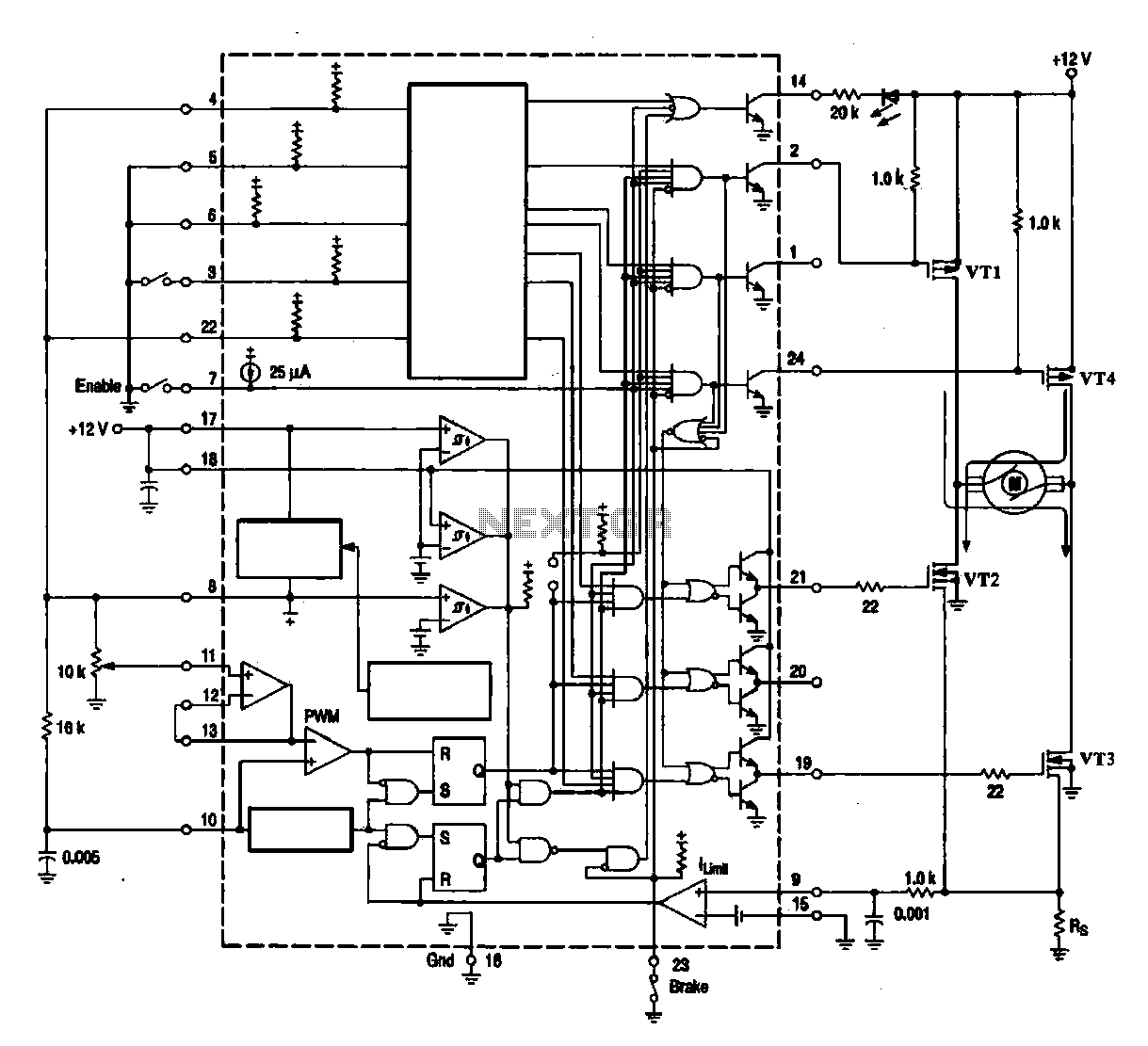
unipolar stepper motor controller
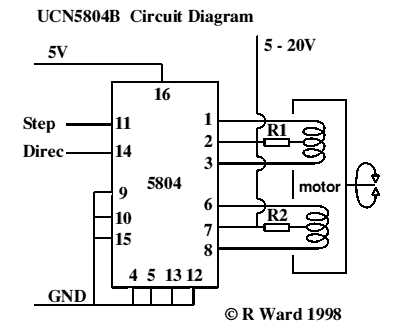
This integrated circuit is highly efficient and does not require any external glue logic for operation. It features two pins for motor control: one pin is dedicated to controlling the direction of the motor, while the other pin is used to trigger the stepping pulses. The design is compact and capable of driving 5, 6, or 8 wire stepper motors.
The integrated circuit in question is designed to facilitate the operation of stepper motors, which are commonly used in applications requiring precise control of angular position. The two control pins simplify the interface, eliminating the need for additional components typically required for motor control, such as logic gates or microcontroller outputs.
The direction control pin allows for easy reversal of the motor's rotation, enabling applications that require bidirectional movement. The pulse triggering pin generates the necessary stepping signals, which dictate the speed and position of the motor. By adjusting the frequency of the pulses sent to this pin, the speed of the stepper motor can be finely tuned to meet specific operational requirements.
This integrated circuit supports various configurations of stepper motors, including 5, 6, and 8 wire types. The ability to drive different motor configurations enhances its versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from robotics to CNC machinery. The compact nature of the design also contributes to space-saving in electronic assemblies, making it an ideal choice for modern, compact devices.
In summary, this integrated circuit provides an efficient and straightforward solution for driving stepper motors, offering enhanced control with minimal external circuitry. Its design allows for a seamless integration into various electronic systems, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications.This is a very good integrated circuit. There is no need for any external glue logic to drive the circuit, there is only 2 pins to drive the motor, one for controlling the direction and the other to trigger the stepping pulses. It provides a very compact design that drives 5 or 6 or 8 wire stepper motors.. 🔗 External reference
The integrated circuit in question is designed to facilitate the operation of stepper motors, which are commonly used in applications requiring precise control of angular position. The two control pins simplify the interface, eliminating the need for additional components typically required for motor control, such as logic gates or microcontroller outputs.
The direction control pin allows for easy reversal of the motor's rotation, enabling applications that require bidirectional movement. The pulse triggering pin generates the necessary stepping signals, which dictate the speed and position of the motor. By adjusting the frequency of the pulses sent to this pin, the speed of the stepper motor can be finely tuned to meet specific operational requirements.
This integrated circuit supports various configurations of stepper motors, including 5, 6, and 8 wire types. The ability to drive different motor configurations enhances its versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from robotics to CNC machinery. The compact nature of the design also contributes to space-saving in electronic assemblies, making it an ideal choice for modern, compact devices.
In summary, this integrated circuit provides an efficient and straightforward solution for driving stepper motors, offering enhanced control with minimal external circuitry. Its design allows for a seamless integration into various electronic systems, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications.This is a very good integrated circuit. There is no need for any external glue logic to drive the circuit, there is only 2 pins to drive the motor, one for controlling the direction and the other to trigger the stepping pulses. It provides a very compact design that drives 5 or 6 or 8 wire stepper motors.. 🔗 External reference