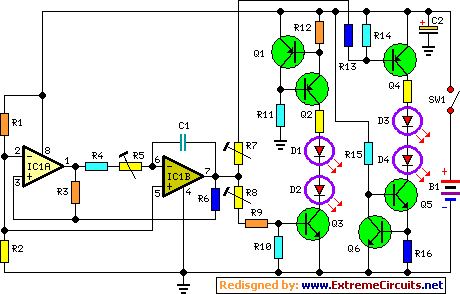
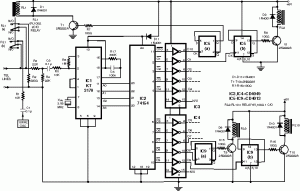
Unity-Gain Four-Input Audio Mixer Circuit

The circuit has four inputs. The voltage gain between each input and the output is maintained at unity by the relative values of the 470 kΩ input resistor and the 470 kΩ feedback resistor.
The described circuit operates as a voltage follower configuration, also known as a buffer amplifier. In this setup, the four inputs are connected to a single output, ensuring that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage without amplification or attenuation. The use of 470 kΩ resistors for both the input and feedback paths establishes a unity gain condition, which is critical for applications where signal integrity must be preserved.
In this configuration, each input can be treated as a separate channel, allowing for the simultaneous processing of multiple signals. The high resistance value of the input resistor (470 kΩ) minimizes the loading effect on the preceding stage, making it suitable for interfacing with high-impedance sources. The feedback resistor of the same value ensures that the operational amplifier remains in a stable state, providing consistent performance across all inputs.
The circuit's design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it ideal for applications in signal conditioning, sensor interfacing, and audio processing where maintaining the original signal level is paramount. The choice of resistors also helps to reduce power consumption while maintaining a high input impedance, which is an essential characteristic in many electronic systems.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to managing multiple input signals with high fidelity and minimal distortion. The circuit has four inputs. The voltage gain between each input and the output is held at unity by the relative values of the 470kH input resistor and the 470kQ feedback resistor. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a voltage follower configuration, also known as a buffer amplifier. In this setup, the four inputs are connected to a single output, ensuring that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage without amplification or attenuation. The use of 470 kΩ resistors for both the input and feedback paths establishes a unity gain condition, which is critical for applications where signal integrity must be preserved.
In this configuration, each input can be treated as a separate channel, allowing for the simultaneous processing of multiple signals. The high resistance value of the input resistor (470 kΩ) minimizes the loading effect on the preceding stage, making it suitable for interfacing with high-impedance sources. The feedback resistor of the same value ensures that the operational amplifier remains in a stable state, providing consistent performance across all inputs.
The circuit's design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it ideal for applications in signal conditioning, sensor interfacing, and audio processing where maintaining the original signal level is paramount. The choice of resistors also helps to reduce power consumption while maintaining a high input impedance, which is an essential characteristic in many electronic systems.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to managing multiple input signals with high fidelity and minimal distortion. The circuit has four inputs. The voltage gain between each input and the output is held at unity by the relative values of the 470kH input resistor and the 470kQ feedback resistor. 🔗 External reference