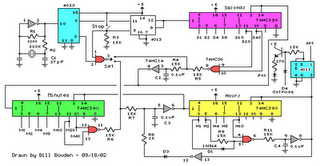
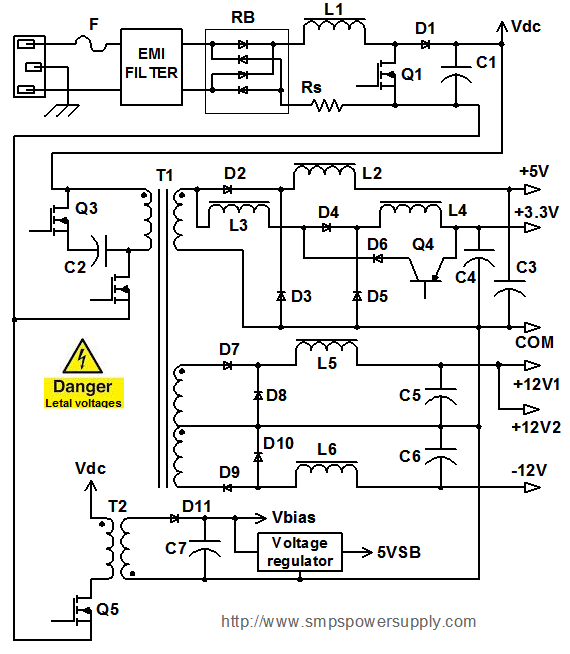
Universal Laboratory Power Supply Circuit
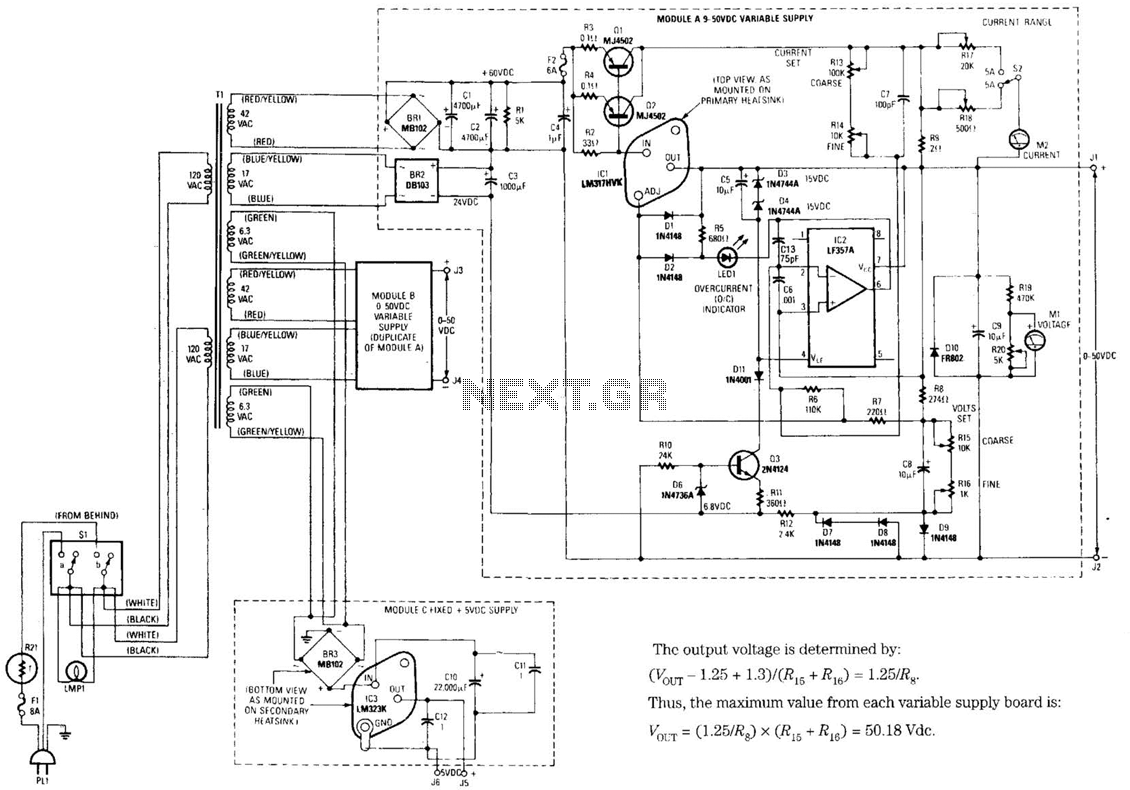
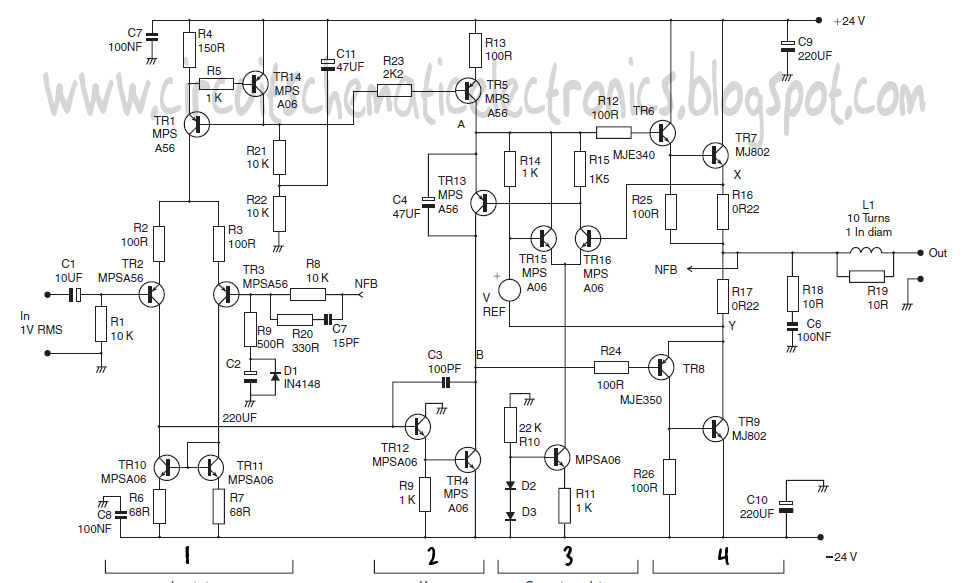
The design's value is derived from the use of IC1, an LM317HVK adjustable series-pass voltage regulator, which provides broad-range performance along with voltage-setting and current-limiting functions. The input to IC1 is sourced from the output of BR1, which is filtered by C1 and C2 to approximately +60 Vdc. Additionally, the input for the current-sense comparator IC2 is obtained from BR2, which also serves as a negative bias supply for regulation down to ground.
The circuit utilizes an LM317HVK voltage regulator, known for its versatility in providing adjustable output voltages and robust current-limiting capabilities. This component is essential for applications requiring a stable voltage supply over a wide range of input voltages. The input stage, represented by BR1, functions as a bridge rectifier, converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The filtering capacitors, C1 and C2, play a critical role in smoothing the rectified output, ensuring that the voltage presented to the LM317HVK is stable and within the operational limits.
The current-sense comparator IC2 is an integral part of the circuit, designed to monitor the output current and provide feedback for regulation purposes. The input from BR2 facilitates the generation of a negative bias voltage, which is crucial for certain configurations of the LM317HVK, particularly in applications where the output voltage needs to be regulated down to ground potential. This negative bias allows for enhanced control over the output voltage, ensuring that the system can maintain desired performance levels even under varying load conditions.
Overall, the combination of these components enables the design to achieve reliable voltage regulation and current limiting, making it suitable for various electronic applications where power management is critical. The value of the design lies in the use of IC1, an LM317HVK adjustable s.eries-pass voltage regulator, for broad-range performance remainder supplies voltage-setting and current-limiting functions. The input to ICI-comes from the output of BR1, which is filtered by CI and C2 to about +60 Vdc, and the input for current-sense comparator IC2 comes from BR2,
which also acts as a negative bias supply for regulation down to ground. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an LM317HVK voltage regulator, known for its versatility in providing adjustable output voltages and robust current-limiting capabilities. This component is essential for applications requiring a stable voltage supply over a wide range of input voltages. The input stage, represented by BR1, functions as a bridge rectifier, converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The filtering capacitors, C1 and C2, play a critical role in smoothing the rectified output, ensuring that the voltage presented to the LM317HVK is stable and within the operational limits.
The current-sense comparator IC2 is an integral part of the circuit, designed to monitor the output current and provide feedback for regulation purposes. The input from BR2 facilitates the generation of a negative bias voltage, which is crucial for certain configurations of the LM317HVK, particularly in applications where the output voltage needs to be regulated down to ground potential. This negative bias allows for enhanced control over the output voltage, ensuring that the system can maintain desired performance levels even under varying load conditions.
Overall, the combination of these components enables the design to achieve reliable voltage regulation and current limiting, making it suitable for various electronic applications where power management is critical. The value of the design lies in the use of IC1, an LM317HVK adjustable s.eries-pass voltage regulator, for broad-range performance remainder supplies voltage-setting and current-limiting functions. The input to ICI-comes from the output of BR1, which is filtered by CI and C2 to about +60 Vdc, and the input for current-sense comparator IC2 comes from BR2,
which also acts as a negative bias supply for regulation down to ground. 🔗 External reference