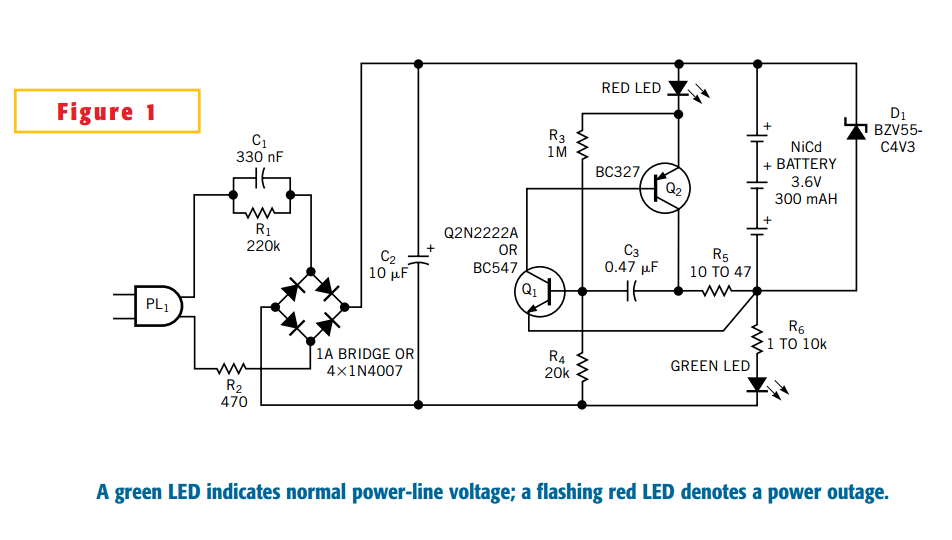
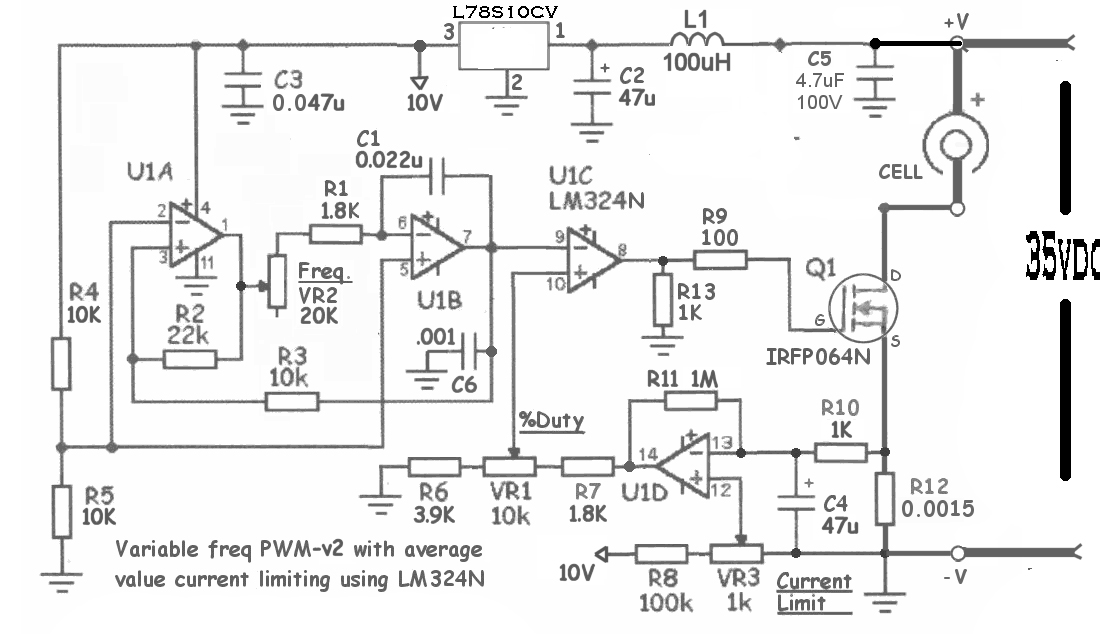
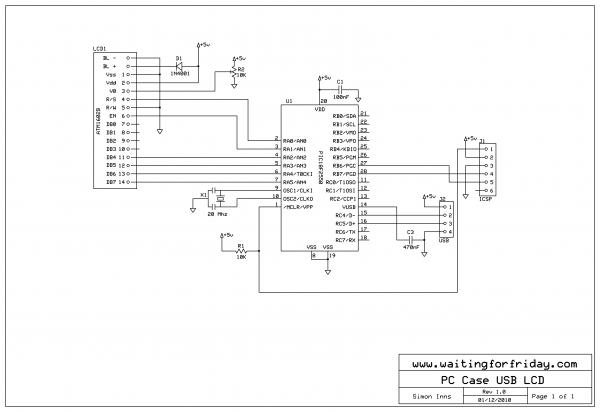
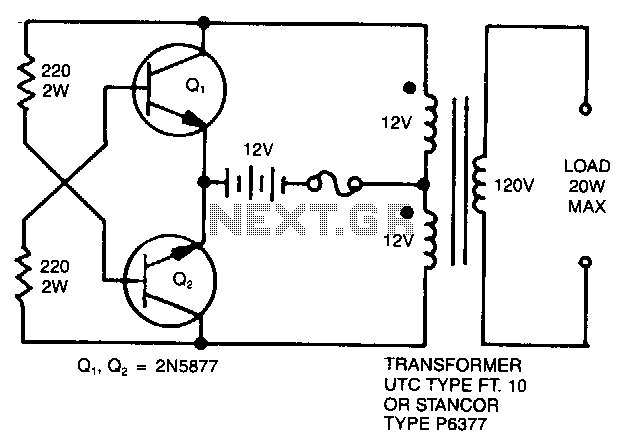
USB DC Power Supply from Cigar Lighter Socket
The diagram illustrates the circuit of a versatile USB power socket that safely converts 12V battery voltage into a stable 5V output. This circuit enables the use of various USB-powered devices.
The circuit design consists of several key components to ensure efficient voltage conversion and regulation. At the core of the circuit is a buck converter, which steps down the 12V input to the desired 5V output. The buck converter typically includes an inductor, a diode, and a switch (usually a transistor) that work together to regulate the output voltage.
The input voltage is first filtered through a capacitor to remove any high-frequency noise, ensuring a clean input signal for the buck converter. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it when the switch is open, allowing for a smooth transition and stable output voltage. The output is further stabilized by a capacitor that reduces voltage ripple, providing a consistent power supply for connected devices.
To protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions, a fuse or resettable polyfuse can be integrated into the design. This component disconnects the load in the event of excessive current flow, safeguarding both the circuit and the connected devices.
Additionally, the circuit may include a USB connector for easy interfacing with various devices. This connector typically consists of four pins: VBUS (5V), D- (data minus), D+ (data plus), and GND (ground). Proper pin configuration and connection are essential for ensuring compatibility with USB standards.
Overall, this USB power socket circuit is designed to provide a reliable and efficient power source for USB-powered devices, making it a valuable addition to applications requiring portable power solutions.The diagram shows the circuit of a versatile USB power socket that safely converts the 12V battery voltage into stable 5V. This circuit makes it possible t.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design consists of several key components to ensure efficient voltage conversion and regulation. At the core of the circuit is a buck converter, which steps down the 12V input to the desired 5V output. The buck converter typically includes an inductor, a diode, and a switch (usually a transistor) that work together to regulate the output voltage.
The input voltage is first filtered through a capacitor to remove any high-frequency noise, ensuring a clean input signal for the buck converter. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it when the switch is open, allowing for a smooth transition and stable output voltage. The output is further stabilized by a capacitor that reduces voltage ripple, providing a consistent power supply for connected devices.
To protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions, a fuse or resettable polyfuse can be integrated into the design. This component disconnects the load in the event of excessive current flow, safeguarding both the circuit and the connected devices.
Additionally, the circuit may include a USB connector for easy interfacing with various devices. This connector typically consists of four pins: VBUS (5V), D- (data minus), D+ (data plus), and GND (ground). Proper pin configuration and connection are essential for ensuring compatibility with USB standards.
Overall, this USB power socket circuit is designed to provide a reliable and efficient power source for USB-powered devices, making it a valuable addition to applications requiring portable power solutions.The diagram shows the circuit of a versatile USB power socket that safely converts the 12V battery voltage into stable 5V. This circuit makes it possible t.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713