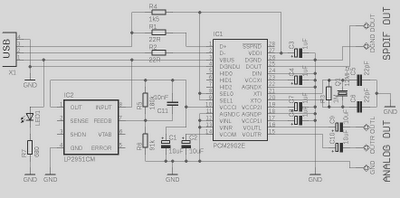
USB Fuse
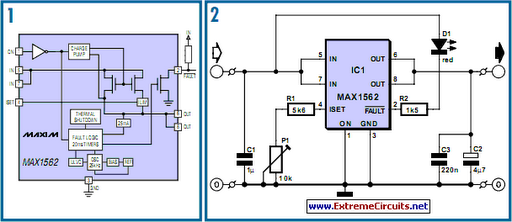
Life in the 21st century would be nearly unbearable without certain computer peripherals that PC users now consider essential. For instance, the USB-powered teacup warmer is an invaluable productivity tool for users, but it could potentially cause issues if the additional current it draws from the USB port leads to overheating on the motherboard. A similar problem could arise from a poorly wired connector during the prototyping and development of a USB peripheral. Therefore, a current limiting device or fuse is necessary to prevent damage to the motherboard. The MAX1562, as shown in Figure 1, is a dedicated USB current limiter manufactured by Maxim. This device operates with a supply voltage ranging from 4.0 to 5.5 V, with a typical operating current of 40 µA or 3 µA in standby mode. The circuit introduces a very low resistance in the power line (typically 26 mΩ, guaranteed to be less than 50 mΩ) through an internal MOSFET. The gate bias voltage for the FET is generated on-chip via a charge pump circuit. The chip can differentiate between an overload and a short circuit condition in the supply line by measuring the voltage drop across its internal resistance; if the voltage is less than 1 V, a short circuit is assumed, and the chip pulses a limited output current every 20 ms in an attempt to raise the output voltage. This method will succeed if the short circuit is due to a large capacitor across the USB supply pins or an external hard drive with a high inrush current at startup. If the supply rail is not restored within the first 20 ms, the FAULT output (pin 2) is driven low. The output current limit is determined by a single resistor connected to pin 4 (ISET): LIM = 17120 / RSET. The circuit diagram illustrates a fixed 5.6 kΩ resistor in series with a 10 kΩ preset resistor, allowing for an adjustable current limit between 1.097 A and 3.057 A. This range is adequate for most applications. Increasing the preset resistance reduces the current limit. Any intermittent connection in the preset (due to a dirty track, for example) will cause the chip to enter shutdown mode. The MAX1562 also features a thermal cutoff that disables the output when the chip temperature exceeds 160 degrees Celsius. Figure 2 depicts the manufacturer’s application circuit, where the FAULT output drives an LED through a series limiting resistor, reducing the LED current to 2 to 3 mA. The MAX1562 is available in two variants: a HESA version with an active high ON signal and an ESA version with an active low ON signal. The chip is housed in an 8-pin SMD package. Figure 3 presents a compact PCB layout for the circuit, utilizing primarily SMD components.
The MAX1562 is designed for integration into various USB-powered devices, ensuring that they operate safely without risking damage to the host system. The low power consumption during normal operation and standby mode makes it suitable for battery-operated devices as well. The internal MOSFET's low on-resistance minimizes power loss, enhancing the efficiency of the device.
The current limiting function is particularly critical in applications where multiple USB peripherals may be connected to a single port, as it prevents excessive current draw that could lead to thermal failure or damage. The adjustable current limit feature allows designers to tailor the device for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance while maintaining safety.
In terms of thermal management, the built-in thermal cutoff provides an additional layer of protection, making the MAX1562 a robust choice for applications where temperature fluctuations may occur. The visual feedback provided by the LED through the FAULT output offers a simple yet effective way for users to monitor the operational status of the device, enhancing user experience and reliability.
Overall, the MAX1562 is a versatile and essential component for modern USB-powered devices, combining functionality, safety, and efficiency in a compact package.Life in the 21st century would be almost unbearable without some of the computer peripherals that PC users now look on as essentials - take for example the USB powered teacup warmer; this device is obviously an invaluable productivity tool for all users but it could prove a little tire some if the extra current it draws from the USB port is suffic ient to produce a localised meltdown on the motherboard. In a slightly more serious vein a similar situation could result from a carelessly wired connector in the design lab during prototyping and development of a USB ported peripheral. What`s needed here is some form of current limiting or fuse to prevent damage to the motherboard. The MAX1562 shown in Figure 1 is a purpose-built USB current limiter from the chip manufacturers Maxim.
The device operates with a supply voltage from 4. 0 to 5. 5 V with an operating current of typically 40 µA or 3 µA in standby mode. The circuit introduces a very low resistance in the power line (typically 26 m but guaranteed less than 50 m) from an internal MOSFET. The FET gate bias voltage is generated on-chip from a charge pump circuit. The chip can distinguish between an overload and a short circuit condition in the supply line by measuring the voltage drop across its internal resistance; if the voltage is less than 1 V a short circuit is assumed and the chip pulses a (limited) output current every 20 ms in an effort to raise the output voltage.
This approach will eventually be successful if the short circuit was caused by a large value capacitor across the USB supply pins or an external hard drive which have a high in-rush at start up. If the supply rail is not pulled up within the first 20 ms the FAULT output (pin 2) is driven low. The output current limit is set by a single resistor on pin 4 (ISET): LIM = 17120 / RSET. The circuit diagram shows a fixed 5. 6k resistor in series with a 10k preset giving an adjustable current limit between 1. 097 and 3. 057 A. This range should be sufficient for the majority of applications. Increasing the preset resistance reduces the current limit level. Any intermittent connection in the preset (caused by a dirty track etc. ) will switch the chip into shut down. The MAX1562 also contains a thermal cut out which turns off the output when the chip temperature exceeds 160 degrees C.
Figure 2 shows a diagram of the manufacturer`s application circuit. The FAULT output drives an LED via a series limiting resistor which reduces the LED current to 2 to 3 mA. The MAX1562 is available in a HESA variant (with an active high ON signal) or ESA version (with an active low ON signal).
The chip is packaged in an 8-pin SMD outline. Figure 3 shows a small PCB layout for the circuit using mostly SMD components. 🔗 External reference
The MAX1562 is designed for integration into various USB-powered devices, ensuring that they operate safely without risking damage to the host system. The low power consumption during normal operation and standby mode makes it suitable for battery-operated devices as well. The internal MOSFET's low on-resistance minimizes power loss, enhancing the efficiency of the device.
The current limiting function is particularly critical in applications where multiple USB peripherals may be connected to a single port, as it prevents excessive current draw that could lead to thermal failure or damage. The adjustable current limit feature allows designers to tailor the device for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance while maintaining safety.
In terms of thermal management, the built-in thermal cutoff provides an additional layer of protection, making the MAX1562 a robust choice for applications where temperature fluctuations may occur. The visual feedback provided by the LED through the FAULT output offers a simple yet effective way for users to monitor the operational status of the device, enhancing user experience and reliability.
Overall, the MAX1562 is a versatile and essential component for modern USB-powered devices, combining functionality, safety, and efficiency in a compact package.Life in the 21st century would be almost unbearable without some of the computer peripherals that PC users now look on as essentials - take for example the USB powered teacup warmer; this device is obviously an invaluable productivity tool for all users but it could prove a little tire some if the extra current it draws from the USB port is suffic ient to produce a localised meltdown on the motherboard. In a slightly more serious vein a similar situation could result from a carelessly wired connector in the design lab during prototyping and development of a USB ported peripheral. What`s needed here is some form of current limiting or fuse to prevent damage to the motherboard. The MAX1562 shown in Figure 1 is a purpose-built USB current limiter from the chip manufacturers Maxim.
The device operates with a supply voltage from 4. 0 to 5. 5 V with an operating current of typically 40 µA or 3 µA in standby mode. The circuit introduces a very low resistance in the power line (typically 26 m but guaranteed less than 50 m) from an internal MOSFET. The FET gate bias voltage is generated on-chip from a charge pump circuit. The chip can distinguish between an overload and a short circuit condition in the supply line by measuring the voltage drop across its internal resistance; if the voltage is less than 1 V a short circuit is assumed and the chip pulses a (limited) output current every 20 ms in an effort to raise the output voltage.
This approach will eventually be successful if the short circuit was caused by a large value capacitor across the USB supply pins or an external hard drive which have a high in-rush at start up. If the supply rail is not pulled up within the first 20 ms the FAULT output (pin 2) is driven low. The output current limit is set by a single resistor on pin 4 (ISET): LIM = 17120 / RSET. The circuit diagram shows a fixed 5. 6k resistor in series with a 10k preset giving an adjustable current limit between 1. 097 and 3. 057 A. This range should be sufficient for the majority of applications. Increasing the preset resistance reduces the current limit level. Any intermittent connection in the preset (caused by a dirty track etc. ) will switch the chip into shut down. The MAX1562 also contains a thermal cut out which turns off the output when the chip temperature exceeds 160 degrees C.
Figure 2 shows a diagram of the manufacturer`s application circuit. The FAULT output drives an LED via a series limiting resistor which reduces the LED current to 2 to 3 mA. The MAX1562 is available in a HESA variant (with an active high ON signal) or ESA version (with an active low ON signal).
The chip is packaged in an 8-pin SMD outline. Figure 3 shows a small PCB layout for the circuit using mostly SMD components. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713