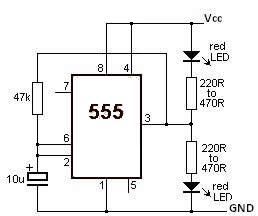
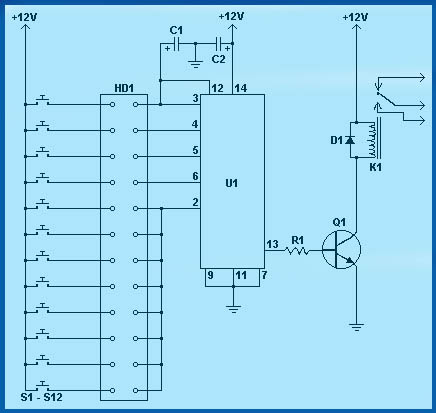
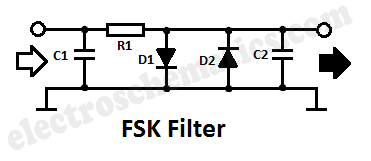
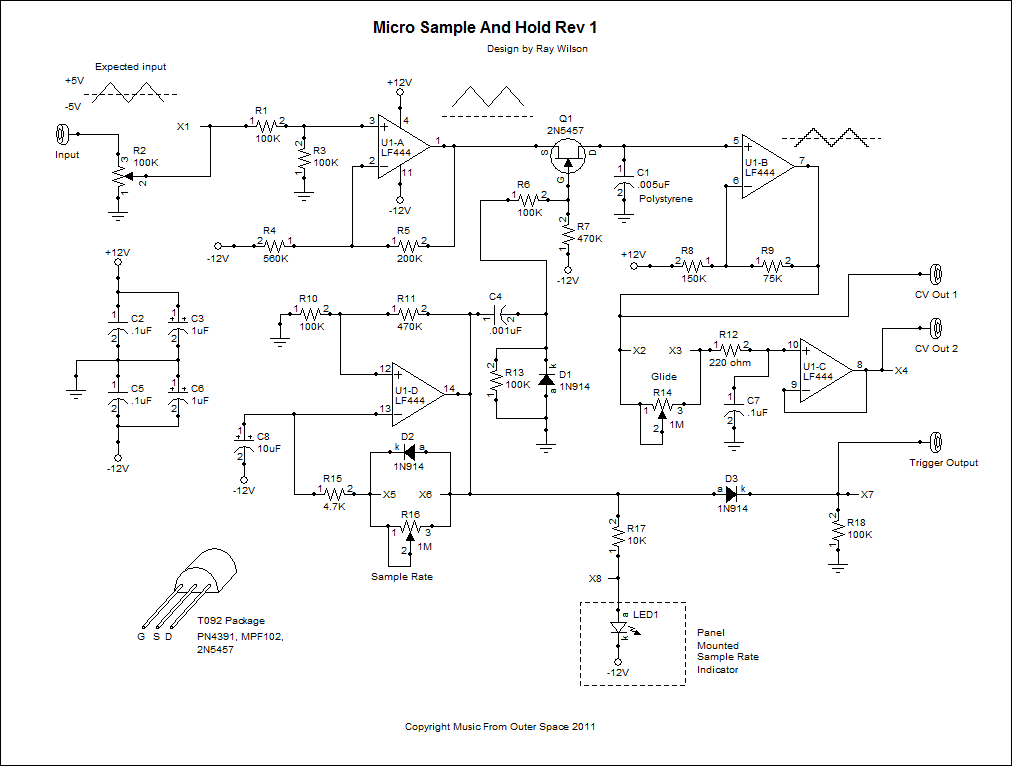
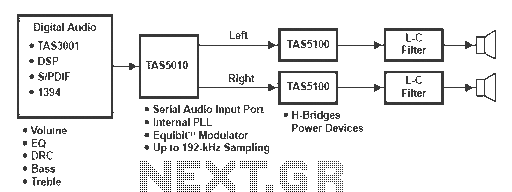
Use SR9F26C ordinary language learning machine tape recorder and circuit diagram
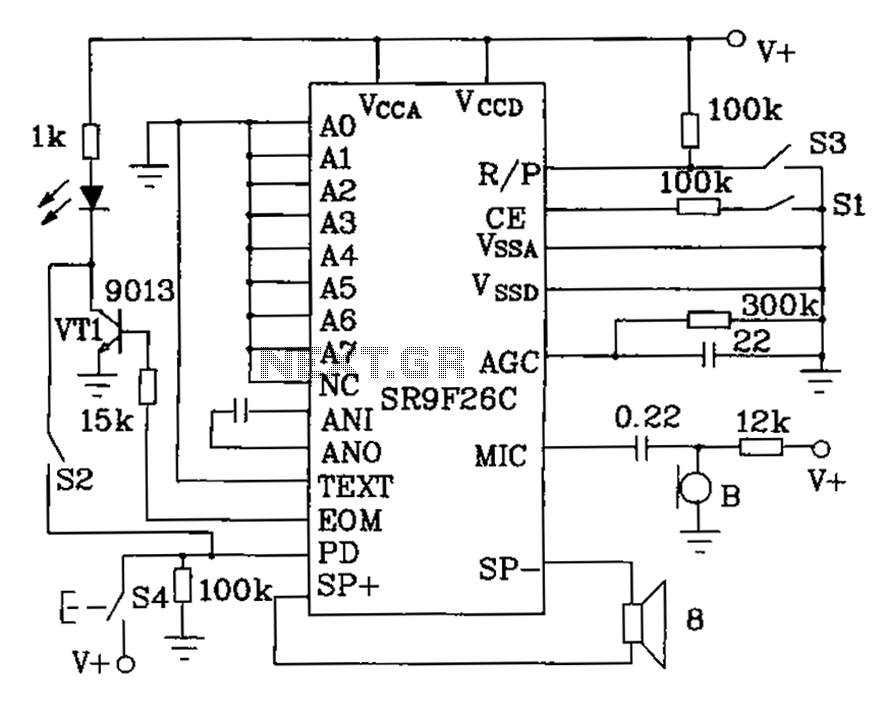
Basic features include an internal 512k-bit EEPROM, allowing for continuous recording and playback at any time, with long-term retention of voice data after power loss. The voice recording time is 20 seconds, and it supports segmented recording and playback. The device comes in a 28-foot flat package, with a chip area of 1mm x 16mm. The pinout diagram for the SR9F26C is also available.
The SR9F26C is a versatile audio recording and playback chip designed for applications requiring reliable long-term data retention. The internal 512k-bit EEPROM provides ample storage for audio data, enabling users to record up to 20 seconds of voice. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as voice recorders, alarm systems, and interactive devices where audio feedback is essential.
The segmented recording capability allows for the storage of multiple audio snippets, which can be played back in sequence or individually, enhancing the chip's utility in complex audio applications. The playback function is designed to be straightforward, ensuring that audio can be accessed and played back with minimal delay.
The physical dimensions of the chip, housed in a 28-foot flat package measuring 1mm by 16mm, make it suitable for compact electronic designs where space is at a premium. The pinout diagram provides detailed information on the connections required for integration into a circuit, facilitating ease of use for engineers and designers.
Overall, the SR9F26C is an efficient solution for embedded systems requiring audio functionality, combining compact size with robust performance features for seamless integration into various electronic projects. Basic features: O internal containing 512k bit EEPROM, you can always recording, playback at any time, long-term retention after power voice. Voice recording time is 20s. can b e segmented recording, playback. 28 feet flat package, the chip area is 1mm 16rnm. SR9F26C pinout diagram.
The SR9F26C is a versatile audio recording and playback chip designed for applications requiring reliable long-term data retention. The internal 512k-bit EEPROM provides ample storage for audio data, enabling users to record up to 20 seconds of voice. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as voice recorders, alarm systems, and interactive devices where audio feedback is essential.
The segmented recording capability allows for the storage of multiple audio snippets, which can be played back in sequence or individually, enhancing the chip's utility in complex audio applications. The playback function is designed to be straightforward, ensuring that audio can be accessed and played back with minimal delay.
The physical dimensions of the chip, housed in a 28-foot flat package measuring 1mm by 16mm, make it suitable for compact electronic designs where space is at a premium. The pinout diagram provides detailed information on the connections required for integration into a circuit, facilitating ease of use for engineers and designers.
Overall, the SR9F26C is an efficient solution for embedded systems requiring audio functionality, combining compact size with robust performance features for seamless integration into various electronic projects. Basic features: O internal containing 512k bit EEPROM, you can always recording, playback at any time, long-term retention after power voice. Voice recording time is 20s. can b e segmented recording, playback. 28 feet flat package, the chip area is 1mm 16rnm. SR9F26C pinout diagram.