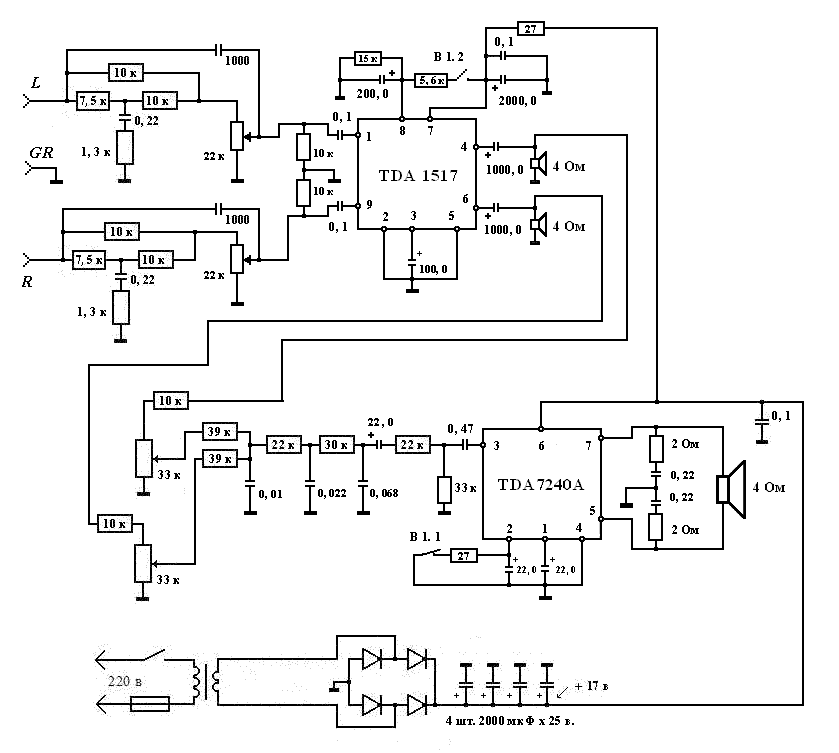
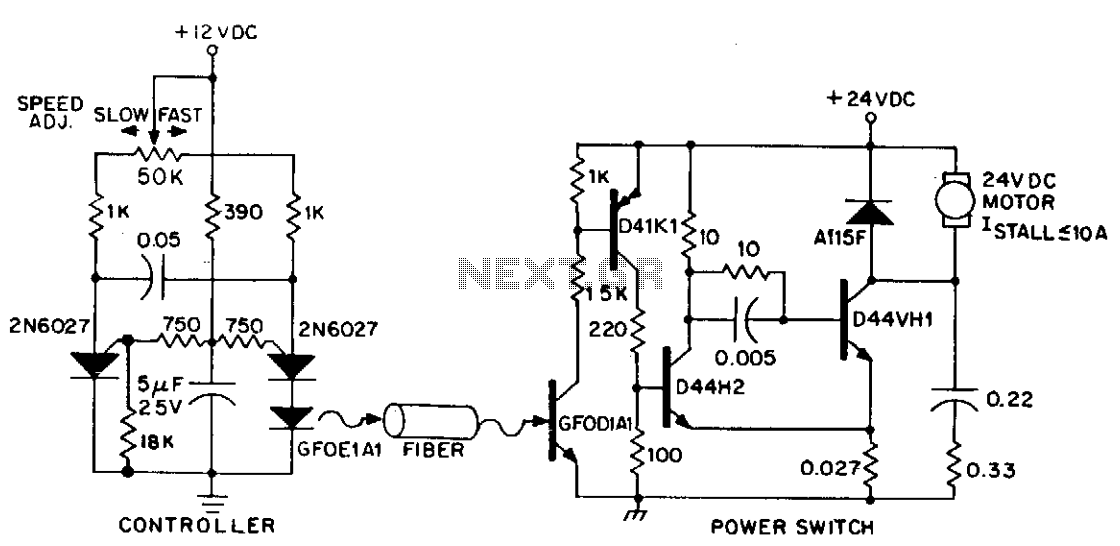
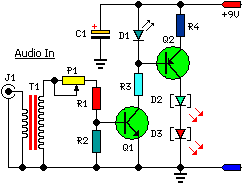
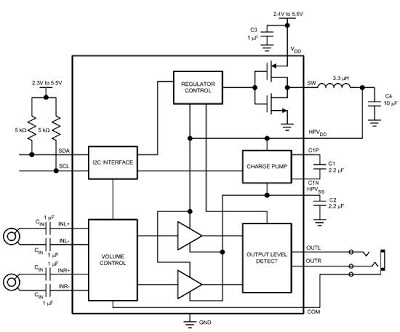
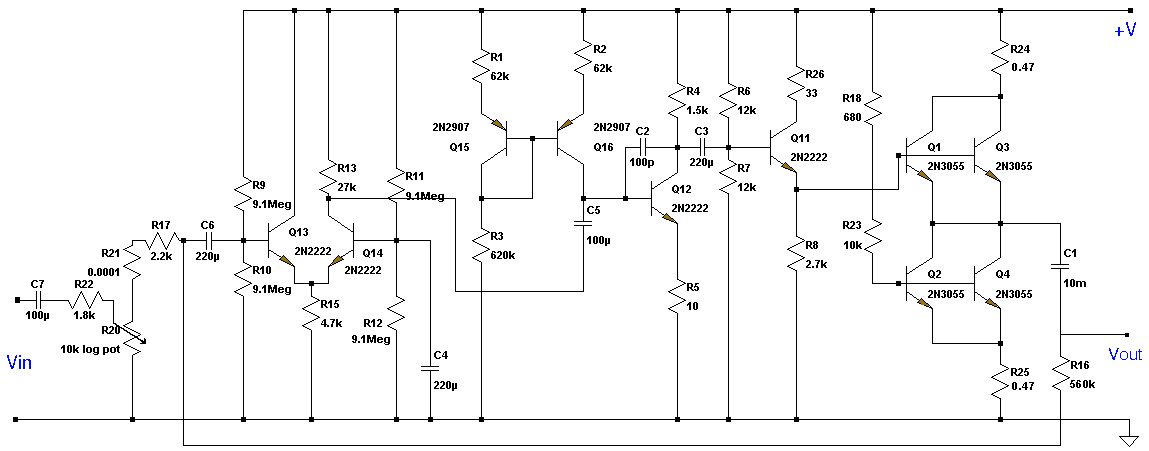
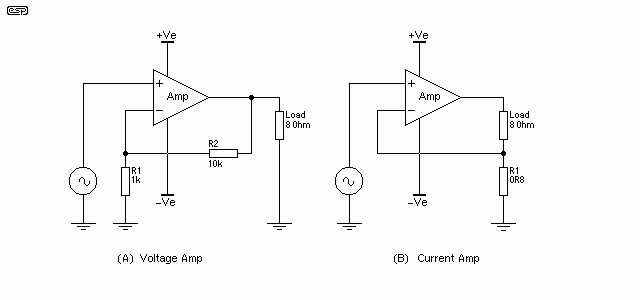
Variable Amplifier Impedance
Not so much a real project as a field day for experimenters, this article describes the methods you can use to tailor an amplifier to a specific driver. Much is empirical (i.e. design by experiment, trial and error), and although formulae are possible, the load presented by a typical loudspeaker is very complex and leaves big holes in the final result if the maths are allowed to take over. Having said that, good results can be obtained by either method (theoretical or practical), so here goes
The described project focuses on the adaptation of an audio amplifier to match the characteristics of a specific loudspeaker driver. This process is essential in audio engineering, as the performance of an audio system can be significantly improved by ensuring that the amplifier and speaker are compatible.
The methodology involves both empirical techniques and theoretical calculations. The empirical approach relies on experimentation and iterative testing, allowing the designer to observe the effects of various configurations and component choices on the sound output. This may include adjusting gain settings, feedback loops, and the frequency response of the amplifier to better match the loudspeaker's impedance and sensitivity.
Theoretical calculations, while important, can be challenging due to the complex nature of loudspeaker loads. Loudspeakers do not present a purely resistive load; they exhibit reactive components that can vary with frequency. Therefore, traditional circuit analysis methods may not yield accurate predictions of performance. Instead, a more practical approach may involve using simulation software to model the amplifier-loudspeaker interaction or directly measuring the response during testing.
Key components in the amplifier design may include transistors or operational amplifiers for signal amplification, capacitors for filtering, and resistors for setting gain and biasing. Additionally, attention must be given to the power supply, as ensuring adequate voltage and current delivery is crucial for optimal performance.
Overall, the successful tailoring of an amplifier to a specific loudspeaker driver requires a balance of theoretical understanding and practical experimentation, allowing for adjustments that lead to enhanced audio fidelity and performance.Not so much a real project as a field day for experimenters, this article describes the methods you can use to tailor an amplifier to a specific driver. Much is empirical (i.e. design by experiment, trial and error), and although formulae are possible, the load presented by a typical loudspeaker is very complex and leaves big holes in the final result if the maths are allowed to take over.
Having said that, good results can be obtained by either method (theoretical or practical), so here goes 🔗 External reference
The described project focuses on the adaptation of an audio amplifier to match the characteristics of a specific loudspeaker driver. This process is essential in audio engineering, as the performance of an audio system can be significantly improved by ensuring that the amplifier and speaker are compatible.
The methodology involves both empirical techniques and theoretical calculations. The empirical approach relies on experimentation and iterative testing, allowing the designer to observe the effects of various configurations and component choices on the sound output. This may include adjusting gain settings, feedback loops, and the frequency response of the amplifier to better match the loudspeaker's impedance and sensitivity.
Theoretical calculations, while important, can be challenging due to the complex nature of loudspeaker loads. Loudspeakers do not present a purely resistive load; they exhibit reactive components that can vary with frequency. Therefore, traditional circuit analysis methods may not yield accurate predictions of performance. Instead, a more practical approach may involve using simulation software to model the amplifier-loudspeaker interaction or directly measuring the response during testing.
Key components in the amplifier design may include transistors or operational amplifiers for signal amplification, capacitors for filtering, and resistors for setting gain and biasing. Additionally, attention must be given to the power supply, as ensuring adequate voltage and current delivery is crucial for optimal performance.
Overall, the successful tailoring of an amplifier to a specific loudspeaker driver requires a balance of theoretical understanding and practical experimentation, allowing for adjustments that lead to enhanced audio fidelity and performance.Not so much a real project as a field day for experimenters, this article describes the methods you can use to tailor an amplifier to a specific driver. Much is empirical (i.e. design by experiment, trial and error), and although formulae are possible, the load presented by a typical loudspeaker is very complex and leaves big holes in the final result if the maths are allowed to take over.
Having said that, good results can be obtained by either method (theoretical or practical), so here goes 🔗 External reference