Various protection circuit structure and working principle diagram
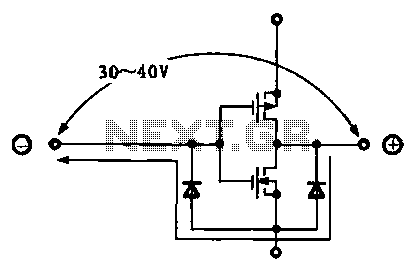
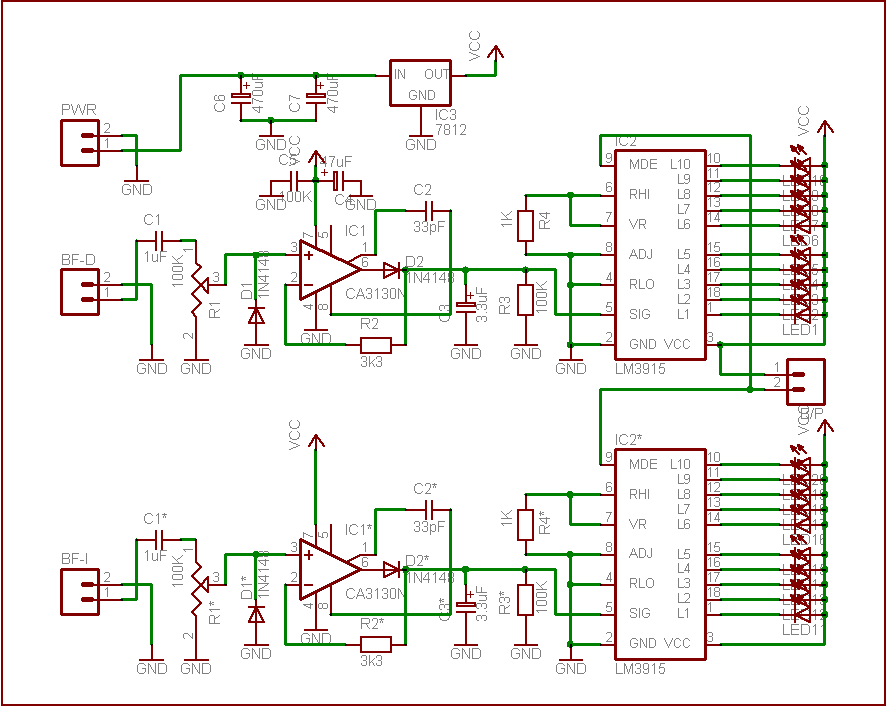
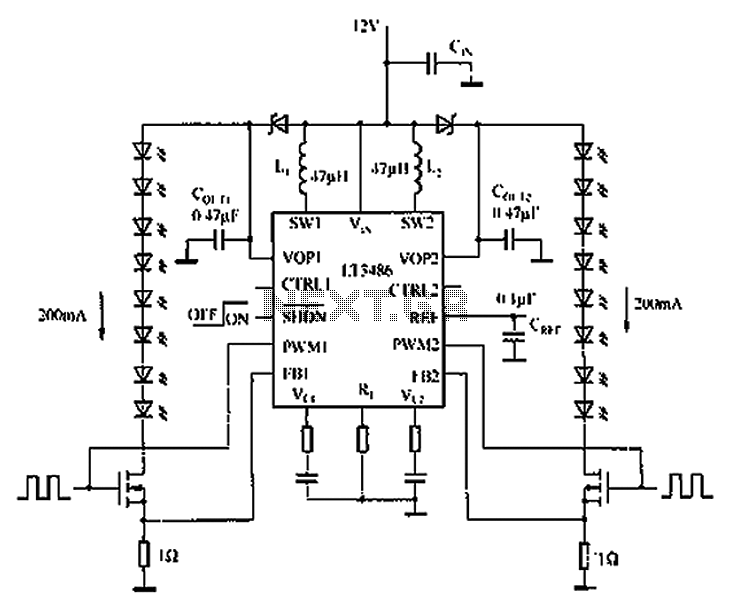
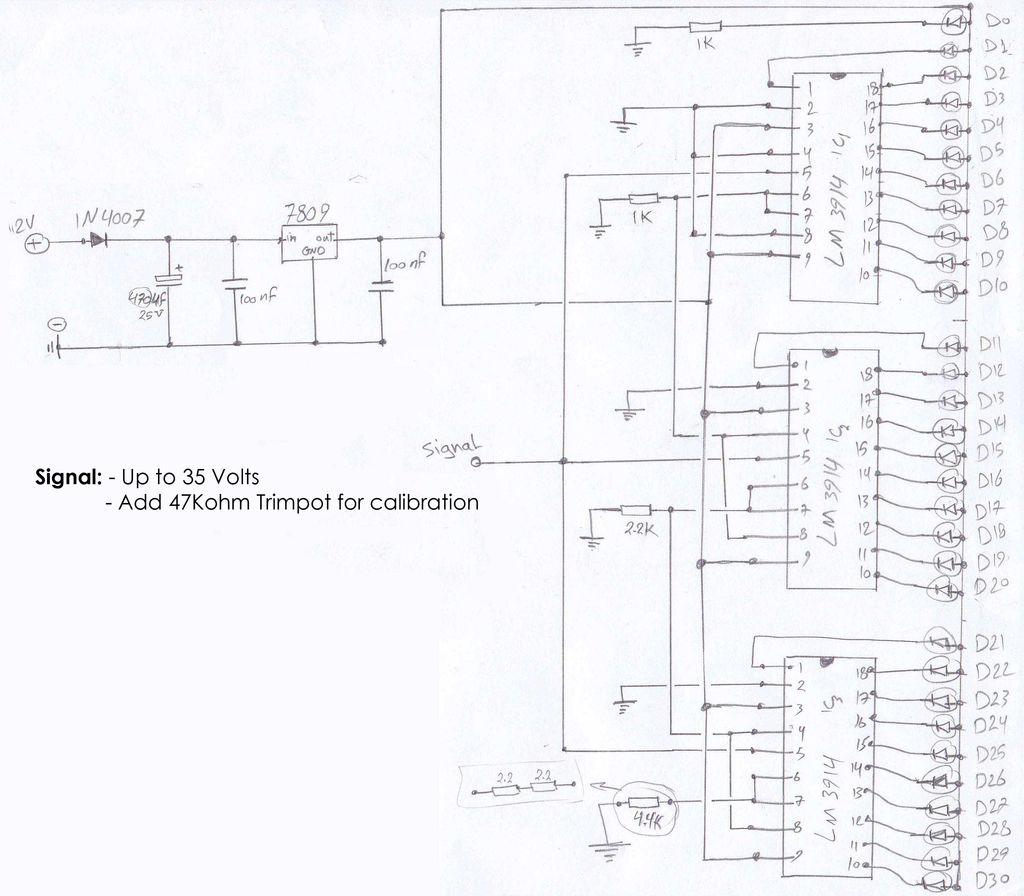
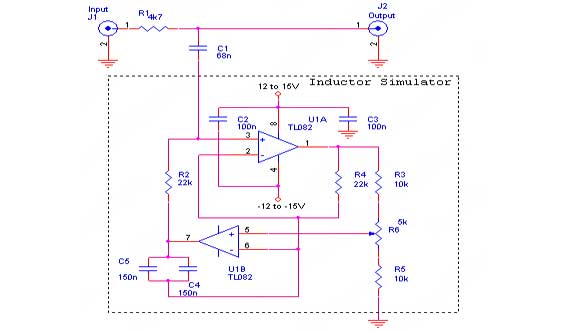
Due to the varying conditions of different input signals, when an abnormal voltage is applied to the pin, protection circuits are designed to create a circuit path that secures the internal protection of large-scale integration (LSI) circuits. The structure and principles of this protection circuit are illustrated.
The protection circuit for LSI devices is essential for safeguarding the integrity of the integrated circuit against voltage spikes and other anomalies that may occur during operation. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including diodes, resistors, and capacitors, which work together to divert excess voltage away from sensitive components.
When an abnormal voltage is detected at the input pin, the protection circuit activates. Diodes are often employed in a clamping configuration to redirect excessive voltage to ground, effectively limiting the voltage that reaches the LSI. This prevents damage that could result from transient voltages or electrostatic discharge (ESD).
The resistors in the circuit can serve multiple purposes, such as current limiting and voltage division, ensuring that the voltage levels remain within safe operating ranges. Capacitors may also be included to filter out high-frequency noise, providing additional stability to the circuit.
Overall, the design of the protection circuit must take into account the specific voltage levels and signal characteristics of the application. Proper selection of components and configuration is crucial to ensure reliable operation and to extend the lifespan of the LSI device. This protective mechanism is a vital aspect of modern electronic design, particularly in environments where signal integrity and reliability are paramount.Due to the different circumstances of the various input signals, when the pin is applied between the abnormal voltage, protection circuits to form a circuit path from while LSI (large scale integration) circuits internal protection. Structure and principles of its protection circuit is shown
The protection circuit for LSI devices is essential for safeguarding the integrity of the integrated circuit against voltage spikes and other anomalies that may occur during operation. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including diodes, resistors, and capacitors, which work together to divert excess voltage away from sensitive components.
When an abnormal voltage is detected at the input pin, the protection circuit activates. Diodes are often employed in a clamping configuration to redirect excessive voltage to ground, effectively limiting the voltage that reaches the LSI. This prevents damage that could result from transient voltages or electrostatic discharge (ESD).
The resistors in the circuit can serve multiple purposes, such as current limiting and voltage division, ensuring that the voltage levels remain within safe operating ranges. Capacitors may also be included to filter out high-frequency noise, providing additional stability to the circuit.
Overall, the design of the protection circuit must take into account the specific voltage levels and signal characteristics of the application. Proper selection of components and configuration is crucial to ensure reliable operation and to extend the lifespan of the LSI device. This protective mechanism is a vital aspect of modern electronic design, particularly in environments where signal integrity and reliability are paramount.Due to the different circumstances of the various input signals, when the pin is applied between the abnormal voltage, protection circuits to form a circuit path from while LSI (large scale integration) circuits internal protection. Structure and principles of its protection circuit is shown