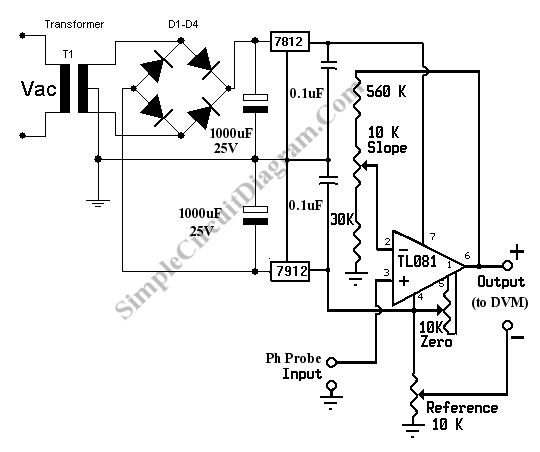
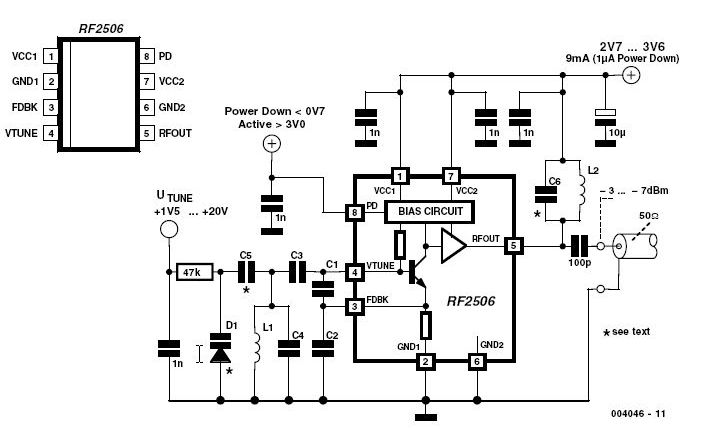
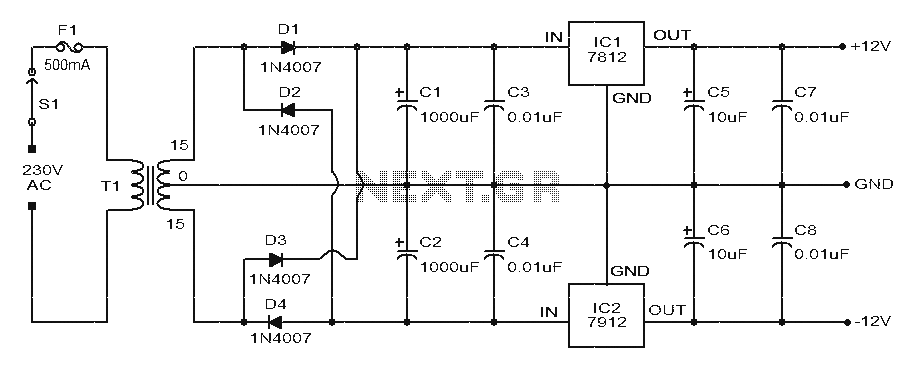
Very Low Distortion Oscillator
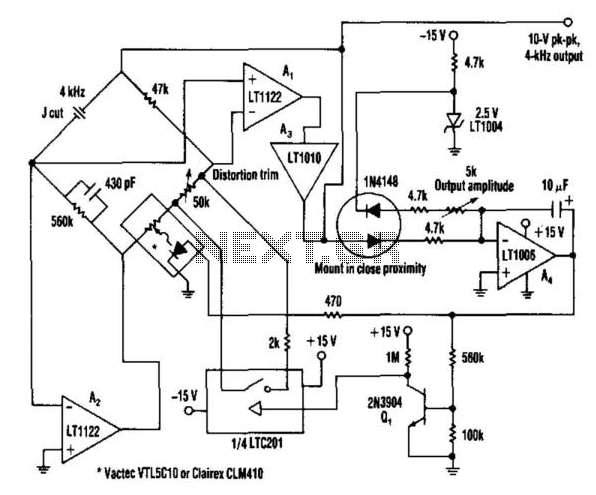
This oscillator utilizes a bridge circuit with an optoisolator functioning as a gain-control device. The resultant distortion can be maintained at 9 ppm (0.0009%) with appropriate adjustments.
The oscillator circuit described operates using a bridge configuration, which is a common approach in precision applications. The bridge circuit typically consists of four resistive components arranged in a diamond shape, allowing for the measurement of voltage differences that can be used to control the output signal. In this specific design, an optoisolator is integrated into the bridge, serving as a gain-control device.
Optoisolators, also known as optocouplers, are crucial in providing electrical isolation between different parts of a circuit while allowing signal transfer. This isolation is particularly beneficial in preventing ground loops and protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes or noise from other parts of the system.
The gain-control feature is essential for maintaining low distortion levels in the oscillator's output. Distortion, measured in parts per million (ppm), indicates the degree to which the output deviates from a pure sine wave. In this case, the design achieves an impressive distortion level of 9 ppm (0.0009%) through careful calibration and adjustment of the circuit parameters.
To achieve such low distortion, it is vital to select high-precision components and implement a robust feedback mechanism within the oscillator. The feedback loop can help stabilize the gain and ensure consistent performance over varying operating conditions. Additionally, the adjustment process may involve tuning the resistive elements in the bridge or modifying the characteristics of the optoisolator to optimize the gain and minimize any potential distortion.
Overall, this oscillator design exemplifies the integration of advanced components and techniques to achieve high performance in electronic signal generation, making it suitable for applications requiring precise frequency stability and low distortion. This oscillator uses a bridge circuit with an optoisolator as a gain-control device. The resultant distortio n can be held to 9 ppm (.000 9%) with proper adjustment.
The oscillator circuit described operates using a bridge configuration, which is a common approach in precision applications. The bridge circuit typically consists of four resistive components arranged in a diamond shape, allowing for the measurement of voltage differences that can be used to control the output signal. In this specific design, an optoisolator is integrated into the bridge, serving as a gain-control device.
Optoisolators, also known as optocouplers, are crucial in providing electrical isolation between different parts of a circuit while allowing signal transfer. This isolation is particularly beneficial in preventing ground loops and protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes or noise from other parts of the system.
The gain-control feature is essential for maintaining low distortion levels in the oscillator's output. Distortion, measured in parts per million (ppm), indicates the degree to which the output deviates from a pure sine wave. In this case, the design achieves an impressive distortion level of 9 ppm (0.0009%) through careful calibration and adjustment of the circuit parameters.
To achieve such low distortion, it is vital to select high-precision components and implement a robust feedback mechanism within the oscillator. The feedback loop can help stabilize the gain and ensure consistent performance over varying operating conditions. Additionally, the adjustment process may involve tuning the resistive elements in the bridge or modifying the characteristics of the optoisolator to optimize the gain and minimize any potential distortion.
Overall, this oscillator design exemplifies the integration of advanced components and techniques to achieve high performance in electronic signal generation, making it suitable for applications requiring precise frequency stability and low distortion. This oscillator uses a bridge circuit with an optoisolator as a gain-control device. The resultant distortio n can be held to 9 ppm (.000 9%) with proper adjustment.