Very low frequency generator
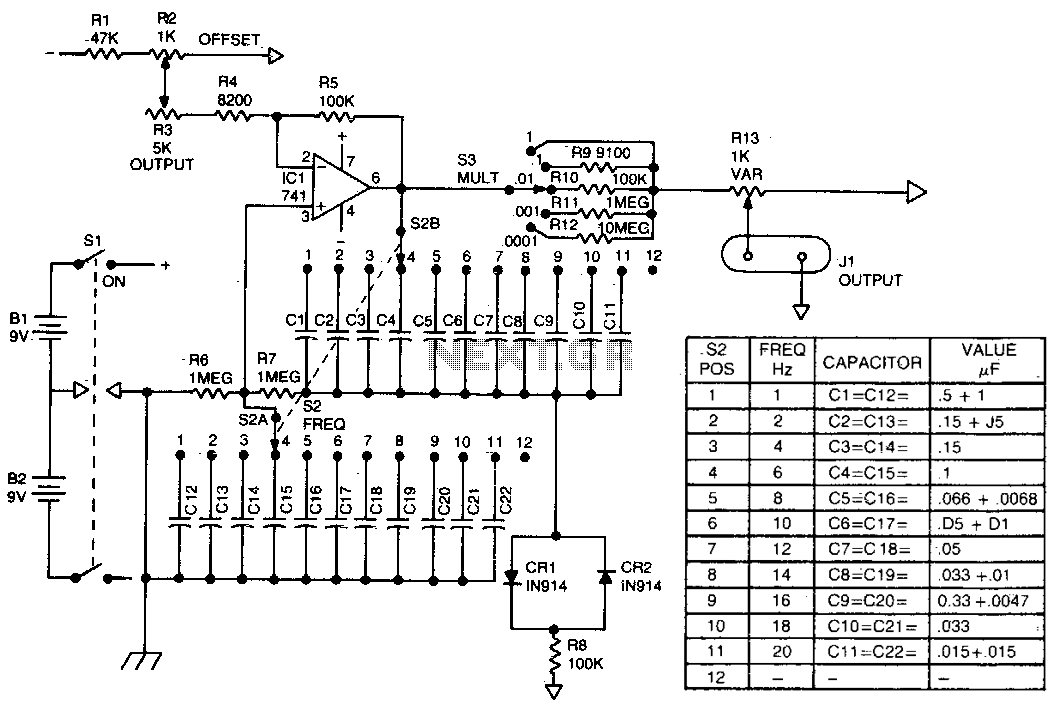
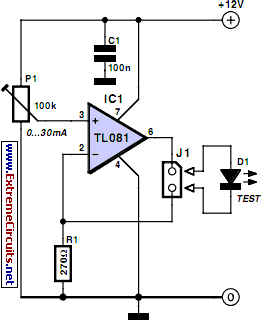
The Wien bridge oscillator generates frequencies of 1 Hz and from 2 to 20 Hz in 2 Hz increments. The maximum output amplitude is 3 volts RMS or 8 volts peak-to-peak. A potentiometer and switch attenuator enable the output level to be adjusted with a reasonable degree of precision across a range of 5 decades.
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that produces sine waves. It is based on a bridge circuit that includes resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration. The oscillator operates by balancing the bridge circuit, allowing it to generate a stable frequency output.
In this design, the frequency range is specified to start at 1 Hz and extend to 20 Hz, with the ability to tune in 2 Hz steps. This is achieved by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the bridge circuit. The frequency can be fine-tuned for applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as in audio testing or signal processing.
The output amplitude is specified as a maximum of 3 volts RMS, which corresponds to 8 volts peak-to-peak. This output level is suitable for a variety of applications, including driving other circuits or providing a reference signal.
To facilitate flexibility in output level, a potentiometer (variable resistor) combined with a switch is incorporated into the design. This allows for precise attenuation of the output signal, enabling the user to set the output level to any desired value within a range of 5 decades. This feature is particularly useful for applications requiring varying signal strengths or for interfacing with other equipment that may have different input sensitivity requirements.
Overall, the Wien bridge oscillator with an adjustable output level provides a versatile solution for generating low-frequency sine wave signals with high precision and control.Wien bridge oscillator generates frequencies of 1 Hz and 2 to 20 Hz in 2 Hz steps. Maximum output amplitude is 3 volts rms of 8 volts peak-to-peak A pot-and-switch attenuator allows the output level to be set with a fair degree of precision to any value within a range of 5 decades. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that produces sine waves. It is based on a bridge circuit that includes resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration. The oscillator operates by balancing the bridge circuit, allowing it to generate a stable frequency output.
In this design, the frequency range is specified to start at 1 Hz and extend to 20 Hz, with the ability to tune in 2 Hz steps. This is achieved by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the bridge circuit. The frequency can be fine-tuned for applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as in audio testing or signal processing.
The output amplitude is specified as a maximum of 3 volts RMS, which corresponds to 8 volts peak-to-peak. This output level is suitable for a variety of applications, including driving other circuits or providing a reference signal.
To facilitate flexibility in output level, a potentiometer (variable resistor) combined with a switch is incorporated into the design. This allows for precise attenuation of the output signal, enabling the user to set the output level to any desired value within a range of 5 decades. This feature is particularly useful for applications requiring varying signal strengths or for interfacing with other equipment that may have different input sensitivity requirements.
Overall, the Wien bridge oscillator with an adjustable output level provides a versatile solution for generating low-frequency sine wave signals with high precision and control.Wien bridge oscillator generates frequencies of 1 Hz and 2 to 20 Hz in 2 Hz steps. Maximum output amplitude is 3 volts rms of 8 volts peak-to-peak A pot-and-switch attenuator allows the output level to be set with a fair degree of precision to any value within a range of 5 decades. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713