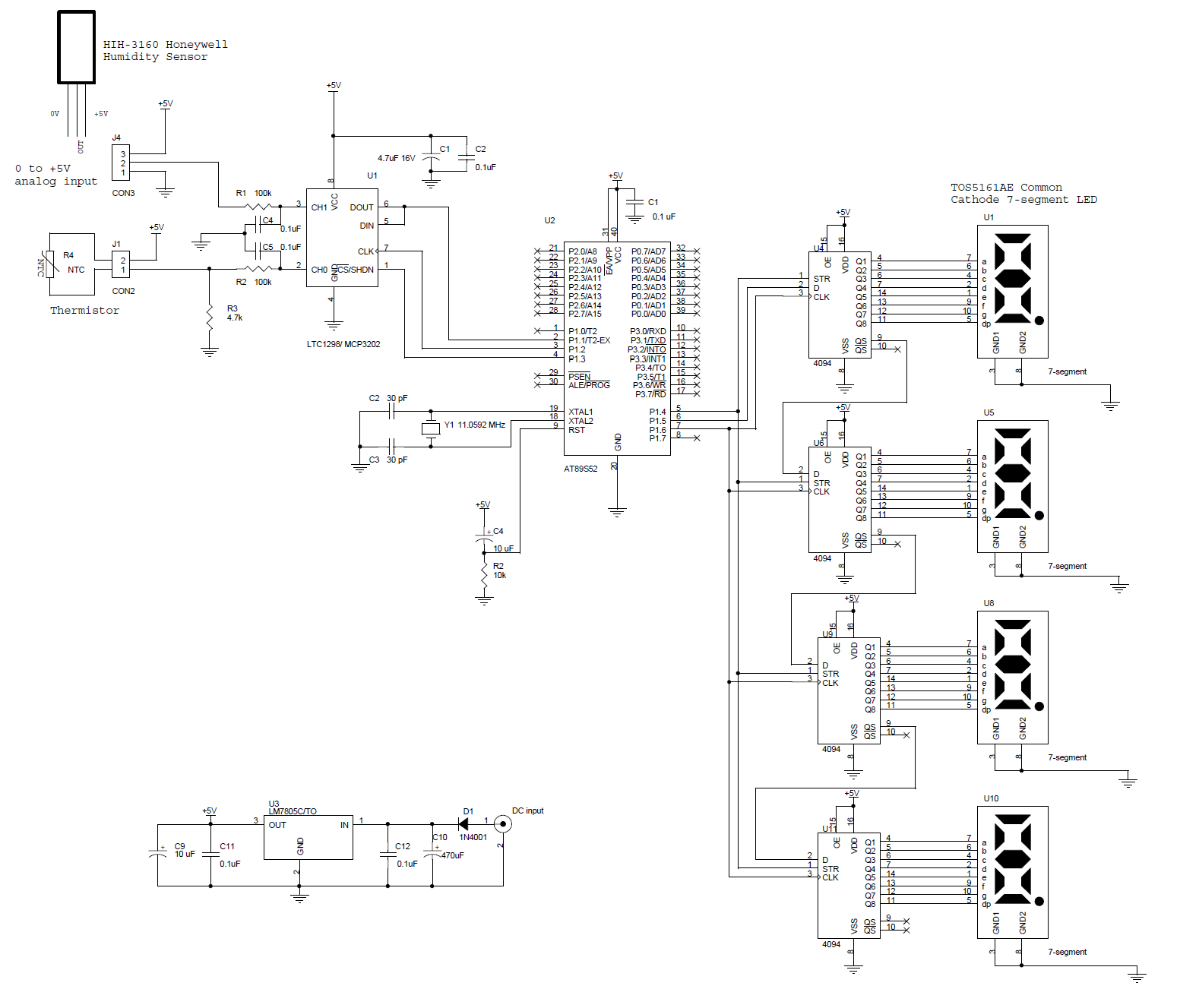
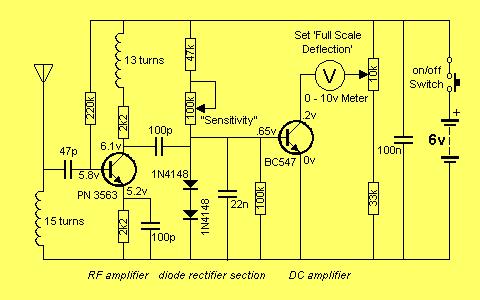
Power-frequency meter

The meter utilizes a zener diode to convert input sine waves into square waves. After calibration with a 5 k ohm potentiometer, the 100 µ meter provides a direct reading in hertz.
The circuit employs a zener diode as a key component in the waveform conversion process. The zener diode is connected in such a way that it operates in reverse breakdown mode, allowing it to clip the peaks of the incoming sine wave. This clipping action transforms the smooth sine wave into a square wave, suitable for frequency measurement.
The calibration process involves adjusting a 5 k ohm potentiometer, which is integrated into the circuit. This potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response to ensure accurate frequency readings. The output from the zener diode is fed into a frequency meter, which is designed to interpret the square wave signal.
The 100 µ meter is calibrated to display frequency directly in hertz, providing a user-friendly interface for measurement. The design of the circuit ensures that it is capable of handling a range of frequencies while maintaining accuracy and reliability. Proper attention to component selection, such as the zener diode's breakdown voltage and the characteristics of the potentiometer, plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the meter.
This type of circuit is commonly used in various applications where frequency measurement is essential, such as in telecommunications, audio equipment testing, and signal processing. The simplicity of the design, combined with the effectiveness of the zener diode for waveform conversion, makes it a practical solution for frequency measurement tasks.The meter uses a zener diode to form square waves from input sine waves. After calibration with the 5 k ohm potentiometer, the 100 µ meter reads directly in hertz.
The circuit employs a zener diode as a key component in the waveform conversion process. The zener diode is connected in such a way that it operates in reverse breakdown mode, allowing it to clip the peaks of the incoming sine wave. This clipping action transforms the smooth sine wave into a square wave, suitable for frequency measurement.
The calibration process involves adjusting a 5 k ohm potentiometer, which is integrated into the circuit. This potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response to ensure accurate frequency readings. The output from the zener diode is fed into a frequency meter, which is designed to interpret the square wave signal.
The 100 µ meter is calibrated to display frequency directly in hertz, providing a user-friendly interface for measurement. The design of the circuit ensures that it is capable of handling a range of frequencies while maintaining accuracy and reliability. Proper attention to component selection, such as the zener diode's breakdown voltage and the characteristics of the potentiometer, plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the meter.
This type of circuit is commonly used in various applications where frequency measurement is essential, such as in telecommunications, audio equipment testing, and signal processing. The simplicity of the design, combined with the effectiveness of the zener diode for waveform conversion, makes it a practical solution for frequency measurement tasks.The meter uses a zener diode to form square waves from input sine waves. After calibration with the 5 k ohm potentiometer, the 100 µ meter reads directly in hertz.