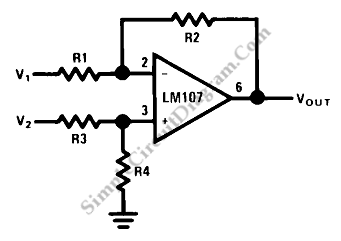
UGN-3501T counter circuit diagram of a Hall sensor
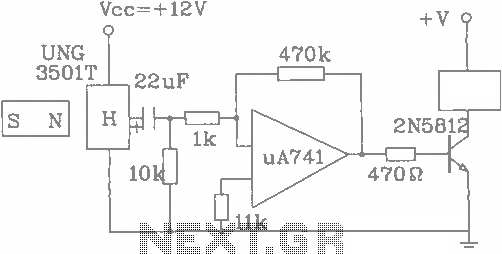
The UGN-3501T Hall sensor features a highly sensitive counter circuit diagram, allowing it to detect very small changes in magnetic fields. This capability enables the detection of ferrous metals. Utilizing this characteristic, it can be employed to count loads. When a ball rolls over the position of the Hall sensor, the sensor outputs a peak pulse of 20 mV. This pulse signal is subsequently amplified to drive an operational amplifier (op-amp) A741 and a 2N5812 transistor, thereby facilitating the on-off process. The counter connected to the output terminal can utilize a 2N5812 counter.
The UGN-3501T Hall sensor operates on the principle of detecting magnetic fields, which is essential for various applications such as proximity sensing and load counting. The sensor's high sensitivity allows it to respond to minimal variations in magnetic flux density, making it suitable for environments where precise detection of ferrous materials is required.
In the described circuit, the output from the UGN-3501T generates a 20 mV peak pulse when a magnetic field, such as that produced by a moving ferrous object (e.g., a ball), is detected. This pulse is a direct result of the Hall effect, where the sensor generates a voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength. To ensure that this signal can effectively control other components, it is necessary to amplify it.
The operational amplifier (A741) serves this purpose by increasing the voltage level of the pulse. The A741 is a versatile op-amp, known for its reliability and performance in signal amplification tasks. Following amplification, the signal is sent to a 2N5812 transistor, which acts as a switch. The transistor allows for the control of higher power loads based on the low-power signal received from the op-amp.
The use of a 2N5812 transistor is advantageous due to its ability to handle higher currents and voltages, making it suitable for driving output devices such as counters or relays. The output terminal connected to the counter can register each pulse generated by the Hall sensor, enabling accurate counting of the objects passing over the sensor's detection zone.
Overall, the integration of the UGN-3501T Hall sensor with the A741 op-amp and 2N5812 transistor presents a robust solution for applications requiring precise detection and counting of ferrous materials in a variety of industrial and commercial settings. This configuration can be further expanded or modified to suit specific operational requirements, enhancing its versatility in electronic design.UGN-3501T Hall sensor due to the composition of the counter circuit diagram UGN-3501T has a high sensitivity, it can feel very small magnetic field changes. Thereby detecting the presence of ferrous metals. We use this characteristic can be made it count loading. When the ball rolled over the position of Hall sensor, the sensor outputs a peak pulse 20mV. After this pulse signal is amplified to drive the op amp A741 2N5812 transistor, so as to complete the on-off process. The counter is connected to the output terminal can constitute a 2N5812 counter.
The UGN-3501T Hall sensor operates on the principle of detecting magnetic fields, which is essential for various applications such as proximity sensing and load counting. The sensor's high sensitivity allows it to respond to minimal variations in magnetic flux density, making it suitable for environments where precise detection of ferrous materials is required.
In the described circuit, the output from the UGN-3501T generates a 20 mV peak pulse when a magnetic field, such as that produced by a moving ferrous object (e.g., a ball), is detected. This pulse is a direct result of the Hall effect, where the sensor generates a voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength. To ensure that this signal can effectively control other components, it is necessary to amplify it.
The operational amplifier (A741) serves this purpose by increasing the voltage level of the pulse. The A741 is a versatile op-amp, known for its reliability and performance in signal amplification tasks. Following amplification, the signal is sent to a 2N5812 transistor, which acts as a switch. The transistor allows for the control of higher power loads based on the low-power signal received from the op-amp.
The use of a 2N5812 transistor is advantageous due to its ability to handle higher currents and voltages, making it suitable for driving output devices such as counters or relays. The output terminal connected to the counter can register each pulse generated by the Hall sensor, enabling accurate counting of the objects passing over the sensor's detection zone.
Overall, the integration of the UGN-3501T Hall sensor with the A741 op-amp and 2N5812 transistor presents a robust solution for applications requiring precise detection and counting of ferrous materials in a variety of industrial and commercial settings. This configuration can be further expanded or modified to suit specific operational requirements, enhancing its versatility in electronic design.UGN-3501T Hall sensor due to the composition of the counter circuit diagram UGN-3501T has a high sensitivity, it can feel very small magnetic field changes. Thereby detecting the presence of ferrous metals. We use this characteristic can be made it count loading. When the ball rolled over the position of Hall sensor, the sensor outputs a peak pulse 20mV. After this pulse signal is amplified to drive the op amp A741 2N5812 transistor, so as to complete the on-off process. The counter is connected to the output terminal can constitute a 2N5812 counter.