Voice-Modulated Pulse Fm Ir Transmitter
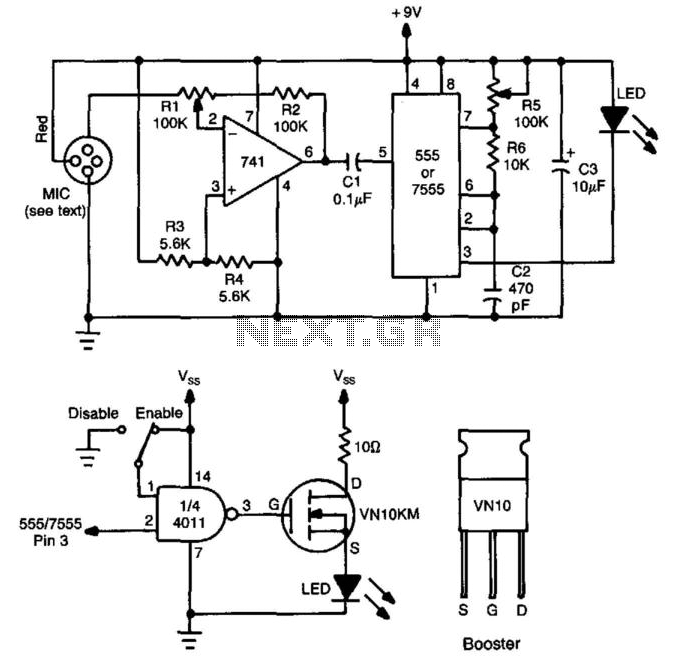
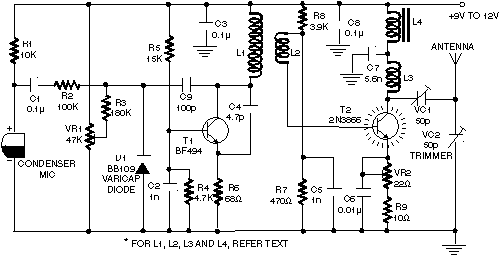
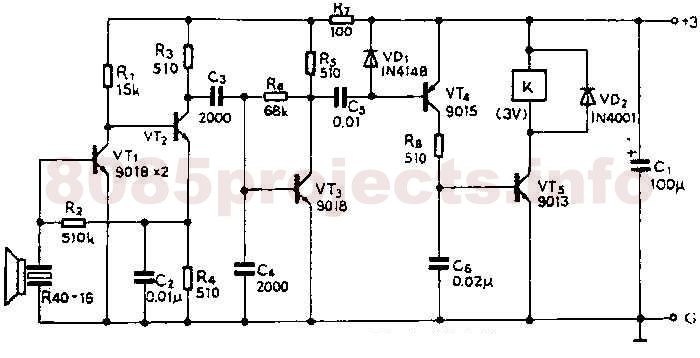
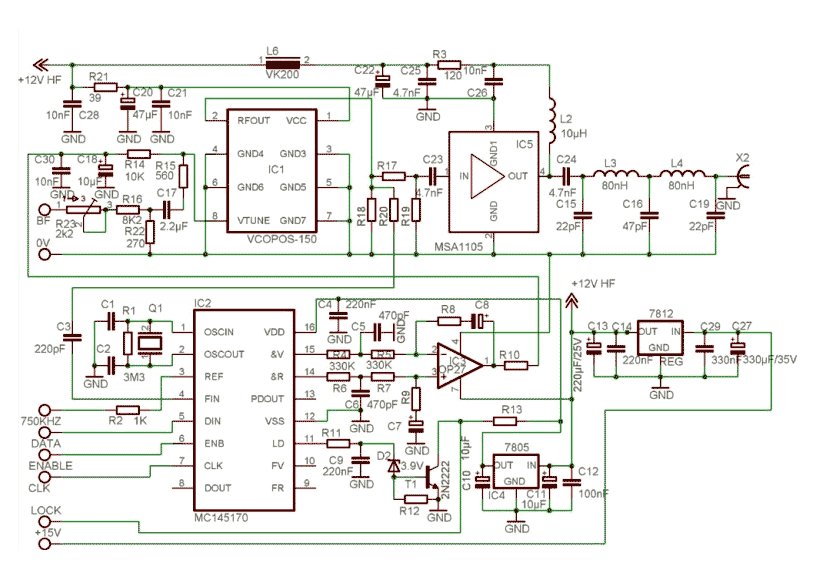
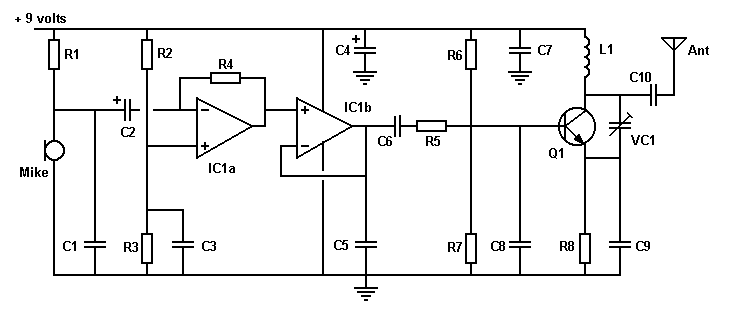
This circuit utilizes a 741 audio amplifier, which is connected to an amplified microphone, an FM modulator, and a CMOS timer functioning as a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The timer output drives an LED, which is pulsed to produce an FM-modulated, pulsed infrared (IR) beam. The booster circuit can be incorporated to enhance the transmission range.
The circuit design begins with the 741 audio amplifier, which amplifies the audio signal captured from the microphone. The microphone should be of an amplified type to ensure sufficient signal strength for further processing. The output from the audio amplifier is then fed into an FM modulator, which modulates the audio signal onto a carrier frequency. This modulation process allows the audio signal to be transmitted over a longer distance using radio frequency waves.
A CMOS timer, configured as a voltage-controlled oscillator, is integrated to produce a square wave output. This output is essential for pulsing the LED, which emits infrared light. The frequency of the pulsing can be adjusted by varying the control voltage supplied to the timer, allowing for flexibility in the modulation frequency.
The pulsed output from the CMOS timer activates the LED, creating a pulsed IR beam that carries the FM-modulated audio signal. This IR beam can be detected by a compatible receiver, which demodulates the signal back into audio for playback.
Additionally, a booster circuit can be included in the design to amplify the IR signal, thereby increasing the effective range of the transmission. This can be particularly useful in applications where the distance between the transmitter and receiver is significant.
Overall, this circuit effectively combines audio amplification, frequency modulation, and infrared transmission to create a versatile communication system that can be utilized in various applications, including remote audio transmission and wireless audio systems. This circuit has a 741 audio amplifier, which is fed by a microphone (use an amplified type), an FM modulator, and a CMOS timer that acts as a VCO. The LED is pulsed with the timer output (the booster circuit can be used for increased range). This yields an FM-modulated, pulsed IR beam. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design begins with the 741 audio amplifier, which amplifies the audio signal captured from the microphone. The microphone should be of an amplified type to ensure sufficient signal strength for further processing. The output from the audio amplifier is then fed into an FM modulator, which modulates the audio signal onto a carrier frequency. This modulation process allows the audio signal to be transmitted over a longer distance using radio frequency waves.
A CMOS timer, configured as a voltage-controlled oscillator, is integrated to produce a square wave output. This output is essential for pulsing the LED, which emits infrared light. The frequency of the pulsing can be adjusted by varying the control voltage supplied to the timer, allowing for flexibility in the modulation frequency.
The pulsed output from the CMOS timer activates the LED, creating a pulsed IR beam that carries the FM-modulated audio signal. This IR beam can be detected by a compatible receiver, which demodulates the signal back into audio for playback.
Additionally, a booster circuit can be included in the design to amplify the IR signal, thereby increasing the effective range of the transmission. This can be particularly useful in applications where the distance between the transmitter and receiver is significant.
Overall, this circuit effectively combines audio amplification, frequency modulation, and infrared transmission to create a versatile communication system that can be utilized in various applications, including remote audio transmission and wireless audio systems. This circuit has a 741 audio amplifier, which is fed by a microphone (use an amplified type), an FM modulator, and a CMOS timer that acts as a VCO. The LED is pulsed with the timer output (the booster circuit can be used for increased range). This yields an FM-modulated, pulsed IR beam. 🔗 External reference